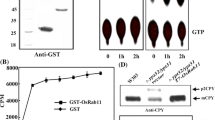
Abstract
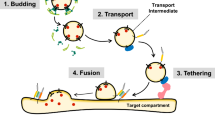
Extensive studies on the molecular mechanisms of vesicular trafficking have revealed that molecules involved in this cellular function are remarkably well conserved from yeast to higher plants. However, it is not clear at all how a variety of organisms maintain the individual divergent systems using the common machinery of vesicular traffic. We have been attempting to understand the roles and regulatory mechanisms of vesicular traffic in plants through the study of Rab/Ypt GTPases. Ara proteins are Rab/Ypt homologues ofArabidopsis, which are implicated in the regulation of vesicular traffic. Their biochemical properties are similar to those of the Rab/Ypt proteins from animal and yeast cells. The overexpression ofARA2 orARA4 causes pleiotropic morphological abnormalities in the transgenic tobacco plants. The GTPase cycle of Ara proteins has to be strictly controlled for their proper functions. We have identified two classes of regulator molecules of Ara2 and Ara4. One is the GTPase activating protein (GAP), and the other is the GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI). GAP has been identified as an activity accelerating the hydrolysis of GTP by Ara2 or Ara4. GDI (AtGDI1) has been isolated as a molecule interacting with Ara4 using a novel method for detecting interactions between foreign molecules in yeast. Further studies on the interacting molecules should unveil the regulatory system of and signal transduction pathway via Ara proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anai, T., Aspuria, E.T., Fujii, N., Ueda, T., Matsui, M., Hasegawa, K., andUchimiya, H. 1995. Immunological analysis of a small GTP-binding protein in higher plant cells. J. Plant Physiol.147: 48–52.
Anai, T., Hasegawa, K., Watanabe, Y., Uchimiya, H., Ishizaki, R. andMatsui, M. 1991. Isolation and analysis of cDNAs encoding small GTP-binding proteins ofArabidopsis thaliana. Gene108: 259–264.
Anai, T., Matsui, M., Nomura, N., Ishizaki, R. andUchimiya, H. 1994.In vitro mutation analysis ofArabidopsis thaliana small GTP-binding proteins and detection of GAP-like activities in plant cells. FEBS Lett.346: 175–180.
Aspuria, E.T., Anai, T., Fujii, N., Ueda, T., Miyoshi, M., Matsui, M. andUchimiya, H. 1995. Phenotypic instability of transgenic tobacco plants and their progenies expressingArabidopsis thaliana small GTP-binding protein genes. Mol. Gen. Genet.246: 509–513.
Bednarek, S.Y., Reynolds, T.L., Schroeder, M., Grabowski, R., Hengst, L., Gallwitz, D. andRaikhel, N.V. 1994. A small GTP-binding protein fromArabidopsis thaliana functionally complements the yeastypt6 null mutant. Plant Physiol.104: 591–596.
Ferro-Novick, S. andNovick, P. 1993. The role of GTP-binding proteins in transport along the exocytic pathway. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol.9: 575–599.
Ma, H. 1994. GTP-binding proteins in plants: new members of an old family. Plant Mol. Biol.26: 1611–1636.
Matsui, M., Sakamoto, S., Kunieda, T., Nomura, N. andIshizaki, R. 1989. Cloning ofara, a putativeArabidopsis thaliana gene homologous to theras-related gene family. Gene76: 313–319.
Nuoffer, C. andBalch, W.E. 1994. GTPases: multifunctional molecular switches regulating vesicular traffic. Annu. Rev. Biochem.63: 949–990.
Pfeffer, S.R., Dirac-Svejstrup, B. andSoldani, T. 1995. Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor: putting Rab GTPases in the right place. J. Biol. Chem.270: 17057–17059.
Terryn, N., Van Montagu, M. andInzé, D. 1993. GTP-binding proteins in plants. Plant Mol. Biol.22: 143–152.
Ueda, T., Anai, T., Tsukaya, H., Hirata, A. andUchimiya H. 1996a. Characterization and subcellular localization of a small GTP-binding protein (Ara4) from Arabidopsis: conditional expression under control of the promoter of the gene for heat-shock protein HSP81-1. Mol. Gen. Genet.250: 533–539.
Ueda, T., Matsuda, N., Anai, T., Tsukaya, H., Uchimiya, H. andNakano, A. 1996b. An Arabidopsis gene isolated by a novel method for detecting genetic interaction in yeast encodes the GDP dissociation inhibitor of Ara4 GTPase. Plant Cell,8: 2079–2091.
Ueda, T., Yoshizumi, T., Anai, T., Matsui, M., Uchimiya, H. andNakano, A. 1998.AtGDI2, a novelArabidopsis gene encoding a Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor. Gene206: 137–143.
Verma, D.P.S., Cheon, C.-I. andHong, Z. 1994. Small GTP-binding proteins and membrane biogenesis in plants. Plant Physiol.106: 1–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchimiya, H., Anai, T., Aspuria, E.T. et al. The biological roles of small GTPases and interacting proteins in plants. J. Plant Res. 111, 257–260 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02512180
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02512180