Abstract
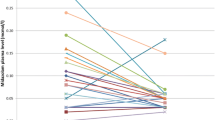
The optimal administration time for intramuscular injection of midazolam as premedication was studied. Sixty patients ranging in age from 40 to 65 were included. A combination of atropine 0.3–0.5 mg and midazolam 0.08 mg·kg−1 was given to four groups of 15 subjects each in intramuscular injections 45, 30, 15 min, and immediately before entering the operating room. Blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, depression of the root of the tongue, eyelash reflex, degree of sedation, and amnestic effect at the time of arriving the operating room were compared among the groups. There was no difference among the groups in blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate. The depression of the root of the tongue, disappearance of verbal response, and eyelash reflex were found in the 30- and 45-min groups. The degree of sedation and amnestic effect were good except for the group who received midazolam immediately before entering the operating room. From the above results, intramuscular injection of midazolam 0.08 mg·kg−1 with atropine 0.3–0.5 mg is considered best when administered 15 min before entering the operating room.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conner JT, Katz RL, Pagano RR, Graham CW (1978) R0 21-3981 for intravenous surgical premedication and induction of anesthesia. Anesth Analg 57:1–5
Fragen RJ, Fink DI, Avram MJ, Costello C, DeBruine K (1983) Midazolam versus hydroxyzine as intramuscular premedicants. Can Anaesth Soc J 30:136–141
McAteer EJ, Dixon J, Whitwam JG (1984) Intramuscular midazolam. A comparison of midazolam with papavertum and hyoscine for intramuscular premedication. Anaesthesia 39:1177–1182
Tabuchi Y (1992) Optimal dose of midazolam as premedicant for combined spinal and epidural anesthesia with midazolam sedation (in Japanese with English Abstract). Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 41:544–560
Tabuchi Y (1992) The effect of age and gender on the effect of midazolam as intramuscular premedicant (in Japanese with English abstract). Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 41:938–944
Shafer A, White PF, Urquhart ML, Doze VA (1989) Outpatient premedication: Use of midazolam and opioid analgesics. Anesthesiology 71:495–501
Tabuchi Y, Ishida H, Nagai K (1991) Comparison of midazolam and hydroxyzine as premedicants for combination of spinal and epidural anesthesia with midazolam (in Japanese with English abstract). Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 40:184–189
Vinik HR, Reves JG, Wright D (1982) Premedication with intra-muscular midazolam: A prospective randomized double-blind controlled study. Anesth Analg 61:933–937
Nishiyama T, Hirasaki A, Odaka Y, Konishi H, Tsubaki N, Seto K (1992) Epidural midazolam with bupivacaine—Optimal dose for postoperative pain relief—(in Japanese with English abstract) Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 41:1113–1118
Behne M, Janshon G, Asskali F, Förster H (1989) Die Pharmakokinetik des Midazolam nach intramuscularer Gabe (in German with English abstract). Anesthesist 38:278–284
Holazo AA, Winkler MG, Patel IH (1988) Effects of age, gender and oral contraceptives on intramuscular midazolam pharmacokinetics. J Clin Pharmacol 28:1040–1045
Reinhart K, Dallinger-Stiller G, Dennhardt R, Heinemeyer G, Eyrich K (1985) Comparison of midazolam, diazepam and placebo i.m. as premedication for regional anaesthesia. A randomized double-blind study. Br J Anaesth 57:294–299
Van de Velde A, Camu F, Claeys MA (1986) Midazolam for intramuscular premedication: dose-effect relationships compared to diazepam, fentanyl and fentanyl-droperidol in a placebo controlled study. Acta Anaesth Belg 37:127–136
Wong HY, Fragen RJ, Dunn K (1991) Dose-finding study of intramuscular midazolam preanesthetic medication in the elderly. Anesthesiology 74:675–679
Artu AA, Dhamee MS, Seifen AB (1984) Premedication with intramuscular midazolam: Effect on induction time with intravenous midazolam compared to intravenous thiopentone or ketamine. Can Anaesth Soc J 31:359–363
Akatsuka M, Sasaki H, Kataoka H, Hyodo M, Ohno F, Umegaki H (1990) Usefulness of midazolam for premedication before local anesthesia (in Japanese with English abstract). Masui (Jpn J Anesthesiol) 39:70–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper was presented at the 40th meeting of the Japan Society of Anesthesiology held in Morioka in 1993
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiyama, T., Nagase, M., Tamai, H. et al. Optimal administration time of intramuscular midazolam premedication. J Anesth 9, 11–14 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482027
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02482027