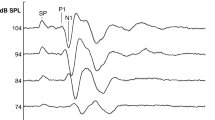
Abstract
The traditional brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) measurement technique (ensemble averaging) is time-consuming and is not acceptable for some time-critical clinical applications. In the paper the application of a pseudorandom binary sequence, the maximum length sequence, to human BAER measurements is examined. This technique permits a faster click rate to stimulate the test subject, and obtaines a higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) response through deconvolution. When compared with conventional averaging, the method can result in an improved SNR or in faster measurement of BAER. The theory of the technique and the experimental setup are presented, and theoretical analysis on the SNR improvement by this technique against averaging is also given. Actual measurements of BAER on both humans and cats indicate that this technique is effective, especially when the measurement time is not too long, or the number of trials is not too large.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, G. (1986) Analytic techniques in the estimation of evoked potentials. InClinical applications of computer analysis of EEG and other neurophysiological signals.Lopes da Silva, F. H., Storm Van Leeuwen, W. andRémond, A. (Eds.), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 311–333.
Boston, J. R. (1985) Noise cancellation for brainstem auditory evoked potentials.IEEE Trans.,BME-32, 1066–1070.
Courjon, J., Manguiere, F. andReevol, M. (Eds.) (1982) Clinical application of evoked potentials in neurology. InAdvances in neurology, Vol. 32. Raven Press.
Davila, C.E., Welch, A. J. andRylander, H. G. III (1986) Adaptive estimation of single evoked potential. Proc. 8th Ann. Conf. IEEE EMBS, Fort Worth, Texas, 7th–10th November, 406–408.
Dawson, G. D. (1954) A summation technique for the detection of small evoked potentials.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,6, 65–84.
De Weerd, J. P. C. (1981a) Facts and fancies about aposteriori Wiener filtering.IEEE Trans.,BME-28, 252–257.
De Weerd, J. P. C. (1981b)A posteriori time-varying filtering of averaged evoked potentials. I. Introduction and conceptual basis.Biol. Cybern.,41, 211–222.
De Weerd, J. P. C. (1981c)A posteriori time varying filtering of averaged evoked potentials. II Mathematical and computational aspects.41, 223–234.
Doncarli, C. andGoerig, L. (1988) Adaptive smoothing of evoked potentials: a new approach. Proc. 10th Ann. Conf. IEEE EMBS, New Orleans, Louisiana, 4th–7th November, 1152–1153.
Eysholdt, U. andSchneiner, C. (1981) Maximal length sequence—a fast method for measuring brainstem auditory evoked responses. Proc. IEEE Frontiers of Engineering in Health, Care, Houston, Texas, 19th–21st Sept., 306–309.
Gasser, T. andMöcks, J. (1983) A method to deal trail-to-trail variability of evoked potentials.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,55, 717–723.
Gasser, T., Möcks, T., Köhler, W. andDe Weerd, J. P. C. (1986) Performance and measures of performance for estimators of brain potentials using real data.IEEE Trans.,BME-33, 949–956.
Hoffmann De Visme, G. (1971)Binary sequences. The English University Press Ltd.
Jamieson, D. G. andSlawinski, E. B. (1988) Recovery of the auditory brainstem response by sign-bit and conventional averaging.IEEE Trans.,BME-35, 308–315.
Li, H. F., Chan, F. H. Y., Poon, P. W. F., Hwang, J. C. andChan, W. S. (1988) Maximum length sequence applied to the measurement of brainstem auditory evoked responses.J. Biomed. Eng.,10, 14–24.
Madhavan, G. P. (1989) Comments on ‘adaptive filtering of evoked potentials’.IEEE Trans.,BME-35, 273–275.
McGillem, C. D. andAunin, J. I. (1987) Analysis of eventrelated potentials. InMethod, of analysis of brain electrical and magnetic signal.Gevins, A. S. andRémond, A (Eds.), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 131–167.
Möcks, J., Gasser, T. andTuan, P. D. (1984) Variability of signal evoked potentials evaluated by two new statistical tests.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,57, 571–580.
Raz, J., Turetsky, B. andFein, G. (1988) Conference intervals for the signal-to-noise ratio when a signal embedded in noise is observed over repeated trials.IEEE Trans.,BME-35, 646–649.
Stockard, J. J., Stockard, J. E. andSharbrough, F. W. (1986) Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in neurology methodology, interpretation, and clinical application. InElectrodiagnosis in clinical neurology.Aminoff, M. J. (Ed.), Churchill Livingstone, New York, 467–503.
Walter, D. O. (1969)A posteriori Wiener filtering of average of evoked potentials.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol., Suppl. 27, 61–70.
Xue, Q. Z., Hecox, K. andTompkins, W. J. (1986) Adaptive filtering of auditory evoked potentials. Proc. 8th Ann. Conf. IEEE EMBS, Fort Worth, Texas, 7th–10th November, 402–405.
Yu, K. andMcGillem, C. D. (1983) Optimum filters for estimating evoked potential waveforms.IEEE Trans.,BME-30, 730–737.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, F.H.Y., Lam, F.K., Poon, P.W.F. et al. Measurement of human BAERs by the maximum length sequence technique. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 30, 32–40 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446190
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02446190