Abstract
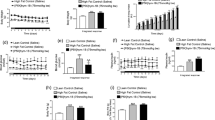
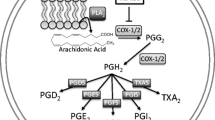
The effects of lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid, hepoxylin B3 epimers, on insulin secretion by a culture of isolated islet cells were studied. The effect was assessed at hepoxylin B3 concentrations of 0.2 to 5.0 μM and different glucose concentrations in the culture medium. Both hepoxylin B3 epimers were shown to boost the stimulating effect of glucose on insulin secretion. This effect manifests itself at glucose concentrations of 5.5 and 11 mM and disappears at an above normal glucose content in the medium (20 mM). The capacity of hepoxylin B3 to stimulate the secretion of insulin by a culture of islet cells in a glucose-free medium has also been demonstrated. This direct, not glucose-mediated, insulinotropic effect may serve as proof that the hepoxylins belong to the category of intracellular messengers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. K. Pivnitskii,Zh. Vsesoyuz. Khim. Obshch. im. D. I. Mendeleeva,36, 418–422 (1991).
V. P. Fedotov, I. S. Komolov, N. V. Sadovnikova, and V. G. Maslennikova,Probl. Endokrinol., No 4, 57–60 (1978).
S. Bevan and J. N. Wood,Nature,238, 20 (1987).
S. Metz,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA,82, 198–202 (1985).
M. H. Nathan and S. Belbez Pek,Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids, No 40, 21–25 (1990).
C. R. Pace-Asciak,Gen. Pharmacol.,24, 805–810 (1993).
C. R. Pace-Asciak and S. Asotra,Free Radic. Biol. Med.,7, 409–433 (1989).
C. R. Pace-Asciak, E. Granstrom, and B. Samuelsson,J. Biol. Chem.,258, 6835–6840 (1983).
C. R. Pace-Asciak, S. P. Lee, and J. M. Martin,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,147, 881–884 (1987).
C. R. Pace-Asciak and J. M. Martin,Prostaglandins Leukot. Med.,16, 173–180 (1984).
C. R. Pace-Asciak, J. M. Martin, and E. J. Corey,Prog. Lipid Res.,25, 625–628 (1986).
C. R. Pace-Asciak, J. M. Martin, E. J. Corey, and W.-G. Su,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,128, 942–946 (1985).
D. Piomelli, A. Vorterra, N. Dale,et al., Nature,328, 38–43 (1987).
J. Turk, J. R. Colca, N. Kotagal, and M. L. McDaniel,Biochim. Biophys. Acta.,794, 125–136 (1984).
L. L. Vasiljeva, T. A. Manukina, P. M. Demin,et al., Tetrahedron,49, 4099–4106 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated fromByulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 120, No 10, pp. 404–406, October, 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedotov, V.P., Sadovnikova, N.V., Baranova, I.N. et al. On the mechanism of insulinotropic action of hepoxylins: Evidence of a direct, glucose-independent effect of hepoxylins B3 on insulin secretion. Bull Exp Biol Med 120, 1036–1038 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02444978
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02444978