Abstract
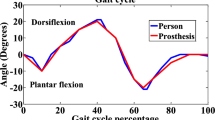
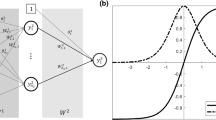
The object of this paper is to present a real-time application of an artificial neural network (ANN). The application for which this network is demonstrated is a motorised orthosis with six degrees-of-freedom for use by a paraplegic; a ‘walking machine’. Theoretical networks and training methods need modification to function correctly with a real application. Several complex phenomena that are very diffucult to model have to be accommodated; the starting threshold of the activators, nonlinearity, noise, and the non-biunivocity between successive system states (position, velocity, actuator controls). The modifications made to the network and the associated training method partially alleviate these difficulties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, J. J., andChizec, H. J. (1991): ‘A neural controller for functional neuromuscular stimulation systems’,Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc.,13, pp. 1456–1457
Beckmann, J., Daunicht, W. J., andHömberg, V. (1992): ‘Control of a paraplegic patient’. Proc. ICANN 92, Brighton, UK 4–7 September
Bleuler, H., Diez, D., Lauber, G., Meyer, U., andZlatnik, D. (1990): ‘Non-linear neural network control with application example’. Proc. INNC 90, Paris, France,1, pp. 201–204
Colombano, P., Compton, M., andBualat, M. (1991): ‘Goal directed model inversion: adaptation to unexpected model changes’. Proc. Neuro-Nîmes, Nîmes, France, 4–8 November, pp. 269–278
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., andWhite, H. (1990): ‘Universal approximation of an unknown mapping and its derivatives using multilayer feedforward networks’,Neural Netw.,3, pp. 551–560
Jacobs, R. A. (1988): ‘Increased rates of convergence through learning rate adaptation’,,1, pp. 295–307
Phillips, C. A., andHendershot, D. M. (1991): ‘A system approach to medically prescribed functional electrical stimulation. Ambulation after spinal cord injury’,Paraplegia,29, pp. 505–513
Rabischong, E., Sgarbi, F., Rabischong, P., Detriche, J. M., Pinguet, N., andRiwan, A. (1990): ‘Control and command of a six degrees of freedom active electrical orthosis for paraplegic patient’. Proc. IEEE Int. Workshop on Intelligent robots and systems, pp. 987–991
Rose, G. K. (Ed.) (1986): ‘Orthotics, principles and practice’ (William Heinemann Medical Books, London, UK) pp. 176–189
Rumelhart, D. E., andMacClelland, C. L. (Eds.) (1986): ‘Parallel distributed processing, exploration in the microstructure of cognition’ (PDP Research Group, MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA) Vol. 1
Tollenaere, T. (1990): ‘SuperSAB: fast adaptative back propagation with good scaling properties’,Neural Netw.,3, pp. 561–573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guiraud, D. Application of an artificial neural network to the control of an active external orthosis of the lower limb. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 32, 610–614 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02524234
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02524234