Abstract
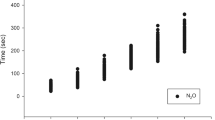
In this study, a vital capacity rapid inhalation induction technique was used, and 4.5% sevoflurane in 100% oxygen and with 66% nitrous oxide in oxygen were compared. Each anesthetic gas was used on a group of 17 unpre-medicated volunteers. The induction time of sevoflurane in nitrous oxide with oxygen and sevoflurane in oxygen were 55±10 s and 81±22 s (SD), respectively, (P<0.05). Notable cardiovascular instability was not observed in either group. Serious complications such as laryngospasm, breath holding, and excessive salivation were not observed in either group. In conclusion, the addition of nitrous oxide to sevoflurane in oxygen is a useful technique because there were no increases in complications during the accelerated rapidity of induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruffle JM, Snider MT, Rosenberger JL, Latta WB (1985) Rapid induction of halothane anaesthesia in man. Br J Anaesth 57:607–611
Wilton NCT, Thomas VL (1986) Single breath induction of anaesthesia, using a vital capacity breath of halothane, nitrous oxide and oxygen. Anaesthesia 41:472–476
Eger EI II (1974) Concentration and second gas effects, anesthetic uptake and action. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 119–120
Lamberty JM, Wilson IH (1987) Single breath induction of anaesthesia with isoflurane. Br J Anaesth 59:1214–1218
Doi M, Ikeda K (1987) Respiratory effects of sevoflurane. Anesth Analg 66:241–244
Strum DP, Eger EI (1987) Partition coefficient for sevoflurane in human blood, saline, and olive. Anesth Analg 66:657–659
Khoo ST, Woo M, Kumar A (1993) Preoxygenation techniques: the value of nitrous oxide. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 37: 23–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Yurino, M., Kimura, H. The influence of additional nitrous oxide during rapid anesthetic induction with sevoflurane. J Anesth 8, 406–409 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514617
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514617