Summary
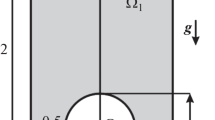
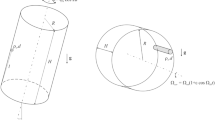
The motion of a gas bubble in a rotating liquid has been investigated theoretically and experimentally. The fluid system gas-liquid is placed into a zero-g-centrifuge. The test apparatus consists essentially of two parallel flat glass plates very close together. The space between the plates is filled with liquid. By means of a syringe bubbles are injected into the latter. In case of horizontally positioned plates the gas liquid system is in a state of effective weightlessness. By rotating the plates about a vertical axis, a centrifugal force field is generated, the action of which upon the bubble is studied. Bubble trajectories and travel time are determined and experimental observations are compared with numerical results. Agreement between observed data and those of numerical calculations is satisfactory in view of the approximations made in the analysis.
By slight inclination of the axis of rotation towards the vertical, a weak gravitational force field is super-imposed on the centrifugal field. It is shown that due to the action of reduced gravity the bubble executes a circular motion with the intersection of the spin axis and the plane of the plates as center. Further observed phenomena (e.g. the influence of titled plates) are discussed briefly. The subject is currently of practical interest in connection with possible applications regarding materials processing in zero gravity, especially degassing of free floating liquid materials.
Übersicht
Die Bewegung einer Gasblase in einer rotierenden Flüssigkeit wird theoretisch und experimentell untersucht. Das System Flüssigkeit-Gas befindet sich in einer sog. Null-g-Zentrifuge. Die Versuchsanordnung besteht im wesentlichen aus zwei eng benachbarten, parallelen, ebenen Glasplatten, deren Zwischenraum mit Flüssigkeit gefüllt ist. Mittels einer Spritze werden Gasblasen in die Flüssigkeit injiziert. Stehen die Platten horizontal, so befindet sich das System im Zustand effektiver Schwerelosigkeit. Durch Drehung der Platten um eine vertikale Achse wird ein Zentrifugalkraftfeld erzeugt, dessen Wirkung auf die Blasenbewegung untersucht wird. Blasenbahn und Reisezeit werden bestimmt und Beobachtungsergebnisse mit numerischen Resultaten verglichen. Die Übereinstimmung zwischen experimentell und numerisch gewonnenen Daten ist angesichts der in der Theorie gemachten Annahmen recht gut.
Durch leichtes Neigen der Drehachse gegen die Vertikale wird ein schwaches Schwerfeld erzeugt und dem Fliehkraftfeld überlagert. Es wird gezeigt, daß infolge reduzierter Schwerewirkung eine Blasenbewegung auf einem Kreis stattfindet, dessen Zentrum mit dem Durchstoßpunkt Drehachse-Plattenebene zusammenfällt. Weitere Beobachtungen (z. B. Einfluß geneigter Plattenebenen) werden kurz erwähnt. Die Untersuchungen sind praktisch interessant im Hinblick auf mögliche Anwendungen in der Raumfahrttechnologie (Werkstoff-Forschung und Materialfertigung im Weltraumlaboratorium Spacelab), insbesondere beim Entgasen von frei schwebendem Schmelzgut.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wuenscher, H. F.: Materials Processing in Zero Gravity (An Overview). Astronautical Research 1972 (L. G. Napolitano et al., (eds.)), D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht-Holland 1973, pp. 295–307
Wang, T. G.; Saffren, M. M.: Elleman, D. D.: Acoustic Chamber for Weightless Positioning. AIAA Paper No. 74-155, AIAA 12th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Washington, D. C., January 30–February 1, 1974
Siekmann, J.; Dittrich, K.: Über die Bewegung von Gasblasen in einem rotierenden Medium. Ing.-Arch. 44 (1975) S. 131–142
Klotter, K.: Technische Schwingungslehre, 2. Band, 2. Aufl., Berlin, 1960
Chetayev, N. G.: The Stability of Motion, New York, 1961
Eck, W.: Blasenbewegungen zwischen parallelen, ebenen Wänden. Dissertation, Technische Hochschule Darmstadt, 1975
Siekmann, J.; Eck, W.; Johann, W.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen über das Verhalten von Gasblasen in einem Null-g-Simulator. Z. Flugwiss.22 (1974), Heft 3 S. 83–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr.-Ing. K. Klotter on the occasion of his seventy-fifth birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siekmann, J., Johann, W. On bubble motion in a rotating liquid under simulated low and zero gravity. Ing. arch 45, 307–315 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482627
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482627