Abstract
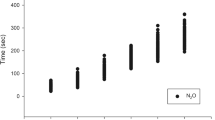
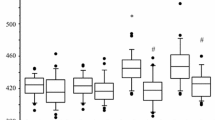
The usefulness of the rapid anesthesia induction method with 7% sevoflurane, not the single-breath method, was investigated in 88 patients with ASA physical status 1. Anesthesia was induced with 3 l·min−1 nitrous oxide in 3 l·min−1 oxygen and sevoflurane 7% for 3 min (group A), 7% for 5 min (group B), 7% for 7 min (group C), and 5% for 7 min in conventional induction (group D). There were 22 patients in each group. Each sevoflurane concentration was given at the same time as the start of nitrous oxide inhalation except for group D. The changes in blood pressure and heart rate were the smallest in group A. The time for the loss of consciousness was shorter in groups A (47.2 s), B (44.9 s), and C (49.8 s) than in group D (73.4 s). During induction, body movements were seen in 18.2% in group A and 13.6% in the other 3 groups, but no other complications such as coughing, breath holding, or laryngospasm were seen in any group. In conclusion, the anesthesia induction method with 3 min of 7% sevoflurane inhalation was useful for rapid induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yurino M, Kimura H (1993) Induction of anesthesia with sevoflurane, nitrous oxide, and oxygen: A comparison of spontaneous ventilation and vital capacity rapid inhalation induction (VCRII) techniques. Anesth Analg 76:589–601
Wallin RF, Regan BM, Napoli MD, Stern IJ (1975) Sevoflurane: a new inhalational anesthetic agent. Anesth Analg 54:758–766
Ruffle JM, Snider MT, Rosenberger JL, Latta WB (1985) Rapid induction of halothane anaesthesia in man. Br J Anaesth 57:607–611
Lamberty JM, Wilson IH (1987) Single-breath induction of anaesthesia with isoflurane. Br J Anaesth 59:1214–1218
Loper K, Reitan J, Bennett H, Benthuysen J, Snook L (1987) Comparison of halothane and isoflurane for rapid anesthetic induction. Anesth Analg 66:776–768
Pandit UA, Steude GM, Leach AB (1985) Induction and recovery characteristics of isoflurane and halothane anesthesia for short operations in children. Anaesthesia 40:1226–1230
Fukuda H, Kasuda H, Saitoh K, Hirabayashi, Y, Akazawa S, Mitsuhata H, Shimizu R (1993) Rapid induction of anesthesia with inhalation of sevoflurane (in Japanese with English abstract). Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 42:1744–1747
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiyama, T., Nagase, M., Tamai, H. et al. Rapid induction with 7% sevoflurane inhalation—not the single-breath method. J Anesth 9, 36–39 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482033
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482033