Abstract
Background
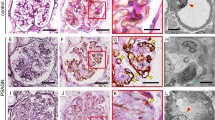
We previously found that glomerular epithelial cells play an important role in the formation of adhesive lesions. Glomerular sclerotic lesions develop after the inital adhesive lesions.
Methods
Two series of experiments were done with spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rats. These rats develop segmental glomerular sclerotic lesions with aging. The first series of experiments was intended to clarify the kinetics of glomerular cells on progressive glomerular damage in these rats. The second series of experiments was designed to study the relationship between proliferation (judged by % bromodeoxyuridine-positive cells) of glomerlar epithelial cells and sclerotic lesions with adhesions.
Results
In the first series, rats having increased proteinuria showed segmental glomerular sclerotic lesions with adhesions. At the same time, increased labeling indices of tuft cells and epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule were observed. In the second series, no significant increase in the labeling indices of tuft cells with sclerotic lesions was observed, compared to tuft cells without sclerotic lesions. In sclerotic lesions with adhesion, bromodeoxyurdine-positive cells were observed that were not distinguishable as podocytes or epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule. The highest labelling index was noted in the epithelial cells of Bowman's capsules with sclerosis.
Conclusion
This study shows that the proliferation of glomerular epithelial cells (mainly epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule) occurs in glomerular sclerotic lesions with adhesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lovett DH, and Sterzel RB. Cell culture approaches to the analysis of glomerular inflammation. Kidney Int 1986;30:246–254.
Striker LJ, Peten EP, Elliot SJ, Doi T, Striker GE. Mesangial cell turnover: effect of heparin and peptide growth factors. Lab Invest 1991;64:446–456.
Mene PM, Simonson MS, Dunn MJ. Physiology of the mesangial cell. Physiol Rev 1989;69:1374–1424.
Abboud HE. Nephrology forum: growth factors in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 1993;43:252–267.
Olson JL, Heptinstall RH. Biology of disease. Nonimmunologic mechanisms of glomerular injury. Lab Invest 1988;59:564–578.
Osawa G, Sasaki T, Sato T, Tamai H, Nomura S, Ishimatsu T. Role of glomerular epithelial cells in progression of renal disease. In Chugh KS (ed) Asian nephrology. London: Oxford University Press, 1994:270–278.
Kihara I, Yaoita E, Kawasaki K, Yamamoto T. Cellular process of glomerular adhesion in aged rats. Acta Med Biol 1990;34(suppl 2):S69-S80.
Kondo Y, Akikusa C. Chronic Masugi nephritis in the rat. An electron microscopic study on evolution and consequences of glomerular capsular adhesions. Acta Pathol Jpn 1982;32:231–242.
Nagata M, Kriz W. Glomerular damage after uninephrectomy in young rats. II Mechanical stress on podocytes as a pathway to sclerosis. Kidney Int 1992;42:148–160.
Nakama K, Shichinohe K, Kobayashi K Naito K, Uchida O, Yasuhara K, Tobe M. Spontaneous diabeticlike syndrome in WBN/Kob rats. Acta Diabetol Lat 1985;22:335–342.
Tsuchitani M, Saegusa T, Narama I, Nishikawa T, Gonda Y. A new diabetic strain of rat (WBN/Kob) Lab Anim 1989;60:205–218.
Sato T. Ultrastructural study of glomerular epithelial cells in a strain of spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rats. J Kawasaki Med Soc (Kawasaki Igakkai Shi) 1992;18:289–304 (in Japanese)
Grantzer HG. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromodexyuridine: a new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science 1982;218:474–475.
Frankel S, Reitman S, Sonnenwirth AC. Gradwohl's Clinical Laboratory Methods and Diagnosis. St Louis: Mosby, 1970.
Sasaki T, Osawa G. A kinetic study of the glomerular cells of developing and mature rat kidneys using an anti-bromodeoxyuridine monoclonal antibody. Jpn J Nephrol 1993;35:1213–1219.
Howie AJ, Kizaki T, Beaman M, Morland CM, Birtwistle RJ, Adu D, Michael J, Williams AJ, Walls J, Matsuyama M, Shimizu F. Different types of segmental sclerosing glomerular lesions in six experimental models of proteinuria. J Pathol 1989;157:141–151.
Eisen HN. Adenomatoid transformation of the glomerular capsular epithelium. Am J Pathol 1946;22:597–601.
Reidbord HE. Metaplasia of the parietal layer of Bowman's capsule. Am J Clin Pathol 1968;50:240–242.
Hughson MD, McManus JFA, Hennigar GR. Studies on “end-stage” kidneys. Embryonal hyperplasia of Bowman's capsular epithelium. Am J Pathol 1978;91:71–84.
Marcus PB. Podocytic “metaplasia” of parietal Bowman's capsular epithelium. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1981;29:209–215.
Gaffney EF, Panner BJ. Membranous glomerulonephritis: clinical significance of glomerular hypercellularity and parietal epithelial abnormalities. Nephron 1981;29:209–215.
Sasaki T, Jyo Y, Tanda N, Tamai H, Osawa G. The role of basic fibroblast grwoth factor (FGF2) in glomerular epithelial cell injury. In: Koide H, Ichikawa I (ed) Progression of renal diseases. Contrib Nephrol 118 Basel: Karger, 1996:68–77.
Pabst R, Sterzel RB. Cell renewal of glomerular cell types in normal rats: an autoradiographic analysis. Kidney Int 1983;24:626–631.
Rasch R, Nogaard JOR. Renal enlargement: comparative autoradiographic studies of [3H]-thymidine uptake in diabetic and uninephrectomized rats. Diabetologia 1983;25:280–287.
Fries JW, Sandstrom DJ, Meyer TW, Rennke HG. Glomerular hypertrophy and epithelial cell injury modulate progressive glomerulosclerosis in the rat. Lab Invest 1989;60:205–218.
Sterzel PB, Pabst R, Kregeler M, Perfetto M. The temporal relationship between glomerular cell proliferation and monocyte infiltration in experimental glomerulonephritis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol 1982;38:337–350.
Kihara I, Yaoita E, Kawasaki K, Yamamoto T. Limitation of podocyte adaptation for glomerular injury in puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis. Pathol Int 1995;45:625–634.
Yamazaki T. Podocytic degeneration and regeneration in puromycin aminonucleoside nephropathy in the rat. Pathol Int 1995;45:465–475.
Kriz W, Hahnel B, Rosener S, Elger M. Long-term treatment of rats with FGF-2 results in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 1995;48:1435–1450.
Polunovsky VA, Chen B, Henke C, Snover D, Wendt C, Ingbar DH, Bitterman PB. Role of mesenchymal cell death in lung remodeling after injury. J Clin Invest 1992;92:388–397.
Shimizu A, Yamanaka N. Apoptosis and cell desquamation in repair process in ischemic tubular necrosis. Virchow Archive B Cell Pathol 1993;64:171–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, T., Sato, T., Jyo, Y. et al. Kinetic study of glomerular epithelial cells associated with segmental glomerular sclerotic lesions with adhesion in spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rats. Clin Exper Neph 1, 32–40 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480653
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480653