Abstract
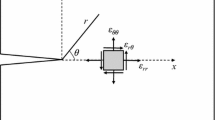
High Strength Cement Mortar (HSCM) with very fine sand exhibits a typical brittle behavior. In the present work, a linear elastic fracture mechanics based model is used for the fracture studies conducted on this material. The experimental testing program is based on the diametral compression test of disc specimens containing an internal slant crack. Under the Mode I loading condition, the test method which has been previously used is applied to determine the critical value of the stress intensity factor, KIC, for HSCM. The same dise specimen is also tested under combined Mode I and Mode II loading conditions. By changing the notch orientation angle with respect to the loading direction, the mode of fracture is varied from pure Mode I to Mixed-Mode. Based on the Mixed-Mode fracture envelope, it is shown that the disc specimen which is currently used for several brittle materials provides a wide range of |KII|/K1 ratios. In pure Mode I loading case, after determining KIC, it is possible to obtain the graph of normalized critical load versus normalized crack length. For the purpose of comparison, some available experimental data on Mode I and/or Mixed Mode fracture of some other brittle materials such as glass, sintered carbide, and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) were also evaluated. It can be concluded that there is a good fit between the experimental results and the theory.
Résumé
Les mortiers à très haute résistance (MTHR) préparés avec du sable très fin ont exhibité un comportement typiquement fragile. Dans cet article un modèle de rupture élastique linéaire est utilisé pour étudier la rupture de ces matériaux. L'étude expérimentale consistait des essait des consistait des essais de compression diamétrale sur des éprouvettes en forme de disques contenant une fissure inclinée. Les essais conformes au Mode I utilisés auparavant sont appliqués pour déterminer la valeur critique du facteur d'intensité de la contrainte KIC du MTHR. Les mêmes éprouvettes ont été ensuite essayées sous charge combinée du Mode I et Mode II. En changeant l'angle d'orientation de l'entaille par rapport à la direction de la force appliquée, le mode de rupture a été modifié du Mode I au Mode-Mixte. En se servant de l'enveloppe du Mode-Mixte de rupture, utilisée actuellement on a montré que l'éprouvette disque pouvait fournir une large pour les rapports |KII|/K1. Au cas de chargement simple de Mode I, après avoir déterminé KIC il était possible d'obtenir un graphique entre la charge critique et la longueur de la fissure normalisées. D'autres résultats expérimentaux obtenus sur d'autres matériaux fragiles comme verre, carbide synthérisé et méthacrylate de polymethyl (PMMA) sont aussi évalués afin de réaliser une comparaison. On peut conclure qu'il existe une bonne conformité entre les résultats expérimentaux et théoriques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dugat, J., Roux, N. and Bernier, G., ‘Mechanical properties of reactive powder concretes’,Mater. Struct. 29 (1996) 233–240.
Richard, P. and Cheyrezy, M., ‘Composition of reactive powder concretes’,Cement and Concrete Research 25 (7) (1995) 1501–1511.
Bonneau, O., Lachemi, M., Dallaire, E., Dugat, J. and Aitcin, P.C., ‘Mechanical properties and durability of two industrial reactive powder concretes’,ACI Materials Journal 94 (4) (1997) 286–290.
Karihaloo, B.L. and De Vriese, K.M.B., ‘Short fiber reinforced reactive powder concrete’, Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on High Performance Fiber Reinforced Cement Composites (HPF RCC3), Mainz, Germany, (1999) 53–63.
Walraven, J., ‘The evolution of concrete’, in ‘Structural Concrete’,Journal of the FIB 1 (1) (1999) 3–11.
Ozyurt, N., Ilki, A., Tasdemir, C., Tasdemir, M.A. and Sengul, O., ‘Mechanical behavior of ultra high strength cement based materials’, 11th National Mechanical Congress, 6–10 September, Abant, Turkey, 1999, 687–696 [In Turkish with English abstract].
Tasdemir, M.A. and Karihaloo, B.L., ‘A proposal for the determination of friction coefficient in concrete using disc specimens’, Internal report (Cardiff University, August 2000).
Erdogan, F. and Sih, G.C., ‘On the crack extension in plates under plane loading transverse shear’,Journal of Basic Engineering 85 (4) (1963) 519–527.
Sih, G.C., ‘Strain-energy-density factor applied the mixed-mode crack problems’,International Journal of Fracture 10 (3) (1974) 305–321.
Hussian, M.A., Pu, S.L. and Underwood, J., ‘Strain energy release rate for a crack under combined Mode I and Mode II’, ASTM STP560 (1974) 2–28.
Tasdemir, M.A., Maji, A.K. and Shah, S.P., ‘Crack propagation in concrete under compression’,Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE 116 (5) (1990) 1058–1076.
Maji, A.K., Tasdemir, M.A. and Shah, S.P., ‘Mixed mode crack propagation in quasi-brittle materials’,Engineering Fracture Mechanics 38 (2–3) (1991) 129–145.
Yarema, S.Ya., Ivanitskaya, G.S., Maistrenko, A.L. and Zboromirskii, A.I., ‘Crack development in a sintered carbide in combined deformation of types I and II’,Problemy Prochnosti 8 (1984) 51–56.
Libatskii, L.L. and Kovchig, S.E., ‘Fracture of dises containing cracks’,Fiziko-Khimicheskaya Mekhanika Materialov 3 (4) (1967) 458–464.
Yarema, S.Ya. and Krestin, G.S., ‘Determination of the modulus of cohesion of brittle materials by compressive tests on disc specimens containing cracks’,Fiziko-Khimicheskaya Mekhanika Materialov 2 (1) (1966) 10–14.
Tasdemir, M.A., Maji, A.K. and Shah, S.P., ‘Crack growth in concrete under combined Mode I and Mode II’,Bulletin of Istanbul Technical University 45 (1/3) (1992) 133–164.
Tasdemir, M.A., Akcakaya, R, Tasdemir, C. and Akyuz, S., ‘Mixed mode fracture in glass’, in Proceedings of International Symposium on Glass Problems, Istanbul, Turkey, Vol. 1 (1996) 222–229.
Tasdemir, M.A. and Karihaloo, B.L., ‘Effect of aggregate volume fraction on the fracture parameters of concrete: A mesomechanical approach’,Magazine of Concrete Research 53 (6) (2001) 405–415.
Karihaloo, B.L., ‘Fracture Mechanics and Structural Concrete’, (Longman Group Ltd., Essex, 1995).
Shah, S.P. and Tasdemir, M.A., ‘Role of fracture mechanics in concrete Technology’, in ‘Advances in Concrete Technology’, Edited by V.M. Malhotra, Second Edition, Ottawa, CANMET, (1994) 161–202.
Atahan, H.N., Kizilaslan, M., Tasdemir, M.A. and Akyuz, S., ‘Size effect on the failure of concrete under Mode I loading condition’, in Proceedings of 10th National Mechanics Congress, Istanbul, Turkey (1997) 105–115 [In Turkish with English abstract].
RILEM TC 89-FMT., ‘Size effect method for determining fracture energy and fracture process zone size of concrete’,Mater. Struct. 23 (1990) 461–465.
Bažant, Z.P., ‘Analysis of work of fracture method for measuring fracture energy of concrete’,Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE 122 (1996) 138–144.
Atkinson, C., Smelser, R.E. and Sanchez, J., ‘Combined mode fracture via the cracked Brazilian disc test’,International Journal of Fracture 18 (4) (1982) 279–291.
Awaji, H. and Sato, S., ‘Combined mode fracture toughness measurement by the disc test’,Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology 100 (1978) 175–183.
Freiman, S.W., Gonzales, A.C. and Mecholsky, J.J., ‘Mixedmode fracture in soda-lime glass’,Journal of American Ceramic Society 62 (3–4) (1979) 206–208.
Shetty, D.K., Rosenfield, A.R. and Duckworth, W.H., ‘Mixed-mode fracture in biaxial stress state: Application of the diametral compression (Brazilian disc) test’,Engineering Fracture Mechanics 26 (6) (1987) 825–840.
Gettu, R. and Shah, S.P., ‘Fracture mechanics’, in ‘High Performance Concretes and Applications’, Edited by. S.P. Shah and S.H. Ahmad, (Edward Arnold Publishers, London, 1994) 161–212.
Sanchez, J., ‘Application of the disc test to Mode I–II fracture analysis’, MS thesis, University of Pittsburgh (1979).
Tasdemir, M.A., Tasdemir, C., Akcakaya, R. and Atahan, H.N., ‘Combined Mode I and Mode II fracture in brittle and quasi-brittle materials’, in Proceeding of 3rd Ceramic Congress, Turkish Ceramic Society, Istanbul, Turkey, Vol. 1 (1996) 282–289. (In Turkish with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atahan, H.N., Tasdemir, M.A., Tasdemir, C. et al. Mode I and mixed mode fracture studies in brittle materials using the Brazilian disc specimen. Mat. Struct. 38, 305–312 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02479295
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02479295