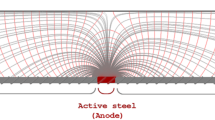
Abstract
The measurement of on site corrosion rate is a technique that has been extended for the increasing necessity to determine the service life of concrete structures. The most reliable method is the Polarization Resistance determination by means of the modulated confinement of the current. In the present paper, a calibration of corrosion rate measurements with the modulated confinement of the current method (MCC) is given, comparing the electrochemical results with the gravimetric losses of the rebars. This gravimetric comparison is the reference for the correct calibration of the corrosion rate measurement, following the RILEM Recommendation of TC 154-EMC. Some concrete slabs with different chloride contents were made. In some cases, a hole was drilled over some steels for an additional chloride introduction during the test in order to develop very localized attack. The comparison of electrochemical and gravimetric metal losses confirms the reliability of the modulated confinement of the current method, except when the concrete is very young due to the very low resistivity. Confinement is then not always reliable when the concrete is very wet, and the attenuation of potential method has to be used instead.
Résumé
La mesure de la vitesse de corrosion sur place est une technique qui a été étendue du fait de la nécessité croissante de déterminer la durée de service d'ouvrages en béton. La méthode la plus fible est la détermination de la Résistance de Polarisation au moyen de l'anneau de garde modulant le courant. Dans ce travail, un calibrage de la mesure de la vitesse de corrosion avec la méthode du confinement modulé du courant (MCC) est etudié et les résultats ont été comparés avec les pertes gravimétriques de l'acier. Cette comparaison gravimétrique est la référence pour le calibrage correct de la mesure de la vitesse de corrosion, selon la Recommandation RILEM de la Commission Technique 154-EMC. Quelques dalles de béton avec différentes concentrations de chlorure ont été fabriquées. Dans certains cas, un trou a été fait sur quelques armatures pour un ajout supplémentaire de chlorure pendant les essais afin de développer une attaque très localisée. La comparaison de pertes électrochimiques et gravimétriques de métal confirme la fiabilité de la méthode du confinement modulé du courant, sauf quand le béton est très jeune, en raison d'une résistivité très basse. Le confinement n'est pas toujours fiable quand le béton est très mouillé, il faut alors utiliser la méthode de l'atténuation du potentiel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade, C. and González, J.A., ‘Quantitative measurements of corrosion rate of reinforcing steels embedded in concrete using polarization resistance measurements’,Werkst. Korros 29 (515) (1978).
Andrade, C., Castelo, V., Alonso, C. and González, J.A., ‘The determination of the corrosion rate of steel embedded in concrete by the Rp on A.C. Impedance methods’,ASTM-STP 906 (1986) 43–64.
Gouda, V.K., Shater, M.A. and Mikhail, R.Sh., ‘Hardened Portland blast-furnace slag cement pastes. II. The corrosion behavior of steel reinforcement’,Cement and Concrete Research 5 (1975) 1–13.
Page, C.L. and Havdahl, J., ‘Electrochemical monitoring of corrosion of steel in microsilica cement pastes’,Mater. Struct. 18 (103) (1985) 41–47.
Sagüés, A.A., ‘Evaluation of corrosion rate by electrochemical impedance in a system with multiple polarization effects’, Corrosion 89, New Orleans (USA), paper 25, April 17–21 (1989).
Feliú, S., González, J.A., Feliú, S.Jr. and Andrade, C., ‘Confinement of the electrical signal or in-situ measurement of Polarization Resistance in Reinforced concrete’,ACI Mater. J. 87 (1990) 457 p.
Elsener, B., Klinghoffer, O., Frolund, T., Rislund, E., Schiegg, Y. and Böhni, H., ‘Assessment of reinforcement corrosion by means of galvanostatic pulse technique’, Proc. International Conference Repair of Concrete Structures, ed. A. Blankvoll, Svolvær Norway (1997) 391.
Andrade, C. and Alonso, C., ‘On-site measurements of corrosion rate of reinforcements’,Construction and Building Materials,15 (2001) 141–145.
Feliú, S., González, J.A. and Andrade, C., ‘Multiple-electrode method for estimating the polarization resistance in large structures’,Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 26 (1996) 305–309.
Andrade, C, Martínez, I, Alonso, C. and Fullea, J., ‘New advanced electrochemical techniques for on site measurements of reinforcement corrosion’,Materiales de Construcción 51 (263–264) (July–December 2001).
Vesikari, E., ‘Reliability of corrosion rate measurements by linear polarization’, RILEM Proc., PRO18 (Measurement and Interpretation of the On-Site Corrosion Rate) (RILEM Publications s.a.r.l., 2000) 15–31.
Lemonine, L., Wenger, F. and Galland, J., ‘Corrosion rates of steel in concrete’, ASTM STP-1065. American Society for Testing Materials, Philadelphia (1990) 118–133.
Dhouibi-Hachani, L., Raharinaivo, A., Triki, E., and Fiaud, C., ‘Assessing the corrosion of rebars in concrete deteriorated by sulfates and carbonation’, Int. Conference on Corrosion and Corrosion Protection of Steel in Concrete. Ed. R.N. Swamy, Sheffield (July 1994) 236–246.
González, J.A., Andrade, C., Alonso, C. and Feliú, S., ‘Comparison of rates of general corrosion and maximum pitting penetration of concrete embedded steel reinforcement’,Cement and Concrete Research 25 (2) (1995) 257–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial Note Dr. Carmen Andrade is a Member of the RILEM Bureau (outgoing, president) as well as a Member of RILEM TAC (Technical Activities Committee) and a RILEM Senior Member. She is the Chairlady of RILEM TC MAM ‘Model assisted life monotoring of corrosion induced damage of reinforced concrete structures’ and she also participates in RILEM TCs 189-NEC ‘Non-destructive evaluation of the ‘covercrete’ (concrete cover)’, LTP ‘Life time performance of materials and structures’, 199-CUA ‘Concrete: use of additions’ and INR ‘Interpretation of NDT results and assessment of RC structures’. The CSIC (Instituto ‘Eduardo Torroja’ de Ciencias de la Construcción, IETcc), Spain, is a RILEM Titular Member. Mrs Isabel Martizez participates in the above-mentioned RILEM TC INR.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrade, C., Martínez, I. Calibration by gravimetric losses of electrochemical corrosion rate measurement using modulated confinement of the current. Mat. Struct. 38, 833–841 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481656
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481656