Abstract
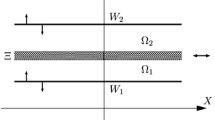
Laminar motion of two viscous incompressible fluids through each other is treated for two cases: flow along the axis of a circular cylinder, and flow between parallel flat plates. Motion of either fluid entails that of the other. Regarding one fluid as a solvent, the other as a solute, and supposing the system to have ends impermeable to the former, it is found that the solvent streams with the solute down the center of the system, to return in the opposite direction out nearer the walls. Thus diffusion of a dissolved substance through a region in which the solvent is confined produces continual streaming in the latter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Young, G. (1938). “Theory of diffusion forces in metabolizing systems,”Growth,2, 165–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, G. Convective diffusion in parallel flow fields. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 2, 49–59 (1940). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478031
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478031