Abstract
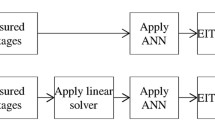
A comparison of in vivo image results is performed for five image-reconstruction programs, featuring an increase in accuracy of boundary modelling from a simple 2-D disk to a true boundary shape with each current drive field individually calculated. Variations are found both in the positions of imaged features and their appearance, but reasonable consistency in reconstructed impedance changes is obtained for both phantom and in vivo data. In terms of quantitative measurements, the programs based on the simpler boundary assumptions generally perform more reliably than the more complex versions. It is concluded that the quantitative use of EIT with simple boundary assumptions is not compromised by body contour variations between patients, provided that the appropriate regions of interest can be correctly identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber, D. C., andBrown, B. H. (1986): ‘Recent developments in applied potential tomography’in Bacharach, S. (Ed.), ‘Information processing in medical imaging’ Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht) pp. 106–121
Brown, B. H., andSeagar, A. D. (1987): ‘The Sheffield data collection system’,Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas.,8,suppl. A, pp. 91–97
Harris, N. D., Suggett, A. J., Barber, D. C., andBrown, B. H. (1987): ‘Application of applied potential tomography (APT) in respiratory medicine,’Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas.,8, (Suppl. A), pp. 155–165
Kotre, C. J. (1993): ‘Studies of image reconstruction algorithms for electrical impedance tomography’. PhD Thesis, University of Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK
Kotre, C. J. (1994): ‘EIT image reconstruction using sensitivity weighted filtered backprojection,’Physiol. Meas.,15, (Suppl 2A), pp. A125-A136
Mangnall, Y. F., Baxter, A. J., Avill, R., Bird, N. C., Brown, B. H., Barber, D. C., andFreeston, I. L. (1987): ‘Applied potential tomography: a new non-invasive technique for measuring gastric function,’Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas.,8, (Suppl. A), pp. 119–129
Older, J. K., andJohns, P. C. (1993): ‘Matrix formulation of computed tomogram reconstruction,’Phys. Med. Biol.,38, pp. 1051–1064
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotre, C.J. Variations inin vivo electrical impedance tomography images due to inaccuracy in boundary representation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 34, 355–358 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02520004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02520004