Abstract
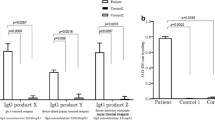
Two patients with kidney transplants were prescribed anti-human lymphocyte γ-globulin (AHLG) as an adjunct immunosuppressive treatment. AHLG was prepared from cultured human lymphocytes as antigen and successive anti-AHLG levels were measured using passive hemagglutination tests during and after the AHLG treatment. Anti-AHLG levels began to increase after 10–14 days of daily AHLG administration. There-after, the levels tends to decrease transiently by the further administration of AHLG. The titer rose again after the discontinuation of AHLG administration reaching a plateau which continued for a considerable length of time. Pretreatment levels were reverted after more than three months. The anti-sheep RBC Ab and anti-horse RBC Ab levels followed the same pattern as that seen with anti-AHLG Ab. The anti-AHLG Ab proved to be specific anti-horse γ-globulin Ab. Alterations in the anti-AHLG levels can thus be used to monitor the optimal dosage and period of administration as well as to predict the anaphylactic reaction due to AHLG treatment. Keeping the anti-AHLG level low is mandatory to maintain good immuno-suppressive conditions yet avoid anaphylactic reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondo, A., Ikeda, M., Saito, Y., Matsuo, E., Hirose, K., Ito, T., Konomi, K., Yamamoto, H., Nakamura, H. and Morisue, S.: Studies on antilymphocyte serum: Preparation and clinical use of antihuman spleen lymphocyte globulin (2nd report). Ishoku (Jpn. J. Transpl.) 12: 124–135, 1977. (in Japaneses)
Kusaba, Y., Hirose, K., Kanetake, H., Saito, Y., Kondo, A. and Morisue, S.: Studies on antilymphocyte serum: Preparation of AHLG using cultured lymphocyte as antigen. Ishoku (Jpn. J. Transpl.) 12: 81, 1977. (in Japanese)
Gold, E.R. and Fudenberg, H.H.: Chromic chloride: A coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J. Immun. 99: 859–866, 1967.
Kashiwagi, N., Brantiggan, C.O., Brettshneider, L., Groth, C.G. and Starzl, T.E.: Clinical reactions and serologic changes after the administration of heterologous antilymphocyt globulin to human recipients of renal homografts. Ann. Int. Med. 68: 275–286, 1968.
Ochiai, T.: Immunological and histological studies of the prolonged administration of G fraction of antilymphocyte serum. Acta Path. Jap. 22: 261–272, 1972.
Waller, M., Pierce, J.C., Moncure, C.W. and Hume, D.M.: Humoral responses in human organ transplantation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 11: 173–186, 1972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konomi, K., Ohta, T., Toyoda, K. et al. Occurrence of ANTI-AHLG in renal transplant patients on AHLG (anti-human lymphocyte globulin). The Japanese Journal of Surgery 10, 315–320 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02468794
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02468794