Abstract
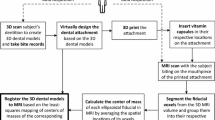
Recently 3-D imaging techniques have been used to shed light on the role of abnormal brain functions in such conditions as nocturnal bruxism and orofacial pain. In order to achieve precise 3-D image fusion between magnetic resonance images (MRI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) data, we developed a removable dental device which attaches rigidly to the teeth. Using this device, correlation of MEG and MRI data points was achieved by the co-registration of 3 or more fiducial points. Using a Polhemus 3-space digitizer the locations of the points were registered on MEG and then a small amount of high-water-content material was placed at each point for registering these same points on MRI. The mean reproducibility of interpoint distances, determined for 2 subjects, was between 0.59 and 0.82 mm. Using a Monte Carlo statistical analysis we determined that the accuracy of a posterior projection from the fiducial points to any point within the strata of the brain is ±3.3 mm. The value of this device is that it permits reasonably precise and repeatable co-registration of these points and yet it is easily removed and replaced by the patient. Obviosly such a device could also be adapted for use in diagnosis and analysis of brain functions related with other various sensory and motor functions (e.g. taste, pain, clenching) in maxillofacial region using MRI and MEG.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lobbezoo, F., Soucy, J.P. and Montplaisir, J.Y.: Striatal D2 receptor binding in sleep bruxism: A controlled study with iodine-123-iodobenzamide and single-photon-emission computed tomography.J. Dent. Res. 75: 1804–1810, 1996.
Laudahn, R., Kohlhoff, H. and Bromm, B.: Magnetoencephalography in the investigation of cortical pain processing.Pain and the Brain: from Nociception to Cognition, pp. 267–282, 1995. “Editors, B. Bromm, J.E. Desmedt, Advanced in Pain Research and Therapy Vol. 22.” Raven Press, Ltd., New York.
Barth, D.S., Sutherling, W.W., Engel, J. and Beatty, J.: Neuromagnetic evidence of spatially distributed sources underlying epileptiform spikes in the human brain.Science 223: 293–296, 1984.
Sutherling, W.W., Crandall, P.H., Cahan, L.D. and Barth, D.S.: The magnetic field of epileptic spikes agrees with intracranial localizations in complex partial epilepsy.Neurol. 38: 778–786, 1988.
Barth, D.S., Sutherling, W.W., Broffman, J. and Beatty, J.: Magnetic localization of a dipolar current source implanted in a sphere and human cranium.Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 63: 260–273, 1986.
Yamamoto, T., Williamson, S.J., Kaufman, L., Nicholson, C. and Llinas, R.: Magnetic localisation of neuronal activity in the human brain.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 8723–8736, 1988.
Ribary, U., Ioannides, A.A., Singh, K.D., Hasson, R., Bolton, J.P.R., Lado, F., Mogilner, A. and Llinas, R.: Magnetic field tomography (MFT) of coherent thalamo-cortical 40 Hz oscillations in humans.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 11037–11041, 1991.
Swerdloff, S.J., Ruegsegger, M. and Wakai, R.T.: Spatiotemporal visualization of neuromagnetic data.Electorenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 86: 51–57, 1993.
Gallen, C.C., Schwartz, B., Rieke, K., Pantev, C., Sobel, D., Hrschkoff, E.C. and Bloom, F.E.: Intrasubject reliability and validity of somatosensory source localization using a large array biomagnetometer.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 90: 145–156, 1994.
Towle, V.L., Bolanos, J., Suarez, D., Tan, K., Grzeszczuk, R., Levin, D.N., Cakmur, R., Frank, S.A. and Spire, J.P.: The spatial location of EEG electrodes: locating the best-fitting sphere relative to cortical anatomy.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 86: 1–6, 1993.
Rogers, R.L., Baumann, S.B., Papanicolaou, A.C., Bourbon, T.W., Alagarsamy, S. and Eisenberg, H.M.: Localization of the P3 sources using magnetoencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 79: 308–321, 1991.
Gill, S.S. and Thomas, D.G.T.: A relocatable frame. Proceedings of the meeting of the Society of British Neurological Surgeons in.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psych. 52: 1460–1461, 1989.
Gill, S.S. Thomas, D.G.T., Warrington, A.P. and Brada, M.: Relocatable frame for stereotactic external beam radiotherapy.Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys. 20: 599–603, 1991.
Graham, J.D., Warrington, A.P., Gill, S.S. and Brada, M.: A non-invasive, relocatable stereotactic frame for fractionated radiotherapy and multiple imaging.Radiotherapy and Oncology 21: 60–62, 1991.
Thomas, D.G.T., Gill, S.S., Wilson, C.B. Darling, J.L. and Parkins, C.S.: Use of relocatable stereotactic frame to integrate positron emission tomography and computed tomography images: Application in human malignant brain tumors.Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 54+55: 388–392, 1990.
Sofat, A., Hughes, S., Briggs, J., Beaney, R.P. and Thomas, D.G.T.: Stereotactic brachytherapy for malignant glioma using a relocatable flame.Brit. J. Neurosurg. 6: 543–548, 1992.
Akhtari, M., McNay, D., Mandelkern, M., Teeter, B., Cline, H.E., Mallick, J., Clark, G.T., Tatar, R., Lufkin, R., Chan, K., Rogers, R.L. and Sutherling, W.W.: Somatosensory evoked surface as the spatial constraint.Brain Topography 7: 63–69, 1994.
Singh, K.D., Holliday, I.E., Furlong, P.L. and Harding, G.F.A.: Evaluation of MRI-MEG/EEG co-registration strategies using Monte Carlo simulation.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 102: 81–85, 1997.
Mosher, J.C., Spencer, M.E., Leahy, R.M., and Lewis, P.S.: Error bounds for EEG and MEG dipole source localization.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 86: 303–321, 1993.
Novak, E.: Error bounds for Monte Carlo methods.Deterministic and Stochastic Error Bounds in Numerical Analysis. pp. 43–52, 1988. “Editors, A. Dold, B. Eckmann.” Lecture Notes in Mathematics 1349, Springer-Verlag Co., Berlin.
Sofat, A., Kratimenos, G. and Thomas, D.G.T.: Early experience with the Gill Thomas Locator for computed tomography-directed stereotactic biopsy of intracranial lesions.Neurosurg. 31: 972–974, 1992.
Kratimenos, G.P., Thomas, D.G.T., Shorvon, S.D. and Fish, D.R.: Stereotactic insertion of intracerebral electrodes in the investigation of epilepsy.Brit. J. Neurosurg. 7: 45–52, 1993.
Gallen, C.C., Sobel, D.F., Waltz, T., Aung, M., Copeland, B., Schwartz, G.J., Hirschkoff, E.C. and Bloom, F.R.: Noninvasive presurgical neuromagnetic mapping of somatosensory cortex.Neurosurg. 33: 260–268, 1993.
Buchner, H., Adams, L., Knepper, A., Ruger, R., Lanorde, G., Gilsbach, J.M., Ludwig, I., Reul, J. and Scherg, M.: Preoperative localization of the central sulcus by dipole source analysis of early somatosensory-evoked potentials and 3-dimensional magnetic-resonance-imaging.Neurosurg. 80: 849–856, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuboki, T., Clark, G.T., Akhtari, M. et al. A newly developed removable dental device for fused 3-D MRI/MEG Imaging. Oral Radiol. 15, 43–52 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02489756
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02489756