Summary
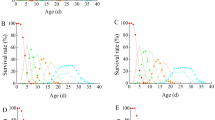
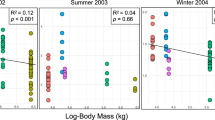
Time-specific life tables were constructed for three pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae), populations using a modification ofHughes' analytical procedure. All populations were studied on second-growth alfalfa (mid-June to mid-July) in south central Wisconsin; data for two populations were collected during 1980, and data for the third population were collected during 1982. The intrinsic rate of increase (r m) estimated on a physiological time (day-degree) scale under field conditions but in the absence of natural enemies, provided a reliable estimate of potential population growth rate and was used in preference toHughes' approach of estimating potential population growth rates directly from stage structure data. Emigration by adult alatae and fungal disease were the major sources ofA. pisum mortality in each of the three populations studied. These factors were most important because of their impact on reducing birth rates within the local population. Parasitism was never greater than 9 percent. Mortality attributable to predation ranged from 0.0 to about 30.0%; however, even at the highest predator densitiesA. pisum populations increased exponentially.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. C. (1976) A modified sine wave method for calculating degree days.Environ. Entomol. 5: 388–396.
Angalet, G. W. andR. Fuester (1977) TheAphidius parasites of the pea aphidAcyrthosiphon pisum in the eastern half of the United States.Ann. Entomol. Sco. Am. 70: 87–96.
Birch, L. C. (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population.J. Anim. Ecol. 17: 15–26.
Campbell, A. andM. Mackauer (1975) Thermal constants for development of the pea aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) and some of its parasites.Can. Entomol. 107: 419–422.
Carter, N., D. P. Aikman andA. F. G. Dixon (1978) An appraisal ofHughes' time-specific life table analysis for determining aphid reproductive and mortality rates.J. Anim. Ecol. 47: 677–687.
Culin, J. D. andK. V. Yeargan (1983) Spider fauna of alfalfa and soybean in central Kentucky.Trans. Ky. Acad. Sci. 44: 40–45.
Fluke, C. L. Jr. (1925) Natural enemies of the pea aphid (Illinoia pisi Kalt.); their abundance and distribution in Wisconsin.J. Econ. Entomol. 18: 612–616.
Frazer, B. D. andN. Gilbert (1976) Coccinellids and aphids: a quantitative study of the impact of adult ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) preying on field populations of pea aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae).J. Entomol. Soc. Brit. Columbia 73: 33–56.
Gilbert, N., A. P. Gutierrez, B. D. Frazer andR. E. Jones (1976)Ecological relationships. W. H. Freeman and Co. San Francisco, CA.
Hamilton, G. C., R. L. Kirkland andI. D. Peries (1982) Population ecology ofSchizaphis graminum (Rondani) (Homoptera: Aphididae) on grain sorghum in central Missouri.Environ. Entomol. 11: 618–628.
Harper, A. M., J. P. Miska, G. R. Manglitz, B. J. Irwin andE. J. Armbrust (1978) The literature of arthropods associated with alfalfa. III. A bibliography of the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Spec. Publ. Ill. Agric. Exp. Stn.50: 1–89.
Hughes, R. D. (1962) A method for estimating the effects of mortality on aphid populations.J. Anim. Ecol. 31: 389–396.
Hughes, R. D. (1963) Population dynamics of the cabbage aphid,Brevicoryne brassicae (L.).J. Anim. Ecol. 32: 393–424.
Hughes, R. D. (1972) Population dynamics. 275–293. InH. F. van Emden (ed)Aphid Technology. Academic Press, London and New York.
Humber, R. A. (1981) An alternative view of certain taxonomic criteria used in the Entomophthorales (Zygomycetes).Mycotaxon. 13: 191–240.
Hutchison, W. D. andD. B. Hogg (1983) Cornicle length as a criterion for separating field-collected nymphal instars of the pea aphid,Acrythosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae).Can. Entomol. 115: 1615–1619.
Hutchison, W. D. andD. B. Hogg (1984) Demographic statistics for the pea aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Wisconsin and a comparison with other populations.Environ. Entomol. 13: 1173–1181.
Mackauer, M. andJ. J. Way (1976)Myzus persicae Sulz., an aphid of world importance. 71–75. InV. L. Delucchi (ed.)Studies in Biological Control. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, London.
Pimentel, D. andA. G. Wheeler, Jr. (1973) Species and diversity of arthorpods in the alfalfa community.Environ. Entomol. 2: 659–668.
Scriber, J. M. andF. Slansky, Jr. (1981) The nutritional ecology of immature insects.Ann. Rev. Entomol. 26: 183–211.
Shaw, M. J. P. (1970) Effects of population density on alienicolae ofAphis fabae Scop II. The effects of crowding on the expression of migratory urge among alatae in the laboratory.Ann Appl. Biol. 56: 197–203.
Simonet, D. E., R. L. Pienkowski, D. G. Martinez andR. D. Blakeslee (1978) Laboratory and field evaluation of sampling techniques for the nymphal stages of the potato leafhopper on alfalfa.J. Econ. Entomol. 71: 840–842.
Sutherland, O. R. W. (1967) Role of host plant in production of winged forms by a green strain of pea aphidAcyrthosiphon pisum Harris.Nature 216: 387–388.
Sutherland, O. R. W. (1969) The role of crowding in the reproduction of winged forms by two strains of the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum.J. Insect Physiol. 15: 1385–1410.
Taylor, F. (1979) Convergence to the stable age distribution in populations of insects.Amer. Natur. 113: 511–530.
Voegtlin, D. J. andD. L. Dahlsten (1982) Observations on the biology ofCinara ponderosae (Williams) (Homoptera: Aphididae) in the westside forests of the Sierra Nevada.Hilgardia 50: 1–19.
Wheeler, A. G., Jr. (1974) Studies on the arthropod fauna of alfalfa. VI. Plant bugs (Miridae).Can. Entomol. 106: 1267–1275.
Wheeler, A. G., Jr. (1977) Studies on the arthropod fauna of alfalfa. VII. Predaceous insects.Can. Entomol. 109: 423–427.
Wheeler, A. G., Jr., J. T. Hayes andJ. L. Stephens (1968) Insect predators of mummified pea aphids.Can. Entomol. 100: 221–222.
Wilding, N. (1970) The effect of temperature on the infectivity and incubation periods of the fungiEntomopthora aphids andE. thaxteriana for the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum.Proc. Int. Colloq. Insect Pathol. 4: 84–88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchison, W.D., Hogg, D.B. Time-specific life tables for the pea aphid,Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris), on alfalfa. Res Popul Ecol 27, 231–253 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02515463
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02515463