Abstract
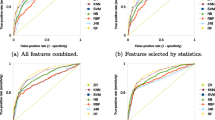
Technegas lung ventilation images sometimes have ‘hot spots’, particularly in patients with respiratory disease. A novel technique is presented for quantifying this ‘spottiness’ using morphological texture analysis. A set of 32 images from patients with various respiratory diseases is studied. Images are filtered at a range of scales using morphological opening, and the slopes of image metrics versus structuring element size are used as texture parameters. The results are compared with the opinions of three experienced nuclear medicine physicians who have classified the images into two groups, ‘spotty’ and ‘non-spotty’, and have ranked the former. For the spotty images, the computer and observer ranks are compared; the highest correlation is rs=0.66 (p=0.01) for a single parameter, andr s =0.71 (p<0.01) for a combination of two parameters. Using a pair of parameters, 83% and 90% correct classification rates are obtained for the spotty and non-spotty classes, respectively. It is concluded that these texture parameters provide a useful measure of image spottiness, and it is demonstrated that this technique is superior to previously published methods. The practical value of the technique is illustrated using two applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, J. E. (1984): ‘Aerosol contributions to the investigation of lung structure and ventilatory functions’Clarke, S. W. andPavia, D. (Eds.): ‘Aerosols and the lung: clinical and experimental aspects’ (Butterworths, London) pp. 92–126
Agnew, J. E., Bateman, J. R. M., Pavia, D., andClarke, S. W. (1984): ‘Radionuclide demonstration of ventilatory abnormalities in mild asthma,’Clin. Sci.,66, pp. 525–531
Agnew, J. E., Francis, R. A., Pavia, D., andCarke, S. W. (1982): ‘Quantitative comparison of99Tcm-aerosol and81Kim ventilation images,’Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas.,3, pp. 21–30
Armitage, P., andBerry, G. (1987): ‘Statistical methods in medical research’ (Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK)
Burch, W. M., Sulijvan, P. J., andMcLaren, C. J. (1986): ‘Technegas—a new ventilation agent for lung scanning,’Nucl. Med. Comm.,7, pp. 865–871
Chatfield, C., andCollins, A. J. (1980): ‘Introduction to multivariate analysis’ (Chapman & Hall, London.)
Cinotti, L., Edery, S., Kahn, E., Susskind, H., Brill, A. B., andDi Paola, R. (1990): ‘Lung scintigraphy clustering by texture analysis,’Eur. J. Nucl. Med.,16, pp. 353–359
Emmet, P. C., Love, R. G., Hannan, W. J., Millar, A. M., andSoutar, C. A. (1984): ‘The relationship between the pulmonary distribution of inhaled fine aerosols and tests of small airways function,’Bull. Eur. Physiopathol. Respir.,20, pp. 325–332
Garrard, C. S., Gerrity, T. R., Schreiner, J. F., andYeates, D. B. (1981): ‘The characterisation of radioaerosol deposition in the healthy lung by histogram distribution analysis,’Chest,80, (Suppl.), pp. 840–842
Haralick, R. M., Sternberg, S. R., andZhuang, X. (1987): ‘Image analysis using mathematical morphology,’IEEE Trans.,PAMI-9, pp. 532–549
Hayes, M., andTaplin, G. V. (1980): ‘Lung imaging with radioaerosols for the assessment of airways disease,’Sem. Nucl. Med.,10, pp. 243–251
Isawa, T., Teshima, Y., Anazawa, Y., Miki, M., andMotomiya, M. (1991): ‘Technigas for inhalation lung imaging,’Nucl. Med. Comm.,12, pp. 47–55
James, J. M., Herman, K. J., Lloyd, J. J., Shields, R. A., Testa, H. J., Church, S., andStretton, T. B. (1991): ‘Evaluation of 99m-Tc Technegas ventilation scintigraphy in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism,’Br. J. Radiol.,64, pp. 711–719
James, J. M., Lloyd, J. J., Leahy, B. C., Shields, R. A., Prescott, M. C., andTesta, H. J. (1992): ‘99mTc-Technegas and krypton-81 m ventilation scintigraphy: a comparison in known respiratory disease,’ ——ibid.,65, pp. 1075–1082
Jasiobedski, P., andTaylor, C. J. (1991): ‘Automated analysis of retinal images’ Proc. British Machine Vision Conf. 1991 (Mowforth, P. (Ed.) (Springer-Verlag, Glasgow) pp. 276–283
Laube, B. L., Links, J. M., Wagner, H. N. J., Norman, P. S., Koller, D. W., Lafrance, N. D., andAdams, G. K. I. (1988): ‘Simplified assessment of fine aerosol distribution in human airways,’J. Nucl. Med.,29, pp. 1057–1065
Lemb, M., Oei, T. H., Eifert, H., andGunther, B. (1993): ‘Technegas: a study of particle structure, size and distribution,’Eur. J. Nucl. Med.,20, pp. 576–579
Lloyd, J. J., James, J. M., Shields, R. A., Testa, H. J. (1994): ‘The influence of inhalation technique on Technegas particle deposition and image appearance in normal volunteers,’Eur. J. Nucl. Med.,21, pp. 394–398
Miller, P., andAstley, S. (1992): ‘Classification of breast tissue by texture analysis,’Image Vis. Comput.,10, pp. 277–282
Peltier, P., Bardies, M., Chetanneau, A., andChatal, J.-F. (1992): ‘Comparison of technetium-99mC and phytate aerosol in ventilation studies,’Eur. J. Nucl. Med.,19, pp. 349–354
Peltier, P., De Faucal, P., Chetanneau, A., andChatal, J.-F. (1990): ‘Comparison of technetium-99m and krypton-81m in ventilation studies for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism,’Nucl. Med. Comm.,11, pp. 631–638
Santolicandro, A., Fornai, E., Marini C., Palla, A., Solfanelli, S., andGiuntini, C. (1975): ‘Uneven distribution of minimicrospheres in patients with obstructive lung disease,’J. Nucl. Biol. Med.,19, pp. 112–120
Serra, J. (1982): ‘Image analysis and mathematical morphology’ (Academic Press, London.)
Strong, J. C., andAgnew, J. E. (1989): ‘The particle size distribution of technegas and its influence on regional lung deposition,’Nucl. Med. Comm.,10, pp. 425–430
Therrien, C. W. (1989): ‘Decision estimation and classification: an introduction to pattern recognition and related topics’ (John Wiley & Son, New York.)
Werman, M., andPeleg, S. (1985): ‘Min-Max operators in texture analysis,’IEEE Trans.,PAMI-7, pp. 731–733
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lloyd, J.J., Taylor, C.J., James, J.M. et al. Texture analysis of technegas lung ventilation images. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 33, 52–57 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522946
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522946