Summary
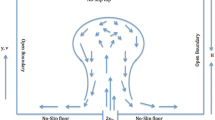
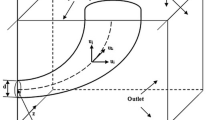
Water tank experiments were conducted to investigate plume rise and diffusion of gases discharged from stacks under calm conditions with field wind velocity less than 0.4 m/s with stable thermal stratification. Similarity rules of scaled model experiments were obtained from nondimensional analysis of the fundamental equation. The densimetric Froude number of a plume and the buoyancy ratio of the plume and the atmosphere were varied during the water tank experiments while plume rise height, plume thickness, etc. were measured. It was found that the experimental results could be expressed in terms of these two dimensionless parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Ogino et al.:Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer,23, 1581 (1980).
G. A. Briggs:Plume Rise, AEC Critical Review Series, TID-25075 (1969).
S. Ito et al.: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Refined Flow Modelling & Turbulence Measurements (IAHR, 1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
To speed up publication, proofs were not sent to the authors and were supervised by the Scientific Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohba, R., Kakishima, S. & Ito, S. Water tank studies of plume rise and diffusion in a stably stratified layer under calm conditions. Il Nuovo Cimento C 13, 1017–1028 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514789
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514789