Abstract
Extrusion shaping of tiles and bricks containing clay meets with lots of problems because of friction at the interface wall-paste in the extruder and in the die.
These frictions lead to wear of the walls and create defects which alter the materials and its mechanical properties.
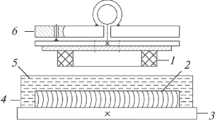
In this paper a new device (tribometer) is presented allowing the study of friction of paste samples (kaolin+water) pressed against a plate put into translation.
The analysis of the results obtained with the tribometer, together with observations made on a model, enables us to understand the mechanisms occurring at the interface paste-steel.
It appears that two types of phenomena are present at the interface, depending on the paste composition and the plate surface characteristics:
-
- The flow of water coming from sample consolidation creating enough pressure to build the normal force.
-
- The movement of particles governed by the relationship between the particle size and the plate roughness amplitude.
Résumé
La mise en fome par extrusion des tuiles et des briques à base d'argile, rencontre de nombreux problèmes liés au frottement qui intervient à l'interface pâte-paroi de l'extrudeuse et de la filière.
Ces frottements entraînent l'usure des parois et favorisent l'apparition de défauts qui altèrent l'esthétique et les propriétés mécaniques du produit fini.
Dans cet article est présenté un nouvel appareil (tribomètre) qui permet l'étude du frottement d'échantillons de pâte (kaolin+eau) pressés contre une plaque interchangeable soumise à un mouvement de translation.
L'analyse des résultats obtenus grâce au tribomètre, complété par des observations effectuées sur un modèle analogique, a permis d'aboutir à la compréhension des mécanismes intervenant à l'interface pâte-acier. Il apparaît que l'interface est le siège de deux types de phénomènes dépendant de la composition de la pâte et de l'état de surface des plaques:
-
- L'un d'eux est l'écoulement de l'eau provenant d'une consolidation de l'échantillon, susceptible de créer des pressions suffisantes pour reprendre une partie de l'effort normal,
-
- L'autre est le mouvement des particules contrôlé par le rapport entre la taille des particules et l'amplitude des rugosités des plaques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benbow, J. and Bridwater, J., ‘The role of frictional forces in extrusion’, in ‘Tribology in particulate technology’, (B.J. Briscoe and Adams, Adam Hilger, 1987).
Robinson, G. C., ‘Extrusion defects in ceramic before firming’, edited by G. Y. Onada and L. L. Hench, Hohn Wiley & Son, New York, 1978, 391–407.
Benbow, J. and Bridwater, J., ‘Paste flow and extrusion’ Oxford series on advanced manufcturing, 1993, 61–82.
Djelal, C. et Doustens, A., ‘Approche expérimentale de l'étude du frottement à l'interface des suspensions eau-argile concentrées contre une surface métallique’, 30e Colloque Annuel du Groupe Français de Rhéologie, Bordeaux, 13–15 septembre 1995, Vol. XIV, N 1, 211–230.
Kendall, K., ‘Inadequacy of Coulomb's friction law for particle assemblies’,Nature 319 (January 1986) 203–205.
Hassan, A., ‘Étude expérimentale et numérique du comportement local et global d'une interface sol granulaire-structure’, PhD thesis, Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, 1995.
Tüzün, U., ‘Effects of consolidation and yield history on the mesured angles of friction of particulate solids’, in Tribology in particulate technology’, edited by B.J. briscoe and M.J.Adams, 1987, 39–61
Mathia, T. and Louis, F., ‘Powder mechanics in tribology’,Powder Technology 37 (1984) 155–167.
Terzaghi, K., ‘Theorical soil mechanics’, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1966.
Casagrande, L., L'application de l'électro-osmose à des problèmes pratiques de fondations et d'ouvrages en terre’,Bldg, Res. Stat. Techn. publ. 30 (1947).
Mitchell, J. K., ‘Fundamental of soil behaviour’, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York 1976.
Camberfort, H. et Caron, C., ‘Électro-osmose et consolidation électrochimique des argiles’, 1967.
Djelal, C., ‘Analyse du phénomène du frottement des mélanges eau-argile concentrés contre des surfaces métalliques’, PhD thesis, INSA, Rennes, 1991.
Beaumel, C., Djelal, C., Piau, J. M. et Magnin, A., ‘Extrusion des pâtes d'argile: Outils expérimentaux’, 13e Rencontres Universitaires de Génie Civil, AUGC 95, Nantes 17–18 mai 1995.
Vanhove, Y., Djelal, C. et Magnin, A., ‘Conception d'un tribomètre pour l'étude du frottement des bétons frais contre une surface métallique’, Rapport, ANVAR no J 98 09 101 N/JJ, Laboratoire d'Artois Mécanique et Habitat, Béthune, mars 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djelal, C. Designing and perfecting a tribometer for the study of friction of a concentrated clay-water mixture against a metallic surface. Mat. Struct. 34, 51–58 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482200
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482200