Abstract
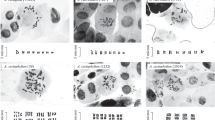
A cytotaxonomic study was made of 90 fern species of Yunnan, southwestern China, based on collections from northwestern, central, and southwestern Yunnan and a few Cheng's collections. The results verified most of the formerly reported basic chromosome numbers of Chinese genera, and recorded for the first time the basic numbers ofGymnogrammitis andSorolepidium and Chinese members of several other genera. Cytotaxonomy of some problematical genera was discussed. Biogeographical relationships between Japanese, Chinese, and Himalayan ferns were compared with special reference to local cyto-reproductive variations inConiogramme, Deparia, Onychium, andPteris cretica. The present evidence indicates that most triploid species examined are agamosporous, as general in filicalean ferns, and also suggests the sexual 32-spored sporogenesis inHypodematium crenatum andSorolepidium graciale as in Lindsaeaceae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bir, S.S. 1973. Cytology of Indian pteridophytes. Glimpses in Plant Research1: 28–119.
Cheng, X. 1991. Notes on the flora and distribution of the pteridophytes of Yunnan, southwest China. J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo Sect. III,15: 73–90.
Ching, R.-C. 1964. On some confused genera of the family Athyriaceae. Acta Phytotax. Sin.9: 41–84.
— 1966. Gymnogrammitidaceae Ching, a new fern family. Acta Phytotax. Sin.11: 12–16.
— 1976 (1988). The geographic distribution of modern pteridophytes in China.In Selected Papers of Ching Ren Chang, pp. 255–263. Scientific Press, Beijing.
— 1978. The Chinese fern families and genera: systematic arrangement and historical origin. Acta Phytotax. Sin.16(3): 1–19 &16(4) 16–37.
Chiu, P.-S. 1981. Observations on the chromosome numbers of Chinese ferns. Acta Phytotax. Sin.19: 451–455.
Christensen, C. 1934. Index Filicum. Supplementum 3. H. Hagerup, Hafniae.
Haufler, C.H. 1987. Electrophoresis is modifying our concepts of evolution in homosporous pteridophytes. Amer. J. Bot.74: 953–966.
Iwatsuki, K. 1964. OnHypodematium Kunze. Acta Phytotax. Gebot.21: 43–54.
— 1975. Taxonomic studies of Pteridophyta X. Acta Phytotax. Geobot.27: 39–55.
—,S.-K. Wu, S. Mitsuta andX. Cheng. 1986. The pteridophytes of Diancangshan, Yunnan: an enumeration of the collections made in August, 1984. J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo, Sect. III,14: 11–36.
Kato, M. 1975a. On the systematic position ofAthyrium mesosorum. Acta Phytotax. Geobot.27: 56–60 (in Japanese).
— 1975b. Taxonomic notes on the cordate scales found inDavallia. Acta Phytotax. Geobot.26: 152–159.
— 1977. Classification ofAthyrium and allied general of Japan. Bot. Mag. Tokyo90: 23–40.
— 1985. A systematic study of the genera of fern family Davalliaceae. J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo III,13: 553–573.
— andS. Mitsuta. 1979 (1980). Stelar organization in davallioid ferns Phytomorphology29: 362–369.
—,N. Nakato, S. Akiyama andK. Iwatsuki. 1990. The systematic position ofAsplenium cardiophyllum (Aspleniaceae). Bot. Mag. Tokyo103: 461–468.
—,T. Suzuki andN. Nakato. 1991. The systematic status ofMatteuccia intermedia (Woodsiaceae: Pteridophyta). Fern Gaz.14: 65–71.
Li, J.-W. 1989. Chromosome numbers of some species in the genusAngiopteris Hoffm. from Yunnan, China, Proc. Int. Symp. Syst. Pteridol. 109–110.
Lin, S.-J., M. Kato andK. Iwatsuki. 1990. Sporogenesis, reproductive mode, and cytotaxonomy of some species ofSphenomeris, Lindsaea, andTapeinidium (Lindsaeaceae). Amer. Fern J.80: 97–109.
Löve, Á., D. Löve andR.E.G. Pichi Sermolli. 1977. Cytotaxonomical Atlas of the Pteridophyta. J. Cramer Vaduz.
Lovis, J.D. 1977. Evolutionary patterns and processes in ferns. Advances Bot. Res.4: 229–415.
Manton, I. 1950. Problems of Cytology and Evolution in the Pteridophyta. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge.
— 1969. Evolutionary mechanisms in tropical ferns. Biol. J. Linn. Soc.1: 219–222.
Masuyama, S. 1984. Reproductive Biology of Ferns. Hojoshokan, Tokyo. (in Japanese)
Matsumoto, S. and T. Nakaike. 1990. Cytological observations of some ferns in Nepal (1). On the related taxa in Japan.In M. Watanabe and S. B. Malla. ed., Cryptogams of the Himalayas. Vol. 2. Central and Eastern Nepal, pp. 163–178. Nat. Sci. Mus. Tsukuba.
Mitsuta, S. 1986. A preliminary report on reproductive type ofCyrtomium (Dryopteridaceae). Acta Phytotax. Geobot.37: 117–122. (in Japanese)
Mitui, K. 1975. Chromosome numbers of Japanese pteridophytes. Bull. Nippon Dental College, General Educ.4: 221–271.
— 1980. Chromosome numbers of Japanese pteridophytes (2). Bull. Nippon Dental College, General Educ.9: 217–229.
—,N. Murakami andK. Iwatsuki. 1989. Chromosomes and systematics ofAsplenium sect.Hymenasplenium (Aspleniaceae). Amer. J. Bot.76: 1689–1697.
Nakato, N. 1988. Notes on chromosomes of Japanese pteridophytes (2). J. Jap. Bot.63: 214–218.
— 1989. Distributions and fron variations in diploid and triploid cytotypes inPteris cretica L. in Kanto District. J. Phytogeogr. Taxon.37: 113–119. (in Japanese)
Roy, S.K. andR.E. Holttum. 1965. Cytological observations of ferns from southern China. Amer. Fern J.55: 154–158
—,B.M.B. Sinba andA.R. Sakya. 1971. Cytology of some ferns of Kathmandu valley. Brit. Fern Gaz.10: 193–199.
Sen, T. andU. Sen. 1971. Morphology and anatomy of the fern genusGymnogrammitis. Ann. Bot.35: 229–235.
Suzuki, T. andK. Iwatsuki. 1990. Genetic variation in agamosporous fernPteris cretica L. in Japan. Heredity65: 221–227.
Tagawa, M. 1936. Spicigelium pteridographiae Asiae orientalis 8. Acta Phytotax. Geobot.5: 189–197.
— 1940.Polystichum of Japan, Korea and Taiwan 1. Acta Phytotax. Geobot.9: 119–138.
— 1959. Coloured Illustrations of the Japanese Pteridophyta. Hoikusha, Osaka.
Wagner, W.H. Jr. andF.S. Wagner. 1980. Polyploidy in pteridophytes.In W.H. Lewis, ed., Polyploidy: Biological Relevance, pp. 199–214. Plenum Press, New York.
Walker, T.G. 1979. The cytogenetics of ferns.In A.F. Dyer, ed., The Experimental Biology of Ferns, pp. 87–132. Academic Press, London.
— 1984. Chromosomes and evolution in pteridophytes.In A.K. Sharma and A. Sharma, ed., Chromosomes in Evolution of Eukaryotic Groups. Vol. 2, pp. 103–141. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
— 1985. Cytotaxonomic studies of the ferns of Trinidad. 2. The cytology and taxonomic implications. Bull. Brit. Mus. Nat. Hist. (Bot.)13: 149–249.
Wang, Z.-R. 1982. Four new species of Athyriaceae from Emei Shan, Sichuan. Acta Phytotax. Sin.23: 236–240.
— 1985. Three new cytotypes ofDryopteris chrysocoma complex. Acta Phytotax. Sin.23: 344–351.
— 1987. Cytotaxonomic observations onMecodium paniculiflorum (Presl) Copel. andM. osmundoides (v.d.B.) Ching. Acta Bot. Sin.29: 145–148.
Wang, Z.-R. 1989a. A preliminary report on the cytology of some species ofAsplenium from China. Proc. Int. Symp. Syst. Pteridol. 133–134.
— 1989b. A preliminary study on cytology of ChinesePteris. Acta Phytotax. Sin.27: 421–438.
— andS.-C. Sun. 1982. Chromosome counts in some Chinese ferns. Acta Phytotax. Sin.20: 59–62.
— andQ. Xia. 1984. Cytological observations on some species ofDryopteris andPolystichum from China. Acta Bot. Sin.26: 24–27.
—,Q. Xia andZ.-X. Zhang. 1984. Cytological observations on 25 species of Chinese ferns. Acta Bot. Sin.26: 595–604.
— andZ.-X. Zhang. 1981. Cytological observation on some Chinese ferns. Acta Bot. Sin.23: 427–433.
Weng, R.-F. 1985a. Observation on chromosomes of some Chinese ferns. J. Wuhan. Bot. Res.3: 367–370.
— 1985b. Chromosome numbers of seven Chinese ferns. Invest. Stud. Nat.5: 161–166.
Weng, R.-F. 1989a. Cytological observations on nine species ofDryopteris in China. Proc. Sino-Jap. Symp. Pl. Chromos. pp. 345–349.
Weng, R.-F. 1989b. Cytological observations onDryopteris from East China. Proc. Int. Symp. Syst. Pteridol. 141–144.
— 1990. Cytological observations on some Chinese ferns. Acta Phytotax. Sin.28: 27–33.
— andS.-P. Qiu. 1988. Chromosome counts of some ferns from Zhejiang. Invest. Stud. Nat.8: 43–52.
Yunnan Institute of Tropical Botany (ed.). 1984. List of Plants in Xishuangbanna.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, M., Nakato, N., Cheng, X. et al. Cytotaxonomic study of ferns of Yunnan, southwestern China. Bot Mag Tokyo 105, 105–124 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02489407
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02489407