Abstract
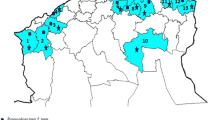
The distribution of three sporulator physiotypes ofBipolaris oryzae, namely, photo-induced, and non-photo-induced (I) and (II), was investigated. Of 407 isolates, 99% belonged to the photo-induced type, in which conidial development was under photo-control of the antagonistic action of blue/UV-A and near-UV radiation mediated through the ‘mycochrome’ system at conidiophore induction and conidiophore maturation stages. Of the remainder, 1 isolate belonged to the non-photo-induced (I) type, and 4 isolates belonged to the non-photo-induced (II) type. Conidial development in the former of these was photo-controlled by the ‘mycochrome’ system at conidiophore maturation stage alone, while in the latter it was not affected by light conditions. No difference was found between the three physiotypes in restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) of rDNA. However, random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) revealed polymorphisms between photo-induced and non-photo-induced isolates and showed that non-photo-induced (I) and (II) strains were clustered in the same group, suggesting that they are genetically close. Photo-induced sporulators ofB. oryzae were confirmed to be widely distributed in paddy fields in Japan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bentley, S., Pegg, K. G. and Dale, J. L. 1995. Genetic variation among a world-wide collection of isolates ofFusarium oxysporum f. sp.cubense analyzed by RAPD-PCR fingerprinting. Mycol. Res.99: 1378–1384.
Bruns, T. D., Fogel, R. and Taylor, J. W. 1990. Amplification and sequencing of DNA from fungal herbarium specimens. Mycologia82: 175–184.
Chen, W. 1992. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNAs of three heterothallicPythium species. Phytopathology82: 1467–1472.
Cubeta, M. A., Echandi, E., Abernethy, T. and Vilgalys, R. 1991. Characterization of anastomosis groups of binucleateRhizoctonia species using restriction analysis of an amplified ribosomal RNA gene. Phytopathology81: 1395–1400.
Erland, S. 1995. Abundance ofTylospora fibrillosa ectomycorrhizas in a South Swedish spruce forest measured by RFLP analysis of the PCR-amplified rDNA ITS region. Mycol. Res.99: 1425–1428.
Kihara, J. and Kumagai, T. 1994. Ecotypes of the fungusBipolaris oryzae with various responses of the mycochrome system. Physiol. Plant.92: 689–695.
Kumagai, T. 1978. Mycochrome system and conidial development in certain fungi imperfecti. Photochem. Photobiol.27: 371–379.
Kumagai, T. 1988. Photocontrol of fungal development. Photochem. Photobiol.47: 889–896.
Leach, C. M. 1967. Interaction of near-ultraviolet light and temperature on sporulation of the fungi,Alternaria, Cercosporella, Fusarium, Helminthosporium, andStemphylium. Can. J. Bot.47: 1999–2016.
Nakada, M., tanaka, C., Tsunewaki, K. and Tsuda, M. 1994. RFLP analysis for species separation in the generaBipolaris andCurvularia. Mycoscience35: 271–278.
Nei, M. and Li, W.-H. 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.76: 5269–5273.
Nicholson, P. and Rezanoor, H. N. 1994. The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA to identify pathotype and detect variation inPseudocercosporella herpotrichoides. Mycol. Res.98: 13–21.
Puterka, G. J., Black, W. C., Steiner, W. M. and Burton, R. L. 1993. Genetic variation and phylogenetic relationships among worldwide collections of the Russian wheat aphid,Diraphis noxia (Mordvilko), inferred from allozyme and RAPD-PCR markers. Heredity70: 604–618.
Tan, K. K. 1978. Light-induced fungal development. In: The filamentous fungi, vol. III. Developmental biology, (ed. by Smith, J. E. and Berry, D. R.), pp. 334–357. Edward Arnold Publ., London.
Theodore, M. L., Stevenson, T. W., Johnson, G. C., Thornton, J. D. and Lawrie, A. C. 1995. Comparison ofSerpula lacrymans isolates using RAPD PCR. Mycol. Res.99: 447–450.
Van de Zande, L. and Bijlsma, R. 1995. Limitations of the RAPD technique in phylogeny reconstruction inDrosophila. J. Evol. Biol.8: 645–656.
Ward, E. and Akrofi, A. Y. 1994. Identification of fungi in theGaeumannomyces-Phialophora complex by RFLPs of PCR-amplified ribosomal DNAs. Mycol. Res.98: 219–224.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. and Taylor, J. 1990. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: PCR protocols: A guide to methods and amplifications, (ed. by Innis, M. A., Gelfand, D. H., Sninsky, J. J., and White, T. J.), pp. 315–322. Academic Press, San Diego.
Williams, J. G. K., Kubelik, A. R., Livak, K. J., Rafalski, J. and Tingey, S. V. 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nuclic Acids Res.18: 6531–6535.
Yamamura, S., Kumagai, T. and Oda, Y. 1978. Mycochrome system and conidial development in a nonphotoinduced isolate ofHelminthosporium oryzae. Can. J. Bot.56: 206–208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kihara, J., Ishikawa, S. & Kumagai, T. Distribution of photo-induced and non-photo-induced sporulator physiotypes ofBipolaris oryzae in Japan. Mycoscience 38, 147–153 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460850
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460850