Abstract
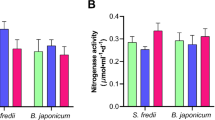
Vegetable soybeam germplasm was screened for its tolerance to 0, 50 and 100 μM Al in solution culture. Plants were inoculated with prescreened acid-Al tolerantBradyrhizobium japonicum strain USDA 110 and a localRhizobium isolate SM867. Aluminum concentrations of 0, 50, and 100 μM affected the root lengths of all germplasm lines in the first few weeks of their growth. At 100 μM, the plants had severely stunted roots throughout the growing period of 35 days, but at 50 μM the initial stunting of the roots was overcome after the third week of growth, and there were no significant differences between the root lengths of these plants and of the controls. The appearance of the first nodule was delayed for 2–3 and 4–5 days at 50 μM and 100 μM Al, respectively. There was a significant reduction in nodule numbers and acetylene reduction activity (ARA) at 100 μM Al. At 50 μM Al, even though the number of nodules was decreased significantly, nodules were larger in size, so there was no significant reduction in nodule fresh weight and ARA. No significant differences in nitrogen fixing abilities of the soybean lines were observed between the twoRhizobium strains. Germplasm line Kahala showed the greatest tolerance to 50 μM Al, and Kahala, Kim and Wolverine tolerated 100 μM Al better than other germplasm lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alva A K, Edwards D G, Asher C J and Suthipradit S 1987 Effects of acid soil infertility factors on growth and nodulation of soybean. Agron. J. 79, 302–306.
Carter T E 1987 Genetic alteration of seed size: Breeding strategies and market potential. USDA-ARS report.
Carvalho M M de, Edwards D G, Asher C J, and Andrew C S 1981 Aluminum toxicity, nodulation, and growth of Stylosanthes species. Agron. J. 73, 261–265.
DeManzi J M and Cartwright P M 1984 The effects of pH and Al toxicity on the growth and symbiotic development of cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). Plant and Soil 80, 423–430.
Franco A A, and Munns D N 1982 Acidity and Al restraints on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth ofPhaseolus vulgaris in solution culture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 296–301.
Hartel P G, Whelan A M and Alexander M 1983 Nodulation of cowpeas and survival of cowpea rhizobia in acid, aluminium-rich soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 47, 514–517.
Hohenberg J S and Munns D N 1984 Effect of soil acidity factors on nodulation and growth ofVigna unguiculata in solution culture. Agron. J. 76, 477–481.
Munns D N, Hohenberg J S, Righetti T L and Lauter D J 1981 Son acidity tolerance of symbiotic and nitrogen-fertilized soybeans. Agron. J. 73, 407–410.
Sharma G C, Sabota C, Schenk J, Anderson J C and Wann E V 1986 Production and marketing of exotic vegetables. Bull. Plant and Soil Science Dept., Alabama A&M Univ., Normal, AL 1, 14–16.
Whelan A M and Alexander M 1986 Effects of low pH and high Al, Mn and Fe levels on the survival ofRhizobium trifolii and the subterranean clover. Plant and Soil 92, 363–371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mookherji, S., Floyd, M. The effect of aluminium on growth of and nitrogen fixation in vegetable soybean germplasm. Plant Soil 136, 25–29 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02465216
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02465216