Abstract
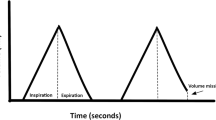
We have studied the effect of spontaneous sighs on maintaining arterial oxygenation in patients receiving epidural morphine for analgesia after upper abdominal surgery. Sixteen patients scheduled for elective gastrectomy were monitored continuously with pulse oximetry and respiratory inductive plethysmography (RIP) during one night preoperatively and for 60 h postoperatively with repeate arterial blood gas analysis. An average of 3.1±1.2 (±SD) sighs were observed per hour preoperatively during sleep while postoperative sighs were significantly depressed to an average less than one per hour throughout the 60 h of the monitoring period (P<0.05). Although postoperative Pao2 values were significantly lower than preoperative values, there was no correlation between the decreases in Pao2 values and number of sighs. Thus, it is unlikely that the long-term absence of spontaneous sighs observed may serve as a contributing factor for the long-lasting hypoxemia in the postoperative period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thach BT, Taeusch HW (1976) Sighing in newborn humans infants: role of inflation-augmenting reflex. J Appl Physiol 41:502–507
Fletcher G, Barber JL (1966) Lung mechanics and physiologic shunt during spontaneous breathing in normal subjects. Anesthesiology 27:638–647
Haldane JS, Meakins JC, Priestley JG (1919) The effects of shallow breathing, J. Physiol 52:433–453
Zikria BA, Spencer JL, Kinney JM, et al. (1974) Alterations in ventilatory function and breathing patterns following surgical trauma. Ann Surg 179:1–7
Okinaka AJ (1967) The pattern of breathing after operation. Surg Gynecol Obstet 125:785–790
Sackner MA, Watson H, Belsito AS, et al. (1989) Calibration of respiratory inductive plethysmography during natural breathing. J Appl Physiol 66(1): 410–420
Craig DB (1981) Postoperative recovery of pulmonary function. Anesth Analg 60:46–52
Meyers JR, Lembeck L, O'kane H, et al. (1975) Changes in functional residual capacity of the lung after operation. Arch Surg 110:576–583
Reynolds LB Jr (1973) The function of the reflex deep breath in pulmonary congestion. Resp Physiol 18:129–141
Bartlett D Jr (1971) Origin and regulation of spontaneous deep breaths. Respir Physiol 12:230–238
Cherniack NS, von Euler C, Glogowska M, et al. (1981) Characteristics and rate of occurrence of spontaneous and provoked augmented breaths. Acta Physiol Scand 111:349–360
Bendixen HH, Smith GM, Mead J (1964) Pattern of ventilation in young adults. J Appl Physiol 19:195–198
Grim PS, Freund PR, Cheney FW Jr (1987) Effect of spontaneous sighs on arterial oxygenation during isoflurane anesthesia in humans. Anesth Analg 66:839–842
Weil JV, McCullough RE, Kline JS, et al. (1975) Diminished ventilatory response to hypoxia and hypercapnia after morphine in normal man. N Engl J Med 292:1103–1106
Egbert LD, Bendixen HH (1964) Effect of morphine on breathing pattern. JAMA 188:485–488
El-Baz NMI, Faber LP, Jensik RJ (1984) Continuous epidural infusion of morphine for treatment of pain after thoracic surgery: a new technique. Anesth Analg 63:757–764
Ravin MB (1966) Value of deep breaths in reversing postoperative hypoxemia. NY State J Med 66:224–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Nozaki-Taguchi, N., Nishino, T. Depression of sighing in the first three postoperative days with epidural morphine analgesia. J Anesth 8, 415–419 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514619
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514619