Abstract
A new physical method of analysis of samples containing small quantities of aluminium is described. The sample is bombarded with fast protons and the resulting γ-rays are analysed by the Ge(Li) technique. The high selectivity of these detectors allows identification of the nuclei responsible for the γ-ray emission.
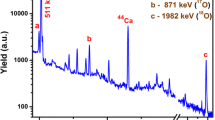
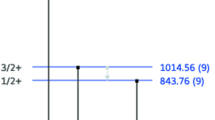
A careful analysis has been made of the different nuclear reactions involved in the production of γ-rays in the bombardment of aluminium. Four γ-rays have been observed with sufficient intensities for rapid determination: 843 keV, 1013 keV, 1368 keV and 1778 keV. Thick-target excitation yields are presented and discussed in view of their use in analysis. A complete tabulation of these reactions is also presented. The method allows the determination of the aluminium concentration in every solid matrix in the 100 ppm range. In some cases concentrations as low as 10 ppm can be observed. All these determinations are quantitative. Lower concentrations can be detected qualitatively. Examples of the application of the method to different substances are the following: stainless steel, inorganic compounds, crystals, evaporated layers, etc. The resonance pattern observed in the intensity curves can be used to measure the homogeneity and the thickness of thin layers containing aluminium (0.2 to 4 μm). In most cases the method can be considered non-destructive and there is no residual radioactivity. Analysis of a sample of a total weight not exceeding 0.1 mg can be achieved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Deconninck, Analyse des surfaces par réactions (p, γ) et (p, p′γ). LARN 702, 1970; Dosage des éléments par réaction nucléaire de basse énergie.Ann. Soc. Scient., Bruxelles, 83 (1969) 45.
G. Demortier, Efficience absolue de deux détecteurs Ge(Li). LARN 703, 1970; to be published in the Proc. on Photon detectors, Varna, 1971.
P. F. Dahl, D. G. Costello, W. L. Walters,Nucl. Phys., 21 (1960) 109.
M. A. Meyer, N. S. Wolmarans, D. Retmann,Nucl. Phys., A 144 (1970) 261.
G. Demortier, F. Bodart (in this Proceedings),J. Radioanal Chem., 12 (1972) 209.
F. Bodart, G. Demortier, G. Deconninck, Dosage du Na par réactions (p, γ), (p, p′ γ) et (p, αγ). LARN 705, 1970.
G. Demortier, G. Deconninck, F. Bodart, L. Thône, Dosage de l'Aluminium par réaction (p, γ), (p, p′ γ), (p, αγ). LARN 704, 1970.
C. F. Williamson, J. P. Boujot, J. Picard, Tables of range and stopping power of chemical elements for charged particles of energy 0.05 to 500 MeV.
G. Deconninck, G. Demortier, Dosage d'échantillons métalliques par réactions atomiques et nucléaires promptes. LARN 725, 1972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deconninck, G., Demortier, G. Quantitative analysis of aluminium by prompt nuclear reactions. J. Radioanal. Chem. 12, 189–208 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02520988
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02520988