Summary
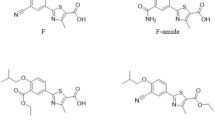
A screening method using nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) has been developed for purity analysis of pyridinyl-methyl-sulfinyl-benzimidazoles (PMSB). Eight different polar organic solvents were tested as background electrolytes.N-Methylformamide (NMF) was found to have the best properties in respect of both electrophoretic behavior and high solubility of five different model compounds. Optimization of the CE separation with regard to the effects of addition of various electrolyte modifiers is reported. An additional feature of amide solvents, rarely utilized in CE, is their intrinsic basic nature; this is of particular interest for analysis of compounds such as the PMSB, the degradation of which is acid-catalyzed. It is shown here that these compounds are stable at room temperature for weeks in NMF solution. Results from quantitative application of the NACE method were highly precise (typically 1.8%RSD for normalized peak area); linearity was good and detection limit in drug purity determination was low (∼0.05 area % relative to the drug compound).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Brändström, P. Lindberg, N.-Å. Bergman, T. Alminger, K. Ankner, U. Junggren, B. Lamm, P. Nordberg, M. Erickson, I. Grundevik, I. Hagin, K.-J. Hoffman, S. Johansson, S. Larsson, I. Löfberg, K. Ohlson, B. Persson, I. Skånberg, L. Tekenbergs-Hjelte, Acta Chem. Scand.43, 536 (1989).
M. Mathew, V. Das Gupta, R. E. Bailey, Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy,21(8), 965 (1995).
Å. Pilbrant, C. Cederberg, Scand. J. Gastroenterol.20 (Suppl. 108), 113 (1985).
Y. Walbroehl, J. W. Jorgenson, J. Chromatogr.315, 135 (1984).
R. S. Sahota, M. G. Khaledi, Anal. Chem.66, 1141 (1994).
A. J. Tomlinson, L. M. Benson, S. Naylor, LC-GC Int. April, 210 (1995).
S. H. Hansen, J. Tjørnelund, I. Bjørnsdottir, Trends Anal. Chem.15, 175 (1996).
I. E. Valkó, H. Sirén, M.-L. Riekkola, LC-GC Int. March, 190 (1997).
M. Jansson, J. Roeraade, Chromatographia40, 163 (1995).
J. Tjørnelund, S. H. Hansen, J. Chromatogr. A779, 235 (1997).
E. Drange, E. Lundanes, J. Chromatogr. A771, 301 (1997).
F. Wang, M. G. Khaledi, Anal. Chem.68, 3460 (1996).
I. E. Valkó, H. Sirén, M.-L. Riekkola, J. Chromatogr. A737, 263 (1996).
I. Valkó, H. Sirén, M.-L. Riekkola, Electrophoresis18, 919 (1997).
Y. Mori, K. Ueno, T. Umeda, J. Chromatogr. A757, 328 (1997).
E. Kenndlen, P. Jenner, J. Chromatogr.390, 169 (1987).
R. G. Bates, Determination of pH—theory and practice, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1973.
E. Örnskov, S. Folestad, in preparation.
A. Tivesten, S. Folestad, S. Norrman, A. P. Larsson, in preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tivesten, A., Folestad, S., Schönbacher, V. et al. Nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis for the analysis of labile pharmaceutical compounds. Chromatographia 49 (Suppl 1), S7–S11 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02468970
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02468970