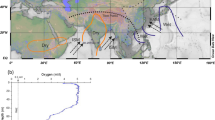
Abstract
According to their microstratigraphical composition the laminated sediments of Baldeggersee are true varves. Two varve time-series from freeze cores taken in the deepest part (66 m) of Baldeggersee have been analysed for annual and seasonal layers. The varve time-series covers the period of 1885 to 1993.
The two freeze-cores from Baldeggersee can be accurately correlated by means of distinct layers (e.g. marker varves, turbidites), lithological units, and varve measurements. The Baldeggersee varve chronology has been checked by independent high-resolution137Cs dating. Mobility of cesium has not been detected in Baldeggersee. A highly positive correlation between phosphorus concentration in the lake water and median grain size of calcite crystals has been observed and allows, together with the results of geochemical analyses, to hindcast the trophic state in Baldeggersee for periods where no limnological data are available.
The main features of the Baldeggersee varve time-series can be summarized as follows: before 1885 there are packets of 5–10 varves interrupted by massive, homogeneous marl beds, indicating oscillating hypolimnetic oxygen levels until the lake ultimately became anoxic in 1885. Between 1885 and 1905 varves are thin, with a high carbonate content. Between 1905 and 1910 the thickness of varves increased steadily, and an increase in calcite grain size suggests a major step in eutrophication. Median grain size values increase again at the end of the 1940s, whereas the thickness of the seasonal layers decreased between the early 1940s and the early 1960s. At the onset of the 1960s, during the time of highest epilimnetic phosphorus concentrations in Baldeggersee, the total phosphorus concentrations in the sediments as well as the varve thickness and the total accumulation rates all increased. At the beginning of the 1980s the median grain size decreased substantially as a result of lower phosphorus concentrations in Baldeggersee.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björck, S., B. Kromer, S. Johnsen, O. Bennike, D. Hammarlund, G. Lemdahl, G. Possnert, T.L. Rasmussen, B. Wohlfarth, C.U. Hammer and M. Spurk, 1996. Synchronized terrestrial-atmospheric deglacial records around the North Atlantic. Science 274:1155–1160.
Brunskill, G.J., 1969. Fayetteville Green Lake, New York. II. Precipitation and sedimentation of calcite in a meromictic lake with laminated sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14:830–847.
Canfield, D.E., 1994. Factors influencing organic carbon preservation in marine sediments. Chem. Geol. 114:315–329.
Crusius, J. and R.F. Anderson, 1995. Evaluating the mobility of137Cs,249+240Pu and210Pb from their distribution in laminated sediments. Journal of Paleolimnology 13:119–141.
De Geer, G., 1912. A geochronology of the last 12 000 years. Proc. 11th Internat. Geological Congress 1910:241–253.
Dickman, M., 1985. Seasonal succession and microlamina formation in a meromictic lake displaying varved sediments. Sedimentology 32:109–118.
Dove, P.M. and M.F. Hochella, 1993. Calcite precipitation mechanisms and inhibition by orthophosphate: in situ observations by scanning force microscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 57:705–714.
Furrer, G. and B. Wehrli, 1996. Microbial reactions, chemical speciation, and multicomponent diffusion in porewaters of a eutrophic lake. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60:2333–2346.
Geyh, M.A., J. Merkt and H. Müller, 1971. Sediment-, Pollen- und Isotopenanalysen an jahreszeitlich geschichteten Ablagerungen im zentralen Teil des Schleinsees. Arch. Hydrobiol. 69:366–399.
Goslar, T., T. Kuc, M. Ralska-Jasiewiczowa, K. Rozanski, M. Arnold, E. Bard, B. van Geel, M.F. Pazdur, K. Szeroczynska, B. Wicik, K. Wieckowski and A. Walanus, 1993. High-resolution lacustrine record of the Late Glacial/Holocene transition in Central Europe. Quaternary Science Reviews 12:287–294.
Goslar, T., M. Arnold, E. Bard, T. Kuc, M.F. Pazdur, M. Ralska-Jasiewiczowa, K. Rozanski, N. Tisnerat, A. Walanus, B. Wicik and K. Wieckowski, 1995. High concentration of atmospheric 14-C during the Younger Dryas cold episode. Nature 377:414–417.
Hajdas, I., S.D. Ivy, J. Beer, G. Bonani, D. Imboden, A.F. Lotter, M. Sturm and M. Suter, 1993. AMS radiocarbon dating and varve chronology of lake Soppensee: 6000 to 12,00014C years BP. Climate Dynamics 9:107–116.
Henrichs, S.M., 1992. Early diagenesis of organic matter in marine sediments: progress and perplexity. Mar. Chem. 39:119–149.
Hupfer, M., R. Gächter and R. Giovanoli, 1995. Transformation of phosphorus species in settling seston and during early diagenesis. Aquatic Sciences 57:305–324.
Itkonen, A. and V.-P. Salonen, 1994. The response of sedimentation in three varved lacustrine sequences to air temperatures, precipitation and human impact. Journal of Paleolimnology 11:323–332.
Kelts, K. and K.J. Hsü, 1978. Freshwater carbonate sedimentation. In: “Lakes. Geology, Chemistry, Physics”. (A. Lerman, Ed.), Springer Verlag, New York. 295–323.
Koschel, R., G. Proft and H. Raidt, 1987. Autochthone Kalkfällung in Hartwasserseen der Mecklenburger Seenplatte. Limnologica 18:317–338.
Kunz, B. and W. Stumm, 1984. Kinetik der Bildung und des Wachstums von Calciumcarbonat. Vom Wasser 62:279–293.
Lamoureux, S.F., 1994. Embedding unfrozen lake sediments for thin section preparation. Journal of Paleolimnology 10:141–146.
Leemann, A., F. Niessen and M. Sturm, 1991. Rhythmite in alpinen Vorgletscherseen-Warvenstratigraphie und Speicherung von Klimainformation. Zbl. Geol. Paläont. Teil I 12:2963–2976.
Lotter, A.F., 1989. Evidence of annual layering in Holocene sediments of Soppensee, Switzerland. Aquatic Sciences 51:19–30.
Lotter, A.F. The recent eutrophication of Baldeggersee (Switzerland) as assessed by fossil diatom assemblages. The Holocene: in press
Lotter, A.F., B. Ammann and M. Sturm, 1992. Rates of change and chronological problems during the late-glacial period. Climate Dynamics 6:233–239.
Lotter, A.F. and M. Sturm, 1993. The study of environmental dynamics by means of laminated sediments; results from Switzerland. PACT 41:15–24.
Lotter, A.F., I. Renberg, H. Hansson, R. Stöckli and M. Sturm, 1997a. A remote controlled freeze corer for sampling of unconsolidated surface sediments. Aquatic Sciences 59:295–303.
Lotter, A.F., J. Merkt and M. Sturm, 1997b. Differential sedimentation versus coring artifacts: a comparison of two widely used piston-coring methods. Journal of Paleolimnology 18:75–85.
Lotter, A.F. and H.J.B. Birks, 1997. The separation of the influence of nutrients and climate on the varve time-series of Baldeggersee, Switzerland. Aquatic Sciences 59:362–375.
Mayer, L.M., 1994. Relationships between mineral surfaces and organic carbon concentrations in soils and sediments. Chem. Geol. 114:347–363.
Niessen, F. and M. Sturm, 1987. Die Sedimente des Baldeggersees (Schweiz)-Ablagerungsraum und Eutrophierungsentwicklung während der letzten 100 Jahre. Arch. Hydrobiol. 108: 365–383.
Nipkow, F., 1927. Über das Verhalten der Skelette planktischer Kieselalgen im geschichteten Tiefenschlamm des Zürich-und Baldeggersees. Thesis, ETH Zürich.
O’Sullivan, P.E., 1983. Annually-laminated lake sediments and the study of Quaternary environmental changes—a review. Quaternary Science Reviews 1:245–313.
Peglar, S.M., 1993. The mid-HoloceneUlmus decline at Diss Mere, Norfolk, U.K.: a year-by-year pollen stratigraphy from annual laminations. The Holocene 3:1–13.
Perkins, J.A. and J.D. Sims, 1983. Correlation of Alaskan varve thickness with climatic parameters, and use in paleoclimatic reconstruction. Quaternary Research 20:308–321.
Ralska-Jasiewiczowa, M., B. Wicik and K. Wieckowski, 1987. Lake Gosciaz—a site of annually laminated sediments covering 12 000 years. Bulletin Polish Academy of Science, Earth Science 35:127–137.
Renberg, I., U. Segerström and J.-E. Wallin, 1984. Climatic reflection in varved lake sediments. In “Climatic changes on a Yearly to Millennial Basis.” (N.-A. Mörner and W. Karlén, Eds.), Reidel. 249–256.
Schaller, T. and B. Wehrli, 1996. Geochemical focusing of manganese in lake sediments—an indicator of deep-water oxygen conditions. Aquatic Geochemistry 2:359–378.
Schaller, T., H.C. Moor and B. Wehrli, 1997. Sedimentary profiles of Fe, Mn, V, Cr, As and Mo recording signals of changing deep-water oxygen conditions in Baldeggersee. Aquatic Sciences 59:345–361.
Simola, H., 1992. Structural elements in varved lake sediments. Geological Survey of Finland Spec. Paper 14:5–9.
Simola, H., I. Hanski and M. Liukkonen, 1990. Stratigraphy, species richness and seasonal dynamics of plankton diatoms during 418 years in Lake Lovojärvi, South Finland. Annales Botanici Fennici 27:241–259.
Simola H., P. Huttunen and J. Meriläinen, 1986. Techniques for sediment freezing and treatment of frozen sediment samples. Univ. Joensuu, Publications of Karelian Institute 79:99–107.
Spengeler, R., 1994. Die Sanierung des Baldeggersees: Besiedlung des Benthals durch Oligochaeten und Chironomiden 12 Jahre nach Beginn der seeinternen Massnahmen. Diploma Thesis, ETH Zürich.
Stadelmann, P., P. Herzog, P. Arnold, J.C. Bernegger, E. Butscher, F. Hirsiger and P. Koller, 1994. Sanierung des Baldegger- und Hallwilersees und deren Einzugsgebiete. Situationsanalyse und Rechenschaftsbericht zuhanden des Gemeindeverbandes Baldegger- und Hallwilersee. Luzern, Kantonales Amt für Umweltschutz.
Sturm, M., 1985. Schwebstoffe in Seen. Mitt. EAWAG 19:9–15.
Sturm, M. and A.F. Lotter, 1995. Lake sediments as environmental archives. EAWAG News 38(E):6–9.
Svensson, J.M. and L. Leonardson, 1996. Effects of bioturbation by tube-dwelling chironomid larvae on oxygen uptake and denitrification in eutrophic lake sediments. Freshwater Biology 35:289–300.
Urban, N.R., C. Dinkel and B. Wehrli, 1996. Solute transfer across the sediment-water surface of a eutrophic lake: I. Porewater profiles from dialysis samplers. Aquatic Sciences 59:1–25.
Urban, N.R., R. Gächter and J. Bloesch, 1997. The significance of C:N ratios in particles in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr.: in press.
Wehrli, B., A.F. Lotter, T. Schaller and M. Sturm, 1997. High-resolution varve studies in Baldeggersee (Switzerland): project overview and limnological background data. Aquatic Sciences 59:285–294.
Wieland, E., P.H. Santschi, P. Höhener and M. Sturm, 1993. Scavenging of Chernobyl137Cs and natural210Pb in Lake Sempach, Switzerland. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 57: 2959–2979.
Wohlfarth, B., S. Björck, G. Possnert, G. Lemdahl, L. Brunnberg, J. Ising, J. Olsson and N.-O. Svensson, 1993. AMS dating Swedish varved clays of the last glacial/integlacial transition and the potential/difficulties of calibrating Late Weichselian “absolute” chronologies. Boreas 22: 113–128.
Zolitschka, B., 1996. High resolution lacustrine sediments and their potential for palaeoclimatic reconstruction. Climatic variations and forcing mechanisms of the last 2000 years. (P.D. Jones, R.S. Bradley and J. Jouzel, eds.), High resolution lacustrine sediments and their potential for palaeoclimatic reconstruction. Berlin, Springer Verlag. NATO ASI Series, I 41:453–478.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lotter, A.F., Sturm, M., Teranes, J.L. et al. Varve formation since 1885 and high-resolution varve analyses in hypertrophic Baldeggersee (Switzerland). Aquatic Science 59, 304–325 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522361
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522361