Summary
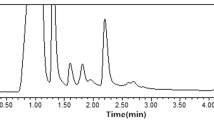
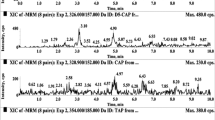
A capillary electrophoresis method for the determination of streptomycin in eggs is described. Analyses were performed on an uncoated silica capillary using a buffer solution of 30 mM sodium dihydrophosphate, 5 mM boric acid and 5 mM sodium tetraborate. Analytes were detected at 200 nm an the calibration curve was linear over the range of 0.16 to 2.0 μg g−1 (r=0.999). The total analysis time was 7 min. The method has been successfully applied to the quantitative determination of streptomycin in hen eggs after drug ingestion and could used for evaluation of maximum residue limits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. F. Prescolt, J. D. Baggot, Antibacterial therapy in veterinary medicine, Iowa State University Press, Ames (1993).
V. Hormazabal, M. Yndestad, J. Liq. Chromatogr.,18, 2695 (1995).
G. C. Gerhardt, C. D. C. Salisbury, J. D. MacNeil, J. AOAC Int.,77, 765 (1994).
N. Kurosawa, S. Kuribayashi, E. Owada, K. Ito, M. Nioka, M. Arakawa, R. Fukuda, J. Chromatogr.,343, 379 (1985).
T. J. Whall, J. Chromatogr.,219, 89 (1981).
C. L. Flurer, J. Pharm. Biomed Anal.,13, 809 (1995).
Codex Committee on Residues of Veterinary Drugs in Foods 1997.
Residues of Certain Veterinary Drugs in Foods, A summary of the conclusions of the Joint FAO WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) at its 48th meeting: Geneva. 18–27 February 1997.
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Fortyseventh Meeting, Rome, 4–13 June 1996.
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products; Committee for Veterinary Medical Products; Streptomycin and Dihydrostreptomycin-Summary Reports 1995.
S. Horii, J. Liq. Chromatogr.,17, 213 (1994).
H. Poiger, Ch. Schlatter, Analyst.101, 808 (1976).
J. P. Sharma, R. F. Bevill, J. Chromatogr.,166, 213 (1978).
W. J. Blanchflower, R. J. McCracken, A. S. Haggan, D. G. Kennedy, J. Chromatogr. B,692, 351 (1997).
J. A. Tarbin, G. Shearer, J. Chromatogr.,579, 177 (1992).
T. Vartiainen, A. Hallikainen, Fresenius J. Anal. Chem.,348, 150 (1994).
S. E. Katz, C. A. Fassbender, J. J. Dowling, J. AOAC Int.,56, 77 (1973).
M. Koketsu, L. R. Juneja, M. Kim, M. Ohta, F. Matsuura, T. Yamamoto, J. Food Sci.,58, 743 (1993).
S. Hoffstetter-Kuhn, A. P. E. Gassmann, H. M. Widmer, Anal. Chem.63, 1541 (1991).
Dihydrosteptomicin and streptomycin in: Evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. WHO Technical Report Series, Geneva879, 25 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kowalski, P., Oledzka, I., Okoniewski, P. et al. Determination of streptomycin in eggs yolk by capillary electrophoresis. Chromatographia 50, 101–104 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02493625
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02493625