Abstract
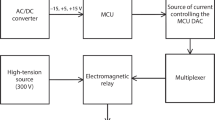
Impedance pneumography signals were characterised during diaphragm pacing using stimulating and recording electrodes placed on the abdominal surface of the diaphragm. These measurements were useful for the detection of muscle contraction without confounding effects from stimulus artifacts. Impedance pneumography signals were measured using 23 epimysial electrodes implanted in seven dogs with 1–5 experiments on each electrode. The polarity of the change in impedance associated with diaphragm pacing differed for each recording electrode and its configuration. Thirty-four of 57 cases produced increased impedance, 11 produced decreased impedance and the remaining 12 depended on the level of diaphragm activation. Impedance pneumography signals were useful for detecting complete airway obstruction. The mean difference between the impedance measured during open and obstructed airway conditions was 80% of the open airway impedance signal. The difference between open and obstructed airway impedance measurements was a mean of 2.3 times larger with a recording electrode on the same hemidiaphragm as the stimulating electrode, compared to an electrode placed on the opposite hemidiaphragm (p<0.05, paired t test, four dogs). In addition, the differences between open and completely obstructed airways were a mean of 2.8 times larger when the second recording electrode was placed on the thorax at the fifth intercostal space, compared to the ninth intercostal space (p<0.05, two-factor ANOVA, one dog, two replicates). It was concluded that impedance pneumograph circuitry could be incorporated into an existing diaphragm pacer using electrodes placed on the diaphragm to provide valuable measurements of the function of the device.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albisser, A. M., andCarmichael, A. B. (1974): ‘Factors in impedance pneumography’,Med. Biol. Eng.,17, pp. 599–605
Baer, G. A., Watt, J., Partanen-Talsta, A. A., Talonen, P. P. andKrishnan, K. R. (1992): ‘Mechanism of unexpected death in a patient with C2 quadriplegia ventilated by aid of a phrenic nerve stimulator’,Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehab.,71, pp. 39–40
Baker, L. E., Geddes, L. A., andHoff, H. E. (1965): ‘Quantitative evaluation of impedance spirometry in man’,Am. J. Med. Electron.,4, pp. 73–77
Baker, L. E., Geddes, L. A., Hoff, H. E. andChaput, C. J. (1966): ‘Physiological factors underlying transthoracic impedance variations in respiration’,J. Appl. Physiol.,21, pp. 1491–1499
Cooley, W. L. (1970): ‘The parameters of transthoracic electrical condution’,Ann. N.Y.: Acad. Sci.,170, pp. 702–712
Glenn, W. W. L., Hogan, J. F., Loke, J. S. O., Ciesielski, T. E., Phelps, M. L. andRowedder, R. (1984): ‘Ventilatory support of the conditioned diaphragm in quadriplegia’,New Engl. J. Med.,310, pp. 1150–1155
Glenn, W. W. L., Holcomb, W. G., Gee, J. B. L. andRath, R. (1970): ‘Long term ventilatory assistance by radio frequency electrophrenic respiration’,Ann. Surg.,172, pp. 755–774
Glenn, W. W. L. andPhelps, M. L. (1985): ‘Diaphragm pacing by electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves’,Neurosurgery,17, pp. 974–984
Kahlafalla, A. S., Spyker, D. A., Stackhouse, S., Simonson, E. andNishijima, K. (1970): ‘Thoracic impedance techniques for the discrimination of normals from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease’,Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.,170, pp. 689–701
Logic, J. L., Maskuo, M. G. andHamilton, M. H. (1967): ‘Factors affecting transthoracic impedance signals used to measure breathing’,J. Appl. Physiol.,22, pp. 251–254
Montgomery, D. C. (1991): ‘Design and analysis of experiments’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York), pp. 270–276
Marzocchi, M., Brouillette, R. T., Weese-Mayer, D. E., Morrow, A. S. andConway, L. P. (1990): ‘Comparison of transthoracic impedance/heart rate monitoring and pulse oximetry for patients using diaphragm pacemakers’,Pediatr. Pulm.,8, pp. 29–32
Neuman, M. R., Huch, R. andHuch, A. (1984): ‘The neonatal oxycardiorespirogram’,Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng.,11, pp. 77–112.
Nochomovitz, M. L., Schmit, B. D. andMortimer, J. T. (1990): ‘Electrical activation of the diaphragm’,Probl. Resp. Care,3, pp. 507–533
Pasquali, E. (1967): ‘Problems in impedance pneumography: electrical characteristics of skin and lung tissue’,Med. Biol. Eng.,5, pp. 249–258
Peterson, D. K., Nochomovitz, M. L., Dimarco, A. F. andMortimer, J. T. (1986): ‘Intramuscular electrical activation of the phrenic nerve’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,33, pp. 342–351
Schmit, B. D. andMortimer, J. T. (1997): ‘The tissue response to epimysial electrodes for diaphragm pacing in dogs’,IEEE Trans Biomed. Eng.,44, pp. 921–930
Schmit, B. D., Stellato, T. A., Miller, M. E. andMortimer, J. T. (1998): ‘Laparoscopic placement of electrodes for diaphragm pacing using stimulation to locate the phrenic nerve motor points’,IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng.,6, pp. 382–390
Schmit, B. D., Stallato, T. A. andMortimer, J. T. (1997): ‘Staple penetration and staple histological response for attaching an epimysial electrode onto the abdominal surface of the diaphragm using a laparoscopic approach’,Surg. Endosc.-Ultras.,11, pp. 45–53
Supinski, G. S., Bark, H., Guanciale, A. andKelsen, S. G. (1986): ‘Effects of alterations in muscle fiber length on diaphragm blood flow’,J. Appl. Physiol.,60, pp. 1789–1796
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmit, B.D., Kayyali, H., Makovos, B. et al. An implantable impedance pneumograph monitor for detection of diaphragm contraction and airway obstruction during diaphragm pacing. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 37, 162–168 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02513283
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02513283