Summary
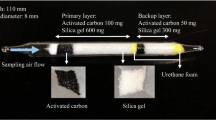
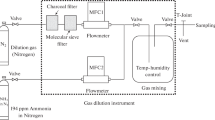
An improved sampling and analytical method for airborne carbon disulfide (CS2) both in the laboratory and in a rayon viscose manufacturing plant is described. A tube-type diffusive sampler (ATD) packed with solid Spherocarb was used for airborne CS2 collection. The ATD was then thermally desorbed and analyzed by (GC-MS). A standard curve range of 0.69 to 103.4 μg was established with correlation coefficient (r)>0.998. Desorption efficiency was 100% mean recovery 97.8% and coefficient of variation<10%. The limit of detection (LOD) was 0.21 μg and limit of quantitation (LOQ) 0.69 μg. Temperature and humidity effects were not significant. There was no influence from tube direction to exposure gas stream. The uptake rate was stable over an 8h period. Even after 90 repeated usages, the uptake rate still remained quite stable. ATD samples were stable at <4°C for at least 2 weeks. Field validation data showed a strong linear correlation (r>0.97) between the proposed method and the current method for fixed-point samples. The proposed method can provide a specific, sensitive, convenient, and reliable tool for assessment of occupational exposure to CS2. Using this method to assess CS2 exposures gives findings comparable to those of the traditional method with respect to accuracy, precision, and effects of environmental interference.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR),Toxicological Profile for Carbon Disulfide, U. S. Public Health Service, U. S. Department of Health and Human Services,1992.
Beauchamp, R. O. Jr.; Bus, J. S.; Popp, J. A.; Boreiko, C. J.; Goldberg, L.Cri. Rev. Toxicol. 1983,11, 169–278.
MacMahon, B.; Monson, R. R.,J. Occup. Med. 1988,30, 698–705.
Phillips, M.Occup. Environ. Health 1992,64, 119–123.
Sweetnam, P. M.; Taylor, S. W. C.; Elwood, C.Br. J. Ind. Med. 1987,44, 220–227.
Council of Labor Affairs,Permissible Exposure Limit at workplace, Taiwan, Republic of China,1995.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration,Federal Register, USA,1989.
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists,Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA,2000.
Cambell, L.; Jones, A. H.; Wilson, H. K.Am. J. Ind. Med. 1985,8, 143–153.
National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health,Manual of analytical methods 4 th ed. NIOSH 1600,1994.
Peltonen, K.J. Chromatogr. 1989,464, 422–427.
Vanhoorne, M.; Van Den Berge, L.; Devreese, A.; Tutgat, E.; Van Poucke, L.; Van Peteghem, C.,Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1991,35, 619–631.
Healt and Safety Executive,Methods for the Determination of Hazardous Substances (MDHS) 80 Volatile organic compounds in air, UK,1995.
Meuling, W.J.A.; Bragt, P.C.; Braun, C.L.J.Am. J. Ind. Med. 1990,17, 247–254.
Tanáka, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Takebayashi, T.; Omae, K.; Seki, Y.Ind. Health 1997 35, 474–479.
Institute of Occupational Safety and Health.Recommended sampling and analytical Method for carbon disulfide, Taiwan, Republic of China,1999.
Institute of Occupational Safety and Health,publication no. IOSH89-A315, Taiwan, Republic of China,2000.
Nelson, A. L.; Kenneth, A. B.,Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology Vol. III, Part A. 3rd ed., New York, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York,1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, V.S., Lai, J.S., Lee, C.C. et al. Improved sampling and analytical method for airborne carbon disulfide measurement in the workplace. Chromatographia 54, 383–388 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02492688
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02492688