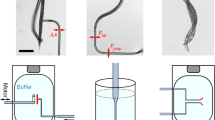
Abstract
A microelectrode puller is described with the following properties: reproducibility of pulling; easy adjusting procedure; the possibility of shaping the electrode; and the possibility of intermittent pulling of different types of electrodes. These properties are obtained by: a well phased pulling scheme; nearly frictionless moving parts; symmetrical and vertical pulling; and fully electronic switching.
Sommaire
On décrit un extracteur de microélectrodes ayant les caractéristique suivantes: reproductivité de l'extraction, réglage facile, possibilité de former l'electrode, possibilité d'extraction intermittente des différents types d'électrodes. Ces caractéristiques sont obtenues par: un système d'extraction bien phasé, des pièces mobiles presque sans frottement, l'extraction symétrique et verticale, et une commutation intégralement électronique.
Zusammenfassung
Es wird ein Mikroelektroden-Ziehgerät mit folgenden Merkmalen beschrieben: Reproduzierbarkeit des Ziehvorganges, leichte Einstellung. Möglichkeit, der Elektrode eine Form zu geben, und evtl. intermittierendes Ziehen von Elektroden verschiedener Art. Diese Merkmale werden erreicht durch: ein gut abgestimmtes Ziehsystem, fast reibungslos bewegliche Teile, symmetrisches und senkrechtes Ziehen sowie vollelektronisches Schalten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, F. L. andYork, D. H. (1971) A reliable technique for making glass microelectrodes of known resistance.Proc. IEEE,59, 1711–1712.
Brown, K. T. andFlaming, D. G. (1974) Bevelling of fine micropipette electrodes by a rapid precision method.Science 185, 693–695.
Chowdhury, T. K. (1969) Fabrication of extremely fine micropipette electrodes.J. Sci. Instrum. S2V2, 1087–1090.
Frank, F. andBecker, M. C. (1964) Microelectrodes for recording and stimulation. In:W. L. Nastuk (ed.)Physical techniques in biological research, vol. V, pp. 22–87, Academic Press, New York and London.
Fry, D. M. (1975) A scanning electron microscope method for the examination of glass microelectrode tips either before or after use.Experientia 31, 695–697.
Hébert, N. C. (1969) Properties of microelectrode glasses. In:M. Lavallée, O. P. Schanne andN. C. Hébert (eds.)Glass microelectrodes, 25–31, J. Wiley.
Ling, G. N. andGerard, R. W. (1949) The normal membrane potential of frog sartorius muscle.J. Cellular Comp. Physiol. 34, 383–396.
Okada, Y. andInouye, A. (1975) Tip potential and fixed charges on the glass wall of microelectrode.Experientia 31, 545–546.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siegenbeek van Heukelom, J., Dijkstra, K. & van Ingen, H. A versatile and reproducibly operating microelectrode puller. Med. & biol. Engng. 14, 644–652 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477042
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477042