Abstract
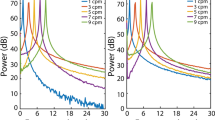
The study aims at determining a characterising configuration useful in obtaining the gastric signal of man from cutaneous electrodes. To do this, a daisy-chain electrode was placed on the abdominal surface making sure that a configuration was on the direction of the antral axis previously defined. The study is based on the analysis of the electrical signals recorded from 13 healthy subjects whose antrum position had been determined by X-rays. In the analysis the gastric signal amplitude was wider in the configuration corresponding with the antral axis than on other ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, W. C. (1922) The electrogastrogram and what it shows.J. Am. Med. Assoc.,78, 1116–1119.
Boiron, M., Gaedau, C. andThouvenot, J. (1978) Etude dynamique et paramétrisation des déformation gastrique.Biomechanics,7, 45–50.
Brown, B. H., Smallwood, R. H., Duthie, H. L. andStoddard, C. J. (1975) Intestinal smooth muscle electrical potentials recorded from surface electrodes.Med. & Biol. Eng.,13, 97–103.
Giorgio, I., Piccioli, E., Scafoglieri, U., Misciagna, G., Mirizzi, N. andAbbattista, N. (1981) Comparison of gastrointestinal myoelectric activityin situ and from abdominal surface in man. Proceedings of the Fourth Annual World Association for Medical Informatics, Strasbourg, 349–353.
Kelly, K. A., Coke, C. F. andElveback, L. E. (1969) Patterns of canine gastric electric activity.Am. J. Physiol.,217, 461–469.
Sarna, S. K., Daniel, E. E. andKingma, Y. J. (1972) Simulation of the electric activity of the stomach by an array of relaxation oscillators.Am. J. Dig. Dis.,17, 299–310.
Sarna, S. K., Bowes, K. L. andDaniel, E. E. (1976) Gastric pacemakers,Gastroenterology,70, 226–231.
Smouth, A. J. M., van der Schee, E. J. andGrashuis, J. L. (1980) What is measured in electrogastrography?Am. J. Dig. Dis.,25, 179–187.
Thouvenot, J. andPenaud, J. (1976) Electrosplancnographie. Monographie Surget, Paris.
Weber, J. andKohatsu, S. (1970) Pacemaker localization and electrical conduction patterns in the canine stomach.Gastroenterology,59, 717–726.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirizzi, N., Scafoglieri, U. Optimal direction of the electrogastrographic signal in man. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 21, 385–389 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442624
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442624