Abstract
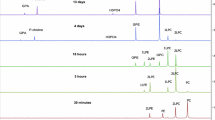
We show that phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy can be used to distinguish and to quantify the alk-1-enylacyl, alkylacyl, and diacyl glycerophosphoethanolamine (GPE) subclasses, and the respective glycerophosphocholine (GPC) subclasses, in their native form without prior degradation or derivatization, provided the phospholipids are observed in the nonaggregated state. Monomeric phospholipid distribution is ascertained by recording the spectra, after removal of metal ions, on CDCI3/CD3OD/D2O (50∶50∶15, by vol) solutions. The utility of this approach is exemplified for the ethanolamine glycerophospholipids (EPL) from bovine brain and the choline glycerophospholipids (CPL) from bovine heart. Sharp and well-resolved resonances are obtained for alkylacylGPE (+0.395 ppm; re 1% H3PO4), alkenylacylGPE (+0.353 ppm), and diacylGPE (+0.315 ppm), and for alkylacylGPC (−0.383 ppm), alkenylacylGPC (−0.436 ppm) and diacylGPC (−0.451 ppm). Integrated peak reas are shown to closely correlate with dose. Accurate quantitation of EPL and CPL subclasses at submicromolar levels can further be facilitated by use of synthetic dialkylGPE (+0.602 ppm) and dialkylGPC (−0.196 ppm) as internal standards. The method is simple, rapid, sensitive and reproducible, and permits the complete resolution and direct quantitation of all ethanolamine and choline glycerophospholipid subclasses quite independent of fatty chain length and degree of unsaturation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPL:
-
choline glycerophospholipids
- EPL:
-
ethanolamine glycerophospholipids
- GPC:
-
glycerophosphocholine
- GPE:
-
glycerophosphoethanolamine
- NMR:
-
nuclear magnetic resonance
- PC:
-
phosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
phosphatidylethanolamine
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
References
Malewicz, B., and Baumann, W.J. (1994) Alk-1-enylacyl, Alkylacyl and Diacyl Subclasses of Natural Ethanolamine and Choline Glycerophospholipids Can Directly Be Quantified by phosphorus-31 NMR,INFORM 5, 499 (Abstract).
Rapport, M.M., and Norton, W.T. (1962) Chemistry of the Lipids,Annu. Rev. Biochem. 31, 103–138.
Horrocks, L.A. (1972) Content, Composition, and Metabolism of Mammalian and Avian Lipids That Contain Ether Groups, inEther Lipids. Chemistry and Biology (Snyder, F., ed.) pp. 177–272, Academic Press, New York.
Rapport, M.M. (1984) The Discovery of Plasmalogen Structure,J. Lipid Res. 25, 1522–1527.
Dawson, R.M.C., Hemington, N., and Davenport, J.B. (1962) Improvements in the Method of Determining Individual Phospholipids in a Complex Mixture by Successive Chemical Hydrolyses,Biochem. J. 84, 497–501.
Owens, K. (1966) A Two-Dimensional Thin-Layer Chromatographic Procedure for the Estimation of Plasmalogens,Biochem. J. 100, 354–361.
Scott, T.W., Setchell, B.P., and Bassett, J.M. (1967) Characterization and Metabolism of Ovine Foetal Lipids,Biochem. J. 104, 1040–1047.
Nakagawa, Y., and Horrocks, L.A. (1983) Separation of Alkenylacyl, Alkylacyl, and Diacyl Analogues and Their Molecular Species by High Performance Liquid Chromatography,J. Lipid Res. 24, 1268–1275.
Sheltawy, A., and Dawson, R.M.C. (1966) The Polyphosphoinositides and Other Lipids of Peripheral Nerves,Biochem. J. 100, 12–18.
Pugh, E.L., Kates, M., and Hanahan, D.J. (1977) Characterization of the Alkyl Ether Species of Phosphatidylcholine in Bovine Heart,J. Lipid Res. 18, 710–716.
Gross, R.W. (1985) Identification of Plasmalogen as the Major Phospholipid Constitutent of Cardiac Sarcoplasmic Reticulum,Biochemistry 24, 1662–1668.
Dawson, R.M.C. (1960) A Hydrolytic Procedure for the Identification and Estimation of Individual Phospholipids in Biological Samples,Biochem. J. 75, 45–53.
Horrocks, L.A. (1968) The Alk-1-enyl Group Content of Mammalian Myelin Phosphoglycerides by Quantitative Two-Dimensional Thin-Layer Chromatography,J. Lipid Res. 9, 469–472.
Waku, K., Ito, H., Bito, T., and Nakazawa, Y. (1974) Fatty Chains of Acyl, Alkenyl, and Alkyl Phosphoglycerides of Rabbit Sarcoplasmic Reticulum. The Metabolic Relationship Considered on the Basis of Structurel Analyses,J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 75, 1307–1312.
Gross, R.W. (1984) High Plasmalogen and Arachidonic Acid Content of Canine Myocardial Sarcolemma: A Fast Atom Bombardment Mass Spectroscopic and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopic Characterization,Biochemistry 23, 158–165.
Vishnubhatla, I., Kates, M., and Adams, G.A. (1988) A Simplified Approach to the Analysis of Subclasses of Phospholipids: Application to Human Platelets,Lipids 23, 609–614.
Schmid, H.H.O., Baumann, W.J., and Mangold, H.K. (1967) Alkoxylipids III. Naturally Occurring D(+)-1-O-cis-Alk-1′-enyldiglycerides,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 144, 344–354.
Baumann, W.J., Schmid, H.H.O., Kramer, J.K.G., and Mangold, H.K. (1968) Alk-1-enyl Ethers of Glycerol and Ethanediol,Z. Physiol. Chem. 349, 1677–1685.
Mangold, H.K., and Baumann, W.J. (1967) Isolation and Gas-Liquid Chromatography of Alkoxy Lipids, inLipid Chromatographic Analysis (Marinetti, G.V., ed.) Vol. 1, pp. 339–359, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Renkonen, O. (1965) Individual Molecular Species of Different Phospholipid Classes. Part II. A Method of Analysis,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 42, 298–304.
Zwaal, R.F.A., Roelofsen, B., Comfurius, P., and van Deenen, L.L.M. (1971) Complete Purification and Some Properties of Phospholipase C fromBacillus cereus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 233, 474–479.
Baumann, W.J., Takahashi, T., Mangold, H.K., and Schmid, H.H.O. (1970) Alkoxylipids VI. Molecular Structure of the Natural Alkoxylipids of Ratfish Liver,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 202, 468–476.
Blank, M.L., Robinson, M., Fitzgerald, V., and Snyder, F. (1984) Novel Quantitative Method for Determination of Molecular Species of Phospholipids and Diglycerides,J. Chromatogr. 298, 473–482.
Blank, M.L., Cress, E.A., and Snyder, F. (1987) Separation and Quantitation of Phospholipid Subclasses as Their Diradylglycerobenzoate Derivatives by Normal-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography,J. Chromatogr. 392, 421–425.
Takamura, H., Narita, H., Urade, R. and Kito, M. (1986) Quantitative Analysis of Polyenoic Phospholipid Molecular Species by High Performance Liquid Chromatography,Lipids 21, 356–361.
Francescangeli, E., Porcellati, S., Horrocks, L.A., and Goracci, G. (1987) Quantitative Analysis of Alkylacyl, Alkenylacyl, and Diacyl Types of Diglycerides Obtained from Glycerophospholipids,J. Liq. Chromatogr. 10, 2799–2808.
Ishinaga, M., Tanimoto, M., Sugiyama, S., Kumamoto, R., and Yokoro, K. (1991) Molecular Species of Phospholipids in Rats in Primary and Transplanted Fibrosarcomas Induced by Soybean Oil Containing Tocopherol Acetate,Biochem. Cell Biol. 69, 655–660.
Bell, M.V., and Dick, J.R. (1993) 1-O-Alk-1′-enyl-2-acyl-glycerophosphoethanolamine Content and Molecular Species Composition in Fish Brain,Lipids 28, 19–22.
Kayganich, K.A., and Murphy, R.C. (1992) Fast Atom Bombardment Tandem Mass Spectrometric Identification of Diacyl, Alkylacyl, and Alk-1-enylacyl Molecular Species of Glycerophosphoethanolamine in Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes,Anal. Chem. 64, 2965–2971.
Baumann, W.J. (1972) The Chemical Syntheses of Alkoxylipids, inEther Lipids. Chemistry and Biology (Snyder, F., ed.) pp. 51–79, Academic Press, New York.
Hermetter, A., and Paltauf, F. (1983) Procedures for the Synthesis of Ether Lipids, inEther Lipids. Biochemical and Biomedical Aspects (Mangold, H.K., and Paltauf, F., eds.) pp. 389–420. Academic Press, New York.
Baumann, W.J., and Mangold, H.K. (1966) Reactions of Aliphatic Methanesulfonates. II. Syntheses of Long-Chain Di-and Trialkyl Glycerol Ethers,J. Org. Chem. 31, 498–500.
Hirt, R., and Berchtold, R. (1957) Zur Synthese der Phosphatide. Eine neue Synthese der Kephaline,Helv. Chim. Acta 40, 1928–1932.
Hansen, W.J., Murari, R., Wedmid, Y., and Baumann, W.J. (1982) An Improved Procedure for the Synthesis of Choline Phospholipidsvia 2-Bromoethyl Dichlorophosphate,Lipids 17, 453–459.
Murari, R., and Baumann, W.J. (1981) Quadrupolar13C−14N Couplings and14N Relaxations in Aggregated and Nonaggregated Choline Phospholipids,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103, 1238–1240.
Murari, R., Abd El-Rahman, M.M.A., Wedmid, Y., Parthasarathy, S., and Baumann, W.J. (1982) Carbon-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Phospholipids in Solution. Spectral and Stereochemical Assignments Based on13C−31P and13C−14N Couplings,J. Org. Chem. 47, 2158–2163.
Murari, M.P., Murari, R., Parthasarathy, S., Guy, C.A., Kumar, V.V., Malewicz, B., and Baumann, W.J. (1990) Lyso Platelet Activating Factor (LysoPAF) and Its Enantiomer. Total Synthesis and Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy,Lipids 25, 606–612.
Henderson, T.O., Glonek, T., and Myers, T.C. (1974) Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Phospholipids,biochemistry 13, 623–628
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Stanley, G.H.S. (1957) A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipides from Animal Tissues,J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509.
Bartlett, G.R. (1959) Phosphorus Assay in Column Chromatography,J. Biol. Chem. 234, 466–468.
London, E., and Feigenson, G.W. (1979) Phosphorus NMR Analysis of Phospholipids in Detergents,J. Lipid Res. 20, 408–412.
Dennis, E.A., and Plückthun, A. (1984) Phosphorus-31 NMR of Phospholipids in Micelles, inPhosphorus-31 NMR. Principles and Applications (Gorenstein, D.G., ed.) pp. 423–446, Academic Press, New York.
Pearce, J.M., and Komoroski, R.A. (1993) Resolution of Phospholipid Molecular Species by31P NMR,Magn. Reson. Med. 29, 724–731.
Sappey Marinier, D., Letoublon, R., and Delmau, J. (1988) Phosphorus NMR Analysis of Human White Matter in Mixed Non-Ionic Detergent Micelles,J. Lipid Res. 29, 1237–1243.
Bradamante, S., Barchiesi, E., Barenghi, L., and Zoppi, F. (1990) An Alternative Expeditious Analysis of Phospholipid Composition in Human Blood Plasma by31P NMR Spectroscopy,Anal. Biochem. 185, 299–303.
Meneses, P., and Glonek, T. (1988) High Resolution31P NMR of Extracted Phospholipids,J. Lipid Res. 29, 779–689.
Sotirhos, N., Herslöf, B., and Kenne, L. (1986) Quantitative Analysis of Phospholipids by31P-NMR,J. Lipid Res. 27, 386–392.
Edzes, H.T., Teerlink, T., and Valk, J. (1991) Phospholipid Identification in Tissue Extracts by Two-Dimensional31P-1H NMR Spectroscopy with Isotropic Proton Mixing,J. Magn. Reson. 95, 387–395.
Edzes, H.T., Teerlink, T., van der Knaap, M.S., and Valk, J. (1992) Analysis of Phospholipids in Brain Tissue by31P NMR at Different Compositions of the Solvent System Chloroform-Methanol-Water,Magn. Reson. Med. 26, 46–59.
Pearce, J.M., Shifman, M.A., Pappas, A.A., and Komoroski, R.A. (1991) Analysis of Phospholipids in Human Amniotic Fluid by31P NMR,Magn. Reson. Med. 21, 107–116.
Rana, F.R., Harwood, J.S., Mautone, A.J., and Dluhy, R.A., (1993) Identification of Phosphocholine Plasmalogen as a Lipid Component in Mammalian Pulmonary Surfactant Using High-Resolution31P NMR Spectroscopy,Biochemistry 32, 27–31.
Liang, M.T.C., Meneses, P., Glonek, T., Kopp, S.J., Paulson, D.J., Schwartz, F.N., and Gierke, L.W. (1993) Effects of Exercise Training and Anabolic Steroids on Plantaris and Soleus Phospholipids: A31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study,Int. J. Biochem. 25, 337–347.
Glonek, T., and Merchant, T.E. (1995)31P NMR Profiling of Phospholipids, inAdvances in Lipid Methodology (Christie, W.W., ed.) Vol. 3, pp. 37–76, The Oily Press, West Ferry, Dundee.
Driscoll, D., Ennis, W., and Meneses, P. (1994) Human Sciatic Nerve Phospholipid Profiles from Non-Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus and Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Individuals. A31P NMR Spectroscopy Study,Int. J. Biochem. 26, 759–767.
Seijo, L., Merchant, T.E., van der Ven, L.T.M., Minsky, B.D., and Glonek, T. (1994) Meningioma Phospholipid Profiles Mesured by31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy,Lipids 29, 359–364.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Malewicz, B., Baumann, W.J. Alk-1-enylacyl, alkylacyl, and diacyl subclasses of native ethanolamine and choline glycerophospholipids can be quantified directly by phosphorus-31 NMR in solution. Lipids 31, 1189–1195 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02524294
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02524294