Abstract
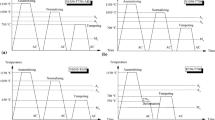
The powder metallurgy process is ideally suited to the mass production of structural parts of complicated shape and with tight tolerances without appreciable loss of material. Because of its unique attributes such as reducing weight and production cost, powder metallurgy has made very significant in roads as a substitution technology in automotive parts, such as cams and gears in this process, we can improve the mechanical properties such as fatigue resistance of PM materials by changing of manufacturing parameters, for example, density, sintering temperature, sintering time, etc. In this research, the fatigue behaviour of sintered steel (Fe-1.5 Mo-3 Mn-0.7 C) was investigated with varying of density and sintering temperature. The results showed that in this steel, increase of porosity plays an important role in the fatigue limit of specimens also with sintering at high temperature which results in more spherical pores, the fatigue strength was improved. In this research, SEM fractography was also used to determine the mechanism of fatigue fracture.
Résumé
Le processus de frittage est une parfaite méthode pour la production en série des pièces de structure compliquée avec des tolérances très limitées sans perte excessive de matières. Sa performance exceptionnelle, telle que la réduction de la masse et du coût de production, en a fait une technologie de substitution pour les pièces de véhicules comme les cames et les engrenages. Ce processus permet d'améliorer les propriétés mécaniques telles que la résistance à la fatigue des matières frittées par un changement des paramètres de production, par exemple, densité, température de frittage, durée de frittage, etc. Dans cette recherche, la conduite de fatigue des aciers frittés (Fe-1.5 Mo-3 Mn-0.7 C) est examinée par les variations de densité et de température de frittage. Le résultat a montré que dans cet acier, l'augmentation de la porosité joue un rôle essentiel dans la limite de fatigue des échantillons ainsi que dans le frittage à haute température qui cause une plus grande porosité et par ailleurs la limite de fatigue peut être améliorée. Dans cette recherche, la fractographie de microscope à balayage électronique est aussi utilisée pour déterminer le mécanisme de limite de fatigue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salak, A., ‘Ferrous Powder Metallurgy’ (Cambridge International Science Publishing, Cambridge, 1995).
James, B., ‘Recent developments in ferrous powder metallurgy alloys’,Metal Powder Report 46 (9) (2001) 26–30.
Danninger, H., Jangg, G., Weiss, B. and Stickler, R., ‘Microstructure and mechanical properties of sintered iron—Part I’,Powder Metallurgy International 25 (3) (1993) 111–117.
Habibi, S.M., Janghorban, K., Khorsand, H. and Yoozbashizade, H., ‘The effect of microstructure on mechanical properties of ferrous P/M materials’, Pm Auto'02, Isfahan, Iran, April 21–25 2002.
Danninger, H., Jangg, G., Weiss, B. and Stickler, R., ‘Microstructure and mechanical properties of sintered iron—Part II’,Powder Metallurgy International 25 (4) (1993) 170–173.
Khorsand, H., Habibi, S.M., Yoozbashizade, H., Janghorban, K. and Reihani, S.M.S., ‘Investigation of microstructure and fatigue properties of low alloy sintered steels by heat treatment’,P/M Science & Technology Briefs 4 (2) (2002) 18–22.
Segall, A.E., Cimino, T., Murphy, T. and Habergerger, T., ‘The influence of microstructure and carbide particles on the creep behaviors of P/M alloys’, Pm2tec 2001, International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, May 13–17, 2001.
Liu, Z.Y., Loh, N.H., Khor, K.A. and Tor, S.B., ‘Microstructure evolution during sintering of injection molded M2 high speed steel’,Materials Science and Engineering A 293 (1) (2000) 46–55.
Davala, A.B., Graham, A.H. and Causton, R.J., ‘Application of high performance materials and processes—Alloy systems’, Pm2tec '98, International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, May 31–June 4, 1998.
Haynes, R., ‘Fatigue behavior of sintered metals and alloy’,Powder Metallurgy 13 (26) (1970) 465–510.
James, W.B. and O'Brien, R.C., ‘High performance ferrous P/M materials: the effect of alloying method on dynamic properties’, The Annual Powder Metallurgy Conference, San Diego, California, USA, June 11–14, 1989.
Esper, E.J. and Sonsino, C.M., ‘Fatigue design for P/M components’, The European Powder Metallurgy Association, Shrewbury, 1994,
Piotrowski, A. and Biallas, G., ‘Influence of sintering temperature on pore morphology’—‘Microstructure and fatigue behaviour of moniCu alloyed sintered steel’,Powder Metallurgy 41 (2) (1998) 109–114.
Lindqvist, B. and Kanno, K., ‘Considerations when sintering oxidation-sensitive Pm steels introduction’, Pm2tec 2002, International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, Orlando, Florida, USA, June 16–21, 2002.
Sonsino, C.M., ‘Methods to determine relevant material properties for the fatigue design of powder metallurgy parts’,Powder Metallurgy International 16 (1) (1984) 34–38.
Lindqvist, B., Kanno, K., Takeda, Y., Takahashi, S. and Kanda, K., ‘Sintering of prealloy 3cr-0.5Mo steel powder in a carbon/carbon composite mesh belt furnace’, Pm2tec 2002, International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, Orlando, Florida, USA, June 16–21, 2002.
Chawla, N., Polasik, S., Narasimhan, K. S., Koopman, M. and Chawla, K.K., ‘Fatigue behavior of binder-treated powder metallurgy steels’,The International Journal of Powder Metallurgy 37 (3) (2001) 49–57.
Ledoux, L. and Prioul, C., ‘Fatigue and fracture of porous steels and Cu-infiltrated porous steels’, Pm2Tec '98, International Conference on Powder Metallurgy & Particulate Materials, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, May 31–June 4, 1998.
Hadrboletz, A.A. and Weiss, B., ‘Fatigue behavior of iron based sintered material’,Intl Mater Rev 42 (1) (1997) 1–44.
Danninger, H., Spoljaric, D. and Weiss, B., ‘Microstructural features limiting the performance of P/M steels’,The International Journal of Powder Metallurgy 33 (4) (1997) 43–53.
Bertilsson, I. and Karlsson, B., ‘Dynamic properties of sintered steel’,Powder Metallurgy 30 (3) (1987) 183–188.
O'Brien, R.C., ‘Impact And Fatigue Characterization of Selected Ferrous P/M Materials’, The Annual Powder Metallurgy Conference, Dallas, Texas USA, May 17–20, 1987.
Holmes, J. and Queeney, R.A., ‘Fatigue crack initiation in a porous steel’,Powder Metallurgy 28 (4) (1985) 231–235.
Khorsand, H., Yoozbashizadeh, H., Habibi, S.M., Jonghorban, K. and Rahmani, S.M.S., ‘Carbon, porosity and fatigue in sintered steel’,Metal Powder Report 57 (4) (2002) 32–36.
Christian, K.D. and German, R.M., ‘Relation between pore structure and fatigue behavior in sintered iron-copper-carbon’,The International Journal of Powder Metallurgy 31 (1) (1995) 51–61.
Spoljaric, D., Danninger, H., Weiss, B. and Stickler, R., ‘Fatigue behavior of Mo-alloyed sintered steels and its consequences for application’, Proc. Pm'94, Paris.,2 (1994) 827–832.
Bergmark, A., Alzati, L. and Persson, U., ‘Fatigue crack initiation in Pm steel’, Pm2tec2002, International Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Particulate Materials, Orlando, Florida, USA, June 16–21, 2002.
Drar, H., ‘Metallographic and fractographic examination of fatigue loaded Pm-steel with and without Mns additive’,Materials Characterization 45 (4) (2000) 211–220.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khorsand, H., Habibi, S.M., Janghorban, K. et al. Fatigue of sintered steels (Fe-1.5 Mo-3 Mn-0.7 C). Mat. Struct. 37, 335–341 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481680
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481680