Abstract
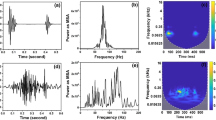
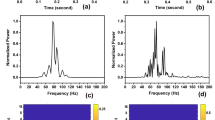
The diagnositic performance of two spectral techniques (the fast Fourier transform, FFT, and autoregressive modelling, ARM) combined with four windowing functions (rectangular, Hanning, Hamming, and sine-cosine) and two classifiers (Bayes and nearest neighbour) to detect valvular degeneration was evaluated in a group of 95 patients. Forth-seven patients had a porcine bioprosthetic valve inserted in the aortic position and 48 patients had a porcine bioprosthetic valve inserted in the mitral position. Among the aortic valves, 24 were normal and 23 were degenerated whereas among the mitral valves, 19 were normal and 29 were degenerated. The aortic and mitral valves were analysed separately. For each type of valve, 21 features were extracted from the spectra of the valve closure sounds to train and test the performance of four pattern recognition systems by using the leave-one-out method. The discriminant properties of all feature combinations between two and five among the 21 features selected were evaluated. Results show that the FFT combined to the nearest neighbour classifier provided the best performances: 87 per cent of correct classifications (CCs) for aortic valves when using the Hanning or the Hamming window and 94 per cent of CCs for mitral valves when using the rectangular window. The best performances obtained with the ARM were 81 per cent of CCs for the aortic valves (nearest neighbour classifier and the Hanning or the Hamming window) and 92 per cent of CCs for the mitral valves (nearest neighbour classifier and the Hamming window or the Bayes classifier and the Hanning or the Hamming window).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barratt-Boyes, B. G. (1964) Homograft aortic valve replacement in aortic incompetence and stenosis.Thorax,19, 131–150.
Carpentier, A., Lamaigre, C. G., Robert, L., Carpentier, S. andDubost, C. (1969) Biological factors affecting long-term results of valvular heterografts.J. Thorac. & Cardiovasc. Surg.,58, 467.
Cloutier, G., Guardo, R. andDurand, L. -G., (1987) Spectral analysis of closing sounds produced by Ionescu-Shiley bioprosthetic aortic heart valves. Part 1 Optimal number of poles and zeros for parametric spectral analysis.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,25, 487–491.
Durand, L. -G., De Guise, J., Cloutier, G., Guardo, R. andBrais, M. (1986) Evaluation of FFT-based and modern parametric methods for the spectral analysis of bioprosthetic valve sounds.IEEE Trans.,BME-33, 572–578.
Durand, L. -G., Blanchard, M., Sabbah, H. N., Hamid, M. S., Kemp, S. R. andStein, P. D. (1988) A Bayes model for automatic detection and quantification of bioprosthetic valve degeneration.Math. Comput. Modell.,11, 158–163.
Durand, L. -G., Blanchard, M., Cloutier, G., Sabbah, H. andStein, P. D. (1990) Comparison of pattern recognition methods for computer assisted classification of phonocardiograms of patients with a porcine bioprosthetic valve implanted in the mitral position.IEEE Trans.,BME-37, 1121–1129.
Feinstein, A. F. (1977) On the sensitivity, specificity, and discrimination of diagnostic tests. InClinical biostatistics. C. V. Mosby Co., St Louis, Chap. 15, 214–226.
Foale, R. A., Joo, T. H., McClellan, J. H., Metzinger, R. W., Grant, G. L., Myers, G. S. andLees, R. S. (1983) Detection of aortic porcine valve dysfunction by maximum entropy spectral analysis.Circ.,68, 42–49.
Foley, D. H. (1972) Considerations of sample and feature size.IEEE Trans.,IT-18, 618–626.
Joo, T. H., McClellan, J. H., Foale, R. A., Myers, G. S. andLees, R. S. (1983) Pole-zero modelling and classification of phonocardiograms. —Ibid.,BME-30, 110–118.
Kalayeh, M. M. andLandgrebe, D. A. (1983) Predicting the required number of training smaples. —Ibid,PAMI-5, 644–667.
Kay, S. M. andMarple, S. L. Jr. (1981) Spectrum analysis—a modern perspective.Proc. IEEE,74, 1380–1419.
Levy, R. J., Shoen, F. J. andGolomb, G. (1986) Bioprosthetic heart valve calcification: clinical features, pathobiology, and prospect for prevention.CRC Crit. Rev. Biocompat.,2, 147–187.
Rosman, H. S., Alam, M., Lakier, J. B., Kemp, S. R., Sabbah, H. N., Magilligan, D. J. Jr andStein, P. D. (1988) Utility of physical examination and noninvasive tests in the diagnosis of degneration of porcine bioprosthetic valves in the mitral position.Am. J. Non-Invasive Cardiol.,2, 48–51.
Ross, D. N. (1962) Homograft replacement of the aortic valve.Lancet, p. 487.
Starr, A. andCrunkemeier, G. L. (1989) The expected lifetime of porcine valves.Ann. Thorac. Surg.,48, 317–318.
Stein, P. D., Sabbah, H. N., Lakier, J. B. andGoldstein, S. (1980) Frequency spectrum of the aortic component of the second heart sound in patients with normal valves aortic stenosis and aortic porcine xenograph.Am. J. Cardiol.,46, 48–52.
Stein, P. D., Sabbah, H. N., Lakier, J. B., Magilligan, D. J. Jr andGoldstein, S. (1981) Frequency of the first heart sound in the assessment of stiffening of mitral bioprosthetic valves.Circ.,63, 200–204.
Stein, P. D., Sabbah, H. N., Lakier, J. B., Kemp, S. R. andMagilligan, D. J. Jr (1984) Frequency spectra of the first heart sound and of the aortic component of the second heart sound in patients with degenerated porcine bioprosthetic valves.Am. J. Cardiol.,53, 557–561.
Stein, P. D., Kemp, S. R., Riddle, J. M., Lee, M. W., Lewis, J. W. Jr andMagilligan, D. J. Jr (1985) Relation of calcification to torn leaflets of spontaneously degenerated porcine bioprosthetic valves.Ann. Thorac. Surg.,40, 175–180.
Thiene, G., Arbustini, E., Bortolotti, U., Talenti, E., Mijano, A., Valente, M., Molin, G. andGallucci, V. (1982) Pathologic substrates of porcine valve dysfunction. InCardiac bioprostheses. Yorke Medical Books, New York, Chap. 34, 378–400.
Trunk, G. V. (1979) A problem of dimensionality: a simple example.IEEE Trans.,PAMI-1, 306–307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durand, L.G., Guo, Z., Sabbah, H.N. et al. Comparison of spectral techniques for computer-assisted classification of spectra of heart sounds in patients with porcine bioprosthetic valves. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 31, 229–236 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458041
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458041