Abstract
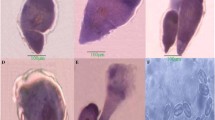
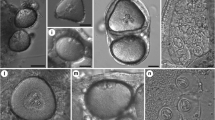
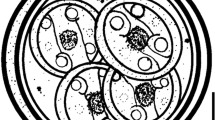
Aphanomyces frigidophilus sp. nov. was obtained from eggs of Japanese char,Salvelinus leucomaenis, from Tochigi Prefectural Fisheries Experimental Station, Utsunomiya, Japan. Vegetative hyphae were delicate, slightly wavy, moderately branched. Zoosporangia were isodiametric with the vegetative hyphae. Oogonia were abundant, originating on short stalks from lateral sides of hyphae. Oogonia were spherical, subspherical or pyriform, with a single subcentric oospore inside. Outer surfaces of oogonia were roughened with short papillate, crenulate or irregular ornaments. Antheridia and oospore germination were not observed. Zoospore germination and vegetative growth were found from pH 5.0 to 11.0. Zoospore production was highest at 10°C, whereas rapid growth occurred at 20–25°C. Vegetative growth of the fungus declined from the maximal level at 25°C to less than half maximal at 30°C and completely disappeared at 35°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Czeczuga, B. and Woronowicz, L. 1993. Aquatic fungi developing on the eggs of certain freshwater fish species and their environment. ACTA Ichthyol. Pisca.23: 39–57.
Dieguez-Uribeondo, J., Cerenius, L. and Soderhall, K. 1994. Repeated zoospore emergence inSaprolegnia parasitica. Mycol. Res.98: 810–815.
Diler, O. 1995.Pythium spp. on infected rainbow trout eggs and fry. Tr. J. Biol.19: 317–321.
Hatai, K. 1980. Studies on pathogenic agents of saprolegniasis in freshwater fishes. Spec. Rep. Nagasaki Pref. Inst. Fish.8: 1–95.
Kitancharoen, N., Hatai, K., Ogihara, R. and Ni Aye, D. N. 1995. A new record ofAchlya klebsiana from snakehead,Channa striatus, with fungal infection in Myanmar. Mycoscience36: 235–238.
Kitancharoen, N., Yuasa, K. and Hatai, K. 1996. Effects of pH and temperature on growth ofSaprolegnia diclina andS. parasitica isolated from various sources. Mycoscience37: 385–390.
Scott, W. W. 1961. A monograph of the genusAphanomyces. Virginia Agri. Exp. Stat. Tech. Bull. 151.
Scott, W. W. and O'Bier, A. H. 1962. Aquatic fungi associated with diseased fish and fish eggs. Prog. Fish Cult.1: 3–15.
Srivastava, G. C. and Srivastava, R. C. 1976a. Fungal infection of the eggs ofChanna punctatus BI. Geobios3: 160.
Srivastava, G. C. and Srivastava, R. C. 1976b. A note on the destruction of the eggs ofCyprinus carpio var.communis by the members of Saprolegniaceae. Sci. and Cult.42: 612–614.
Willoughby, L. G., Robert, R. J. and Chinabut, S. 1995.Aphanomyces invaderis sp. nov., the fungal pathogen of freshwater fish affected by epizootic ultcerative syndrome. J. Fish Dis.18: 273–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Kitancharoen, N., Hatai, K. Aphanomyces frigidophilus sp. nov. from eggs of Japanese char,Salvelinus leucomaenis . Mycoscience 38, 135–140 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460848
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460848