Abstract
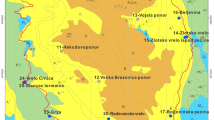
A hydrogeochemical study of the impact of land use on the composition of natural waters in the Vouzela region in northern Portugal was carried out during the summer of 1983. Water samples were collected from spring and major streams in the area and analyzed for major constituents and some trace elements. Analysis of variance and subsequent pairwise contrast tests demonstrated that waters from agricultural areas are significantly enriched in constiluents such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, Sr, Cl, SO4, and NO3. High concentrations of these ions in agricultural areas are the result of both the application of fertilizers and enhanced evaporation by the intensive irrigation of agricultural lands. Constitutents such as H4SiO4, HCO3, F, and probably Li, which are typically related to mineral weathering, were not affected by land use. In waters from forested areas the concentration of most constituents was about 20% higher than in waters from uncultivated areas with mainly a grass cover. This reflects the difference in the evapotranspiration of these two vegetation types. The chemistry of the Rio Zela clearly reflects differences in land use in the Rio Zela valley.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Andersen, L.J., and H. Kristiansen, 1984, Nitrate in ground-water and surface water related to land use in the Karup Basin, Denmark: Environ. Geol., v.5, p. 207–212.
Baumgartner, A., 1967, Energetic bases for differential vaporization from forest and agricultural lands.In Sopper, W. E., and H. W. Lull, eds., International symposium on forest hydrology: London Pergamon Press, p. 381–389.
Dekkers, M. J., S. P. Vriend, C. H. van der Weijden, and Ph. van Diest, 1986, The São Pedro do Sul granite, Portugal: Hydrogeochemistry related to the exploration of uranium: Uranium, v. 2, p. 261–277.
Dixon, W. J., ed., 1981, BMDP statistical software 1981: Berkeley University of California Press, 725 p.
Dixon, W. J., and F. J. Massey, Jr., 1957, Introduction to statistical analysis, 2nd ed.: New York, McGraw-Hill, 488 p.
Dougenik, A. J., and D. E. Sheehan, 1976, SYMAP user's reference manual, 5th ed.: Cambridge, Mass. Harvard University Press, 170 p.
Douglass, J. E., 1967, Effects of species and arrangement of forests on evapotranspiration.In Sopper, W. E., and H. W. Lull, eds. International symposium on forest hydrology: London, Pergamon Press, p. 451–461.
Gorham, E., 1961, Factors influencing supply of major ions to inland waters, with special reference to the atmosphere: Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. v. 72, p. 795–840.
ten Haven, H. L., R. Konings, M. A. A. Schoonen, J. B. H. Jansen, S. P. Vriend, C. H. van der Weijden, and J. Buitenkamp, 1985, Geochemical studies in the drainage basin of the Rio Vouga (Portugal). II. A model for the origin of hydrothermal water in the Vouzela region. Chem. Geol., v. 51, p. 225–238.
Johnson, D. W. (1984), Sulfur cycling in forests: Biogeochemistry, v. 1, p. 29–43.
Likens, G. E., F. H. Bormann, R. S. Pierce, J. S. Eaton, and N. M. Johnson, 1977, Biogeochemistry of a forested ecosystem New York, Springer-Verlag New York Inc., 146 p.
Meybeck, M., 1983, Atmospheric inputs and river transport of dissolved substances.In Dissolved loads of rivers and surface water quantity/quality relationships (proceedings of the Hamburg symposium, Augus 1983): IAHS publication no. 141, p. 173–192.
Phillips, A. B., and J. R. Webb, 1971, Production, marketing, and use of phosphorus fertilizers.In Olson, R. A., T. J. Army, J. J. Hanway, and V. J. Kilmer, eds., Fertilizer technology and use: Madison, Wisconsin, Soil Science Society of America, Inc., p. 271–300.
Piper, A. M., 1944, A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, v. 25, p. 914–923.
Taylor, A. W., W. M. Edwards, and E. C. Simpson, 1971, Nutrients in streams draining woodland and farmland near Coshocton, Ohio: Water Resour. Res., v. 7, p. 81–89.
van der Weijden, C.H., H.L. ten Haven, H.A. Boer, C.F.A.M. Hopstaken, and S.P. Vriend, 1984, Geochemical studies in the drainage basin of the Rio Vouga (Portugal). I. General hydrogeochemistry from its origin to the Ria de Aveiro.In Hydrochemical balances of freshwater systems (proceedings of the Uppsala symposium, September 1984): IAHS publication no. 150, p. 263–276.
van der Weijden, C. H., M.G. Oosterom, J. Bril, C. G. Walen, S. P. Vriend, and B. W. Zuurdeeg, 1983, Geochemical controls of transport and deposition of uranium from solution, case study: Fundão (Portugal): Utrecht, Publ. Inst. Earth Sci., Univ. of Utrecht, Contr. 007.79.3 EXU NL, 67 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comans, R.N.J., Van Der Weijden, C.H. & Vriend, S.P. Geochemical studies in the drainage basin of the Rio Vouga, Portugal. IV. Impact of land use on the hydrogeochemistry of natural waters in the Vouzela region. Environ. Geol. Water Sci 9, 119–128 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02449943
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02449943