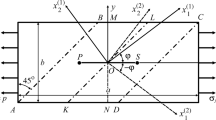
Abstract
This study is concerned with the mechanical properties of a fibreglass reinforced polyester resin of laminar construction with consideration given to the application of the results to the analysis, in bending, of a plate of similar material.
Tension and compression tests were performed to obtain the stress-strain relationship and ultimate stresses and strains. Because of the inherent scatter of results due to the nature of the material, average values, along with maximum and minimum limits, are determined. Flexural tests were conducted and moment-curvature relationships were obtained both theoretically and experimentally. Creep tests showed that, for loads well below the failure load, creep effects are almost negligible when the fibres are oriented to the longitudinal axis of the specimen. As the results in bending are not as scattered as those for tension and compression, this leads one to believe that they might be more appropriate for use in plate theory.
Résumé
On étudie les propriétés mécaniques d’une rśine polyester renforcée de fibres de verre et de structures laminaires, en ayant en vue l’application des résultats à l’étude en flexion d’une plaque d’un matériau similaire.
Les essais de traction et de compression ont été réalisés afin d’obtenir la relation contrainte/déformation ainsi que les contrainteses et déformations ultimes. La nature du matériau déterminant une dispersion des résultats, on a fixé des valeurs moyennes comportant des limites maximales et minimales. On a réalisé des essais de flexion tant théoriques qu’expérimentaux, et obtenu des relations moment-courbure. Les essais de fluage montrent que pour des charges nettement au-dessous de la charge de rupture les effets du fluage sont presque négligeables si les fibres sont disposées longitudinalement dans l’éprouvette. Comme les résultats en flexion sont moins dispersés que ceux obtenus en traction et en compression, on peut supposer qu’ils se prêtent mieux à être utilisés dans la théorie des plaques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsai S. W.—Structural behaviour of composite materials. NASA CR-71, Washington, D.C., July, 1964.
Kitzmiller A. H., De Haven C. C., Young R. E.—Design Considerations for spirally glass-reinforced filament wound structures as rocket inert parts. ARS Preprint 983-59, 1959.
Zickel J.—Isotensoid pressure vessels. ARS Journal, 32, 1962.
Read W. S.—Equilibrium shapes for pressurized fibreglass domes. ASME Paper 62-AV-4, 1962.
Hoffman O.—Stresses and deformation in filament reinforced structures. IAS Paper 62-26, 1962.
Shaffer B. W.—Stress-strain relations of reinforced plastics parallel and normal to their internal filaments. AIAA Journal, Vol. 2, No. 2, February 1964.
Tsai S. W., Azzi V. O.—Elastic moduli of laminated anisotropic composites. Experimental Mechanics, Vol. 5, No. 6, June 1965.
Krolikowski W.—Stress-strain characteristics of glass fibre reinforced polyester. SPE Journal, Vol. 20, No. 9, September 1964.
Outwater J. O., West D. C.—Stress distribution in the resin of reinforced plastics. Modern Plastics, September 1961.
Ratch Jr. H.—What’s wrong with data on reinforced plastics? Materials in Design Engineering, May 1961.
Barnet R. R., Prosen F. P.—Validity of mechanical tests for glass reinforced plastics. Materials Protection, June 1964.
Martin J.—Theories of strength for combined stresses and non-isotropic materials, Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences, Vol. 24, April 1957.
Azzi V. D., Tsai S. W.—Anisotropic strength of composites, Experimental Mechanics, Vol. 5, No. 9, September 1965.
Fried N.—Role of resin in reinforced plastics. Modern Plastics, September 1963.
Broutman L. J.—Failure mechanisms for filament reinforced plastics. Modern Plastics, Vol. 42, April 1965.
Biot M. A.—Theory of stress-strain relations in anisotropic visco-elasticity and relaxation phenomena. Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 25, No. 11, November 1954.
Kaye A., Saunders D. W.—Creep in an anistropic medium. British Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 15, 1964.
Engineering design properties of glass reinforced plastics. British Plastics, Vol. 38, No. 2, February 1965.
Bershtein V. A., Glikman L. A.—Mechanism of delayed failure in polyester fibreglasses, Soviet Physics-Solid State, Vol. 5, No. 8, February 1964. Translated from Fizika Tverdogo Tela, Vol. 5, No. 8, August 1963.
Brink N. O.—Mechanical behaviour of reinforced plastics at cryogenic temperatures. SPE Journal, Vol. 20, No. 10, October 1964.
Howse Jr. P. T., Pears C. D.—Thermal properties of reinforced plastics, Modern Plastics, Vol. 39, September 1961.
Barnet R. L.—Review of structural design techniques for brittle components under static loads. Contract AF 33(657)-8339, ARF Report, No. 8259, May 1963.
Weibull W.—A statistical theory of the strength of materials. Royal Swedish Academy of Engineering Sciences, No. 151, 1939.
Bradstreet S. W.—Principles affecting high strength to density-composites with fibres or flakes. Technical Documentary Report, No. ML TDR 65-85, May 1964.
Sonneborn R. H.—Fibreglass reinforced plastics. Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York, 1954.
Van Echo J., Remely G. R., Simmons W. F.—High temperature creep-rupture properties of glass fabric plastic laminates. Dept. AF, WADC 53-491, December 1953.
Steel D. J.—The creep and stress-rupture of reinforced plastics. Transactions, J. Plastics Inst., October 1965.
Shand E. B.—Glass engineering handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc., New York, 1958.
McAbee E., Chmura M.—Effects of high rates compared with static rates of loading on the mechanical properties of glass reinforced plastics. 16th Annual Technical and Management Conference, Reinforced Plastics Division. The Society of the Plastics Industry Inc., Paper 13-D, 1961.
Medwadowski S. J.—Refined theory of elastic orthotropic plates. A.S.M.E. Paper No. 58-APM-16, September 1958.
Hearmon R.F.S.—An introduction to applied anisotropic elasticity. Oxford University Press, 1961.
Baer E.—Engineering design for plastics. Reinhold Publishing Corp., Chap. 14, New York, 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Topper, T.H., Sherbourne, A.N. & Saari, V. Bending of glass fibre-reinforced plastic (GFRP) plates on elastic supports. Mat. Constr. 11, 75–91 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478954
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478954