Abstract
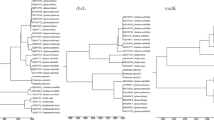
To apply random amplified polymorphic DNA for analysis of phylogenetic relationships, we used 34 synthetic oligonucleotides as primers to examine interspecific and intraspecific variations among 18 genotypes, nine species ofNicotiana. The nine species used in this study belong to sectionsTomentosae andAlatae. In addition, we attempted to clarify the taxonomic position ofN. sylvestris. A total of 354 distinct DNA fragments were obtained by polymerase chain reaction. Pair-wise comparisons of unique and shared amplification products were used to generate Jaccard's similarity coefficients and Nei and Li's similarity coefficients with the computer software of numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. On the basis of the dendrogram constructed with the similarity coefficients, the 18Nicotiana genotypes were divided into two clusters. The classification analyzed by RAPD markers is in accordance with the classification of Goodspeed thatN. sylvestris is a member of sectionAlatae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backeljau, T., De Bruyn, L., De Wolf, H., Jordaens, K., Van Dongen, S. andWinnepennickx, B. 1996. Multiple UPGMA and neighbor-joining trees and the performance of some computer packages. Mol. Biol. Evol.13: 309–313.
Beckmann, J.S. andSoller, M. 1983. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in genetic improvement methodologies, mapping and costs. Theor. Appl. Genet.67: 35–43.
Chaparro, J.X., Werner, D.J., O'Malley, D. andSederoff, R.R. 1994. Targeted mapping and linkage analysis of morphological isozyme, and RAPD markers in peach. Theor. Appl. Genet.87: 805–815.
Demeke, T., Adams, R.P. andChibbar, R. 1992. Potential taxonomic use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD): a case study inBrassica. Theor. Appl. Genet.84: 990–994.
Goodspeed, T.H. 1954. The GenusNicotiana. Waltham, Massachusetts, Chronica, Botanica.
Joshi, C.P. andNguyen, H.T. 1993. RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) analysis based intervarietal genetic relationships among hexaploid wheats. Plant Sci.93: 95–103.
Kostoff, D. 1943. Cytogenetics of the GenusNicotiana. Karyosystematics, Genetics, Cytology, Cytogenetics and Phylesis of Tobaccos. Sofia, State Printing House.
Lamboy, W.F. 1994. Computing genetic similarity coefficients from RAPD data: the effects of PCR artifacts. PCR Methods Applic.4: 31–37.
Martin, G.B., Williams, J.G.K. andTanksley, S.D. 1991. Rapid identification of markers linked to aPseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA88: 2336–2340.
Reiter, R.S., Williams, J.G.K., Feldmann, K.A., Rafalski, J.A., Tingey, S.V. andScolnik, P.A. 1992. Global and local genome mapping inArabidopsis thaliana by using recombinant inbred lines and random amplified polymorphic DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA89: 1477–1481.
Rogers, S.O. andBendich, A.J. 1988. Extraction of DNA from plant tissues.In S.B. Gelvin, R.A. Schilperoot, and D.P.S. Verma, eds., Plant Molecular Biology Manual, Dordrecht, Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. A6: 1–10.
Rohlf, F.J. 1993. NTSYS-pc Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, Version 1.80. New York, Applied Biostatistics.
Tanksley, S.D., Young, N.D., Paterson, A.H. andBonierale, M.W. 1989. RFLP mapping in plant breeding: new tools for an old science. Biotechnology7: 257–264.
Tingey, S.V. anddel Tufo, J.P. 1993. Genetic analysis with random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Plant Physiol.101: 349–352.
Torres, A.M., Weeden, N.F. andMartin, A. 1993. Linkage among isozyme, RFLP and RAPD markers inVicia faba. Theor. Appl. Genet.85: 937–945.
Welsh, J. andMcClelland, M. 1990. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res.18: 7213–7218.
Williams, J.G.K., Hanafey, M.K., Rafalski, J.A. andTingey, S.V. 1993. Genetic analysis using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Method. Enzymol.218: 704–740.
Yang, D.I., Feng, T.Y., Chen, C.C. andLai, Y.K. 1992. Physical maps ofNicotiana chloroplast DNA constructed by an efficient procedure. Theor. Appl. Genet.83: 515–527.
Yu, L.X. andNguyen, H.T. 1994. Genetic variation detected with RAPD markers among upland and lowland rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet.87: 668–672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, YL., Lin, TY. Construction of phylogenetic tree forNicotiana species based on RAPD markers. J. Plant Res. 110, 187–193 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02509307
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02509307