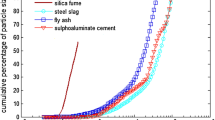
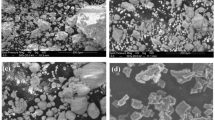
Abstract
This paper discussed the application of the method of the simplex-lattice design for predicting the properties of cement-based composites. On the basis of the compressive strength, its use was demonstrated on ternary paste systems composed of cement, silica fume and fly ash with constant water to binder ratio and a mass fraction of mineral admixtures not exceeding 30%. The regression model between compressive strength of paste and binder proportion was built up. The F-test method was utilized for validation of the regression model. The nonlinear programming system with upper and lower bound was solved. This allowed assessment of optimum mixture proportions and corresponding maximum compressive strength. It was shown that: (1) the 3rd-order regression model constructed by using the simplex-lattice design method could accurately predict the compressive strength in ternary paste system made of cement, silica fume and fly ash (the total mass fraction of all mineral admixtures was up to 30%); (2) to solve the nonlinear programming with the constraints of upper and lower bound played an important role in getting the optimum compressive strength and its corresponding mixture proportion at different ages; (3) the combination of the simplex-lattice design method and the optimization theory could be valuable tool for optimization of cement-based composites' properties.
Résumé
Cet article concerne l'application de la méthode du plan treillis-simplex visant à prévoir les propriétés des composites à base de ciment. Sur la base de la résistance à la compression, son utilisation a été prouvée sur des systèmes de pâte ternaire composés de ciment, de fumée de silice et de cendres volantes avec un rapport eau-liant constant et une fraction de masse d'adjonctions minérales n'excédant pas 30%. Les modèle de régression entre la résistance à la compression de la pâte et la proportions de liant a été élaboré. La méthode d'essai F a été utilisée pour la validation de ce modèle de régression. Le système de programmation non-linéaire avec des faces supérieures et inférieures a été conçu. Ceci a permis d'évaluer les proportions de mélange optimales et la résistance maximale à la compression correspondantes. Il a été démontré que: (1) le modèle de régression de 3ème ordre construit en utilisant la méthode du plan treillis-simplex pouvait prévoir avec précision la résistance à la compression dans des systèmes de pâte ternaire faite de ciment, de fumée de silice et de cendres volantes (la fraction de masse totale de toutes les adjonctions minérales a été jusqu'à 30%); (2) concevoir la programmation non-linéaire avec des contraintes de faces supérieures et inférieures a joué un rôle important dans l'obtention de la résistance à la compression maximale et ses proportions de mélange optimales correspondantes à différents âges; (3) la combinaison de la méthode du plan treillis-simplex et de la théorie d'optimisation pouvait constituer un bon outil pour l'optimisation des propriétés des composites à base de ciment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh, I.C., ‘Modeling concrete strength with augment-neuron networks’,Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, ASCE 10(4) (1998) 263–268.
Wang, J. and Ni, H., ‘Prediction of compressive strength of cement-based on BP neural networks’Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society 27 (4) (2000) 408–414.
Douglas, E. and Pouskouleli, G., ‘Prediction of compressive strength of mortars made with Portland cement-blast fumace slag-fly ash blends’,Cement and Concrete Research 21 (4) (1991) 523–534.
Wang D. and Chen, Z., ‘On prediction compressive strength of mortars with ternary blends of cement, GGBFS and fly ash’,Cement and Concrete Research 27 (4) (1997) 487–493.
Ding, J., Yan, P. and Liu, S.et al., ‘The application of simplex-centroid design in the mix proportion of cementitious system incorporated with admixture’, in ‘Application of HSC and HPC’, Proceedings of the Third Symposium, (Press of Shangdong Institute of Architecture and Engineering, Jinan 1998) 148–152.
Guan, Y., ‘Mixture Experimental Design’, (Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, 1990) 13–166.
MATLAB, Optimization Toolbox User's Guide (online version), the Math Work Inc., May 1997, 12–15.
Mao, S., Zhou, J. and Ding, Y. etc. ‘Regression Analysis and Its experimental design’, (East China Normal University, Shanghai, 1986) 74–108.
Wei, H., ‘The Application of Optimization Technology’, (Tongji University Press, Shanghai, 1987).
Sun, G., ‘Optimization Design and Its Application’, (Jiaotong Press, Beijing, 1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial Note Dr. Piet Stroeven is a RILEM Senior Member. Delft University of Technology is a RILEM Titular Member.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H.S., Sun, W. & Stroeven, P. Prediction of compressive strength and optimization of mixture proportioning in ternary cementitious systems. Mat. Struct. 36, 396–401 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481065
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481065