Abstract
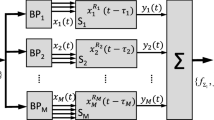
The coherence function for two time functions can be computed using certain mathematical methods, such as correlation and Fourier transforms. If one time function is identical to a single response and the other, to an average response (averaged evoked potential) determined from many responses, the coherence function gives the degree of correlation with respect to frequency. Under certain assumptions, the cortical adaptation time course can be inferred from the coherence function of single responses.
An example is used to show the determination of the coherence time course of multiple acoustic evoked responses recorded extracranially from man.
Sommaire
La fonction de cohésion peut être calculée pour deux fonctions de temps par certaines méthodes mathématiques, telles que la méthode de corrélation et les transformations de Fourier. Si une fonction de temps est identique à une réaction isolée et l'autre à une réaction moyenne (potentiel évoqué moyen) déterminée pour de nombreuses réactions, la fonction de cohésion indique le degré de corrélation par rapoort à la fréquence. Le temps d'adaptation corticale peut, sous certaines conditions, être déduit de la fonction de cohésion de réactions isolées.
L'auteur illustre par un exemple la détermination de l'évolution du temps de cohésion de multiples réactions suscitées chez l'homme par des moyens acoustiques et relevées par enregistrement extracranien.
Zusammenfassung
Unter Verwendung bestimmter mathematischer Methoden, wie der Korrelation und Fouriertransformation kann die Koheränzfunktion für zwei Zeitfunktionen berechnet werden. Wenn eine Zeitfunktion mit einer einzelnen Reizantwort und die andere mit einer aus mehreren Reizantworten gebildeten mittleren Antwort (gemitteltes evoziertes Potential) identisch ist, gibt die Koheränzfunktion den Grad der Korrelation im Frequenzbereich wieder. Unter bestimmten Voraussetzungen kann von der Koheränzfunktion einzelner Antworten, auf den Verlauf der langsamen biphasischen PotentialschwankungN 1 P 2 und im weiteren auf den corticalen Adaptationszeitgang geschlossen werden.
An Hand eines Beispiels wird der Koheränzzeitgang mehrerer akustisch ausgelöster Reizantworten, die extracranial am Menschen abgeleitet wurden, bestimmt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackman, R. andTukey, J. (1958)The Measurement of Power Spectra Dover Publications N. Y.
Davis, H. (1965) Slow cortical responses by acoustic stimuli.Acta oto-lar. 59, 179–185.
Fruhsdorfer, H., Soveri, P. andJärvilehto, T. (1970) Short-term habituation of the auditory evoked response in man.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 28, 153–161.
Gestring, G. andJantsch, H. (1969) EEG Computer Analyse zur objektiven Registrierung der Reizantwort auf periphere elektrische Stimuli.Wien. klin. Wschr. 81, 83–86.
Keidel, W. D. undSpreng, M. (1965) Audiometric aspects and multisensory power function of electronically averaged slow evoked cortical responses in man.Acta oto-lar. 59, 201–208.
Stange, G. undSoda, T. (1968) Quantitative Untersuchungen der Hörschwelle, Adaptation und Lautheitsempfindung am gesunden und hörgeschädigten Menschen mittels der “objektiven Audiometrie”,Arch. klin. exp. Ohr-Nas. -Kehlk. -Heilkunde 190, 210–228.
Walter, D. andAdey, W. (1963) Spectral analysis of EEG's recorded during learning in the cat, before and after subthalamic lesions.Expl. Neurol. 7, 481–501.
Welch, P. (1961) A direct digital method of power spectrum estimation.IBM Jnl Res. Den. 141–156.
Zerlin, S. andDavis, H. (1967) The variability of single evoked vertex potentials in man.Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 23, 468–472.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfurtscheller, G. The use of spectral analysis to determine the cortical adaptation time course from extracranially recorded responses in man. Med. & biol. Engng. 8, 367–372 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477664
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477664