Summary
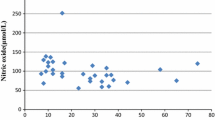
The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD; EC 1.15.1.1) and glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx; EC 1.11.1.9.), the enzymes that metabolize the superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide, respectively, were measured in serum from healthy subjects and patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). The activities of SOD and GSHPx in patients with PD were higher than those in normal healthy individuals. These results suggest that the increased activities of these enzymes could be due to oxidative stress in the initial stages of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanner CM: The role of environmental toxins in the etiology of Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci 12: 49–54, 1989
Finch CE: Age-related changes of dopaminergic functions. In: F Hefti and WJ Weiner (eds.) Progress in Parkinson Research. Plenum Press, New York, 1988, pp 173–179
Spina MB, Cohen G: Dopamine turnover and glutathione oxidation: Implications for Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 1398–1400, 1989
Dexter DT, Carter CJ, Wells FR, Agid F, Agid Y, Lees A, Jenner P, Marsden CD: Basal lipid peroxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 52: 381–389, 1989
Cohen G: The pathobiology of Parkinson's disease: Biochemical aspects of dopamine neuron senescence. J Neural Transm 19 (Suppl): 89–103, 1983
Ambani LM, Van Woert MH, Murphy S: Brain peroxidase and catalase in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 32: 114–118, 1975
Mizuno Y, Ohta K: Regional distribution of thiobarbituric acidreactive products, activities of enzymes regulating the metabolism of oxygen free radicals, and some of the related enzymes in adult and aged rat brains. J Neurochem 46: 1344–1352, 1986
Kish SJ, Marito C, Hornykiewicz O: Glutathione peroxidase activity in Parkinson's disease brain. Neurosci Lett 58: 343–346, 1985
Saggu H, Cooksey J, Dexter D, Wells FR, Lees A, Jenner P, Marsden CD: A selective increase in particulate superoxide dismutase activity in Parkinsonian substantia nigra. J Neurochem 53: 692–697, 1989
Sun Yi, Peterson TE, McCormick ML, Oberley LW, Osborne JW: Improved superoxide dismutase assay for clinical use. (Letter) Clin Chem 35: 1265–1266, 1989
Paglia DE, Valentine WN: Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70: 158–169, 1967
Lawrence RA, Burk RF: Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71: 952–958, 1976
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AZ, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275, 1951
Marttila RJ, Lorentz H, Rinne VK: Oxygen toxicity protecting enzymes in Parkinson's disease. Increase of superoxide-dismutase like activity in the substantia nigra and basal nucleus. J Neurological Sci 86: 321–331, 1988
Stocks J, Gutteridge JMC, Sharp RJ, Dormandy TL: The inhibition of lipid auto-oxidation by human serum and its relation to serum proteins and α-tocopherol. Clin Sci 47: 223–233, 1974
Gregory EM, Fridovich I: Induction of superoxide dismutase by molecular oxygen. J Bacteriol 114: 543–548, 1973
Crapo JD, Tierney DF: Superoxide dismutase and pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Am J Physiol 226: 1401–1407, 1974
Niwa Y, Ishimoto K, Kanoh T: Induction of superoxide dismutase in leukocytes by paraquat: Correlation with age and possible predictor of longevity. Blood 76: 835–841, 1990
Ceballos I, Lafon M, Javoy-Agid F, Hirsch E, Nicole A, Sinet PM, Agid Y: Superoxide dismutase and Parkinson's disease. Lancet 3335: 1035, 1990
Scott MD, Meshnick SR, Eaton JW: Superoxide dismutase-rich bacteria. Paradoxical increase in oxidant toxicity. J Biol Chem 262: 3640–3645, 1987
Perry TL, Yong VW: Idiopathic Parkinson's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and glutathione metabolism in the substantia nigra of patients. Neurosci Letts 67: 269–274, 1986
Lash LH, Jones DP: Distribution of oxidized and reduced forms of glutathione and cysteine in rat plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys 240: 583–592, 1985
Fantone JC, Ward PA: Role of oxygen-derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocytes-dependent in inflammatory reactions. Am J Pathol 107: 397–417, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalra, J., Rajput, A.H., Mantha, S.V. et al. Serum antioxidant enzyme activity in Parkinson's disease. Mol Cell Biochem 110, 165–168 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02454194
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02454194