Abstract
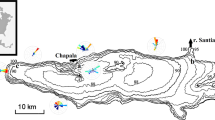
A computational analysis of the periods and structure of surface seiches of Lake of Zürich and its experimental verification from three simultaneous water gauge recordings, mounted along the shores in Zürich. Pfäffikon and Rapperswil is given. After a brief historical account the governing equations and the procedure, how they were discretized by a finite element technique are introduced. Computational results concern seiche periods and seiche structure, in particular co-range and co-tidal lines for the first seven free oscillations which are discussed in detail.
Experimental verification is from recordings taken during January 1982. Inspection by eye allows identification of the three lowest order seiche periods including the phase shift between the recordings of Zürich and Rapperswil. Higher order modes (up to order 19) are also detected by this method. Power spectral analysis including interstation phase shift and coherence allow identification of over fifteen seiche periods. Agreement between the theoretically predicted and experimentally determined periods is excellent for the first, second, third, fair for the fourth, fifth and sixth mode and good for the other higher modes, but statistical reliability is low for these.
Zusammefassung
Die Perioden und die Struktur der Oberflächenseiches des Zürichsees werden rechnerisch ermittelt und mittels dreier simultan arbeitender Pegel, die dem Ufer entlang bei Zürich, Pfäffikon und Rapperswil aufgebaut waren, bestätigt und erweitert. Nach einer kurzen, historischen Übersicht werden die Grundgleichungen und deren Approximation mit einer Finite-Element-Methode diskutiert. Die rechnerischen Resultate betreffen die Seicheperioden und die Seichestruktur, speziell die Linien konstanten Hubes und konstanter Phase für die sieben ersten freien Schwingungen, die im Detail diskutiert werden.
Die experimentelle Überprüfung erfolgt mit Zeitreihen vom Januar 1982. Deren Sichtung erlaubt, die drei Seiches mit den längsten Perioden von Auge zu isolieren samt den Phasendifferenzen zwischen den Messreihen von Zürich und Rapperswil. Eigenschwingungen höherer Ordnung (bis zur Ordnung 19) lassen sich mit dieser Methode ebenfalls angeben. Spektralanalysen, einschliesslich der Phasendifferenz und der Kohärenz aus Messreihenpaaren. erlauben eine Identifikation von mehr als 15 Seicheperioden. Die Übereinstimmung zwischen den rechnerisch vorausgesagten und den experimentell bestimmten Perioden ist für die Schwingungen der ersten, zweiten, dritten und siebten Ordnung ausgezeichnet, für die vierte, fünfte und sechste befriedigend und gut für die anderen höheren Seicheperioden, aber mit wenig statistischer Verlässlichkeit.
Résumé
Les périodes et la structure des seiches de surface du lac de Zurich sont calculées et vérifiées simultanément au moyen de trois jauges installées à Zurich. Pfäffikon et Rapperswil. Use brève introduction historique est suivie de la discussion des équations de base et de leur approximation au moyen d'une méthode à éléments finis. Les résultats des calculs concernent les périodes des seiches et leur structure, en particulier les lignes d'élévation constante et de phase constante pour les sept premières oscillations libres, qui sont discutées en détail.
La vérification expérimentale est effectuée au moyen d'enregistrements de seiches pendant le mois de janvier 1982. L'analyse visuelle permet d'identifier les trois seiches avec les plus longues périodes ainsi que les différences de phases entre les enregistrements de Zurich et de Rapperswil. Les oscillations d'ordre supérieur (jusqu'à 19) sont détectées de la même manière. Les analyses spectrales y compris la différence de phase et la cohérence permettent d'indentifier plus de 15 périodes de seiches. L'accord entre les périodes déterminées théoriquement et par mesure est excellent pour le premier, le deuxième et troisiéme, satisfaisant pour le quatrième, cinquième et sixième ordre et bon pour les ordres supérieurs avec moins de sécurité statistique pour ces derniers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous: Report by M.E. Sarasin, Geneva, on seiches in Lake of Zurich. Arch. Sci. phys. Nat.16, 210–212 (1886).
Anonymous: Jahresbericht der Zürichseekommission für das Jahr 1904. Mitt. Phys. Ges. Zürich (1909).
Anonymous:Les Dénivellations du Lac Léman, Recherches exécutées de 1949, à 1951 Département fédéral des postes et des chemins de fer, communications du service fédéral des eaux, No. 40 (1954).
Bauer, S.W.:Three-dimensional irregular gird finite difference model of wind induced water level fluctuations and currents in a homogeneous lake with applications to the Lake of Geneva. Dr. sc. tech. dissertation, presented to the Department of Civil Engineering, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne,. 158 p. (1979).
Blackman, R.B., and Tukey, J.W.: The measurement of power spectra from the point of view of communications engineering. Dover publ. Inc., New York 1958.
Boys, du P.: Sur le mouvement de balancement rythmé de l'eau des lacs (seiches).C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 62, No 1202 (not seen: ref. Forel 1895) (1891).
Chrystal, J.: Some results in the mathernatical theory of seiches. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb.25 (1904).
Chrystal, J.: On the hydrodynamical theory of seiches. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb.41, part 3, No. 25 (1905).
Defant, A.: Neue Methoden zur Ermittlung der Eigenchwingungen (Seiches) von abgeschlossenen Wassermassen (Seen, Buchten usw.) Ann. Hydrogr. Berl.46 (1918).
Defant, A.: Physical Oceanography. Pergamon, London 1961.
Doodson, A.T., Carey, R.M., and Baldwin, R.: Theoretical determination of the longitudinal, seiches of Lake Geneva. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb.52, part 3 No. 25 (1920).
Forel, F.A.: La formule des seiches. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris83 (1876a).
Forel, F.A.: Le limnimètre enregistrateur de Morges. Arch. Genève61 (1876b).
Forel, F.A.: Die Schwankungen des Bodensees. Deutsche Übersetzung von Eberhard Graf Zeppelin. Schr. Ver. Gesch. Bodensees22 (1893).
Forel, F.A., Le Léman, Monographie Limnologique, tome 2, Ed. F. Rouge. Librairie de l'Université, Lausanne (1895).
Forel, F.A.: Die Seen-Bibliographie der Schw Landeskunde. Verlag K.J. Wyss, Bern 1913.
Gasser, O.: Die Wasserspiegelschwankungen des Bodensees und ihre meteorologischen Grundlagen. Ber. dt. Wetterd.5, No. 35, 25 p. Bad Kissingen (1957).
Hamblin, P.F.: Some free oscillations of a rotating natural basin. Ph.D. thesis, submitted to the University of Washington, Seattle, USA (1972).
Hamblin, P.F., and Hollan, E.: On the gravitational seiches of Lake Constance and their generation. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol.40/1, 119–154 (1978).
Hollan, E.: Erfahrungen mit der mathematischen Modellierung grossräumiger Bewegungsvorgänge im Bodensee. Mitt. Inst. Meeresk., Universität Hamburg25, 1–45 (1981).
Holland, E., Rao, D.B., and Bäuerle, E.: Free surface oscillations, in Lake Constance with an interpretation of the ‘Wonder of the rising water at Konstanz’, in 1549. Arch. Met. Geophys. Biokl. (A)29, 301–325 (1980).
Hutter, K., and Raggio, G.: A Chrystal model describing gravitational barotropic motion in elongated lakes. Arch. Met. Geophys. Biokl. (A) (1982).
Hutter, K., Ramming, H.-G., and Oman, G.: Das Verhalten des homogenen Zürichsees unter verschiedenen Windlasten. Mitteilung No. 61 der Versuchsanstalt für Wasserbau, Hydrologie und Glaziologie an der ETH Zürich (1982a).
Hutter, K., Bucher, C., and Salvadè, G.: Messungen von Wasserspiegelschwankungen mit Hilfe von Seichelimnigraphen im Zürichsee. Interner Bericht, Versuchsanstalt für Wasserbau, Hydrologie und Glaziologie an der ETH Zürich (1982b, unpublished).
Hutter, K., Raggio, G., Bucher, C., Salvadè, G., and Zamboni, F.: The gravitational seiches of Lake of Lugano. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol.40/2, 455 (1983).
Krauss, W.: Methoden und Ergebnisse der Theoretischen Ozeanographie. II. Interne Wellen. Gebrüder Bornträger, Berlin 1965.
Merian, J.R.: Über die Bewegung tropfbarer Flüssigkeiten Basel 1828 (referenced in Forel 1876a).
Mortimer, C. H.: The resonant response of stratified lakes to wind. Revue suisse hydrol.15/1 (1953).
Mortimer, C.H.: Frontiers in physical limnology with particular reference to long waves in rotating basins. Proc. 6th Conf. Great Lakes Res., Publ. Nr. 10, Great Lakes Res. Div., The University of Michigan, 1963.
Mortimer, C.H.: Lake Hydrodynamics. Mitt. int. Verein., Limnol.20, (1974).
Mortimer, C.H.: Strategies for coupling of data collection and analysis with dynamic modelling of lake motions. In: Hydrodynamics of Lakes. Ed. W. H. Graf and C. H. Mortimer. Elsevier Scientific Publ. Comp. Amsterdam 1979.
Mortimer, C.H. Preliminary examination of temperature, current and wind records obtained in the 1978 Lake of Zürich field experiment. Internal Report, Laboratory of Hydraulics, Hydrology and Galciology at ETH Zürich (1982).
Mortimer, C.H., and Fee, E.J.: Free surface oscillations and tides of Lakes Michigan and Superior. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. (A)281, 1–61 (1976).
Mühleisen, R., and Kurth, W.: Experimental investigations on the seiches of Lake Constance. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol.40, 155–168 (1978).
Raggio, G., and Hutter, K.: An extended channel model for the prediction of motion in elongated homogeneous lakes. Part I: Theoretical introduction. J. Fluid Mech. Vol. 121, 231–255 (1982a).
Raggio, G., and Hutter, K.: An extended channel model for the prediction of motion in elongated homogenous lakes. Part II: First order model applied to ideal geometry. Rectangular basins with flat bottom. J. Fluid. Mech. Vol. 121, 257–281 (1982b).
Raggio, G., and Hutter, K.: An extended channel model for the prediction of motion in elongated homogeneous lakes. Part III: Free oscillations in natural basins. J. Fluid. Mech. Vol. 121, 283–299 (1982c).
Rao, D.B., and Schwab, D.J.: Two-dimensional normal modes in arbitrary enclosed basins on a rotating earth: Application to Lakes Ontario and Superior. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. (A)281, 63–96 (1976).
Schwab, D.J.: Determination of wind stress from water level fluctuations. Ph.D. dissertation, The University of Michigan (1981).
Schweitzer, A.: Die Seiches des Walensees. Mitt. Phys. Ges. Zürich14, 21–40 (1909).
Wetli, K.: Die Bewegung des Wasserstandes des Zürichsees während 70 Jahren und Mittel zur Senkung seines Hochwassers, 79 p., 16 plates. Verlag Hofer & Burger, Zürich (1885).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutter, K., Raggio, G., Bucher, C. et al. The surface seiches of Lake of Zürich. Schweiz. Z. Hydrologie 44, 423–454 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02502301
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02502301