Abstract
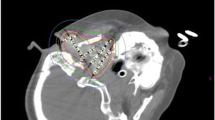
Focal irradiation has emerged as a useful modality in the management of malignant brain tumors. Its main limitation is radiation necrosis. We report on the radiation dose distribution in the cerebellum of a patient who developed imaging and autopsy diagnosis of radiation necrosis after permanent iodine-125 implants for a solitary osseous plasmacytoma of her left occipital condyle. A 55-year-old woman initially presented with neck and occipital pain and a lytic lesion of her left occipital condyle. A cytological diagnosis of solitary osseous plasmacytoma was made by transpharyngeal needle biopsy. After an initial course of external beam radiation, the patient required further treatment with systemic chemotherapy 21 months later for clinical and radiographic progression of her disease. She ultimately required subtotal surgical resection of an anaplastic plasmacytoma with intracranial extension. Permanent low-activity iodine-125 seeds were implanted in the tumor cavity. Satisfactory local control was achieved. However, clinical and imaging signs of radiation damage appeared 28 months after iodine-125 seed implantation. Progressive systemic myeloma led to her death 11 years after presentation and 9 years after seed implantation. Radiation dose distribution is described, with a discussion of toxicity from focal radiation dose escalation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bampoe J, Glen J, Mackenzie I, et al. (1997) Effect of implant dose/ volume and surgical resection on survival in a rat glioma brachytherapy model: implications for brain tumor therapy. Neurosurgery 41:1374–1384
Bernstein M, Cabantog A, Laperriere N, et al (1995) Brachytherapy for recurrent single brain metastasis. Can J Neurol Sci 22:13–16
Bernstein M, Laperriere N, Leung P, et al (1990) Interstitial brachytherapy for malignant brain tumors: preliminary results. Neurosurgery 26:371–380
Halligan JB, Stelzer KJ, Rostomily RC, et al (1996) Operation and permanent low activity125I brachytherapy for recurrent high-grade astrocytomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35:541–547
Laperriere NJ, Leung PMK, McKenzie S, et al (1998) Randomized study of brachytherapy in the initial management of patients with malignant astrocytoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 41:1005–1011
Schulder M, MclBlack P, Shrieve DC, et al (1997) Permanent lowactivity iodine-125 implants for cerebral metastases. J Neurooncol 33:213–221
Selker RG, Shapiro WR, Green S, et al (1995) A randomized trial of interstitial radiotherapy (IRT) boost for the treatment of newly diagnosed malignant glioma (glioblastoma multiforme, anaplastic astrocytoma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma, malignant mixed glioma): BTCG study 87-01. Neurosurgery 37:573 (Abstract)
Zamorano L, Yakar D, Dujovny M, et al (1992) Permanent iodine-125 implant and external beam radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant brain tumors. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 59:183–192
Bleehen NM, Stenning SP (1991) A medical research council trial of two radiotherapy does s in the treatment of grades 3 and 4 astrocytoma. Br J Cancer 64:769–774
McDermott MW, Sneed PK, Gutin PH (1998) Interstitial brachytherapy for malignant brain tumors. Semin Surg Oncol 14:79–87
Bampoe J, Bernstein M (1998) Advances in radiotherapy of brain tumors: radiobiology versus reality. J Clin Neurosci 5:5–14
Sheline GE, Wara WM, Smith V (1980) Therapeutic irradiation and brain injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 6:1215–1228
Marks JE, Baglan RJ, Prassad SC, et al (1981) Cerebral radionecrosis: incidence and risk in relation to dose, time, fractionation and volume. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 7:243–252
Mikhael MA (1979) Rahation necrosis of the brain: correlation between patterns on computed tomography and dose of radiation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 3:241–249
Peylan-Ramu N, Poplack DG, Pizzo PA, et al (1978) Abnormal CT scans of the brain in asymptomatic children with acute lymphocytic leukemia after prophylactic treatment of the central nervous system with radiation and intrathecal chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 298:815–818
Pezner RD, Archambeau JO (1981) Brain tolerance unit: a method to estimate risk of radiation brain injury for various dose schedules. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 7:397–402
Sneed PK, Lamborn KR, Larson DA, et al (1996) Demonstration of brachytherapy boost dose-response relationships in glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 35:37–44
Bernstein M, Marotta T, Stewart P, et al (1990) Brain damage from125I brachytherapy evaluated by MR imaging a blood-brain barrier tracer, and light and electron microscopy in a rat model. J Neurosurg 73:585–593
Fike JR, Cann CE, Phillips TL, et al (1985) Radiation brain damage induced by interstitial125I sources: a canine model evaluated by quantitative computed tomography. Neurosurgery 16:530–537
Groothuis DR, Wright DC, Ostertag CB, et al (1987) The effect of125I interstitial radiotherapy on blood-brain barrier function in normal canine brain. J Neurosurg 67:895–902
Ostertag CB, Weigel K, Warne P, et al. (1983) Sequential morphological changes in the dog brain after interstitial iodine-125 irradiation. Neurosurgery 13:523–528
Kohli CM, Kawazu T (1982) Solitary intracranial plasmacytoma. Surg Neurol 17:307–312
Krumholz A, Weiss HD, Jiji VH, et al (1982) Solitary intracranial plasmacytoma: two patients with extended follow-up. Ann Neurol 11:529–532
Mancardi GL, Mandybur TI (1983) Solitary intracranial plasmacytoma. Cancer 51:2226–2233
Meredith WJ (ed) (1967) Radium dosage. The Manchester System, 2nd edn. E. & S. Livingstone, Edinburgh and London
Kondziolka D, Somaza S, Martinez AJ, et al (1997) Radioprotective effects of the 21-aminosteroid U-74389G for stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 41:203–208
Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Bissonette DJ, et al (1997) Survival benefit of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with malignant glial neoplasms. Neurosurgery 41:776–785
Mehta MP, Masciopinto J, Rozental J, et al (1994) Stereotactic radiosurgery for glioblastoma multiforme: report of a prospective study evaluating prognostic factors and analyzing long-term survival advantage. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 30:541–549
Shrieve DC, Alexander E, Wen PY, et al (1995) Comparison of stereotactic radiosurgery and brachytherapy in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurgery 36:275–284
Siddiqi SN, Provias J, Laperriere N, et al (1997) Effects of iodine-125 brachytherapy on the proliferative capacity and histopathological features of glioblastoma recurring after initial therapy. Neurosurgery 40:910–918
Larson DA, Gutin PH, McDermott M, et al (1996) Gamma knife for glioma: selection factors and survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36:1045–1053
Cosgrove GR, Hochberg FH, Zervas NT, et al (1997) Interstitial irradiation of brain tumors, using a miniature radiosurgery device: initial experience. Neurosurgery 40:518–525
Bampoe J, Glen J, Salhia B, et al (1999) Adehoviral vector mediated gene transfer: timing of wild-type p53 gene expression in vivo and effect of tumor transduction on survival in a rat glioma brachytherapy model. Can J Neurol Sci 26 (Suppl 1):S68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bampoc, J., Nag, S., Leung, P. et al. Brain necrosis after permanent low-activity iodine-125 implants: case report and review of toxicity from focal radiation. Brain Tumor Pathol 17, 139–145 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02484285
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02484285