Abstract
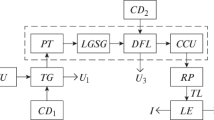
Presented here is a description of an ultrahigh-energy hydrogen thyratron/SCR bidirectional waveform research defibrillator having a sinusoidal voltage source for inducing fibrillation and three pulse generators for generating defibrillatory waveforms. The first pulse generator uses an 18 kJ capacitor bank at 0·8, 1·6 or 2·4 kV discharged through the chest by two series-connected silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs). Two other series-connected SCRs in parallel with the bank terminate the discharge. The second pulse generator uses an 18 kJ bank at 5, 10 or 15 kV. Ceramic-enveloped hydrogen thyratrons in series with the chest initiate the discharge, and in parallel with the bank terminate the discharge. The third pulse generator supplies a reverse-current pulse when used with either the first or second pulse generators to produce bidirectional waveforms. An 18 kJ bank at 2·5, 5 or 10 kV is discharged by an SCR chain in series with the chest. The discharge is terminated by an SCR chain in parallel with the bank. Symmetrical bidirectional rectangular, truncated exponential, and untruncated exponential waveforms are generated by the first and third pulse generators with their respective banks at 2·4 and 2·5 kV, the second and third pulse generators with their banks at 5 kV, or the second and third pulse generators with their banks at 10 kV. The full energy-storage capabilities of the capacitor banks can be used in the first two arrangements; usable energy storage in the third arrangement is limited to about 10 kJ per bank.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gold, J. H., Schuder, J. C., Stoeckle, H., Granberg, T. A., Hamdani, S. Z. andRychlewski, J. M. (1977) Transthoracic ventricular defibrillation in the 100 kg calf with unidirectional rectangular pulses.Circulation,56, 745–750.
Negovsky, V. A., Smerdov, A. A., Tabak, V. Y., Venin, I.V. andBogushevich, M. S. (1980) Criteria of efficiency and safety of the defibrillating impulse.Resuscitation,8, 53–67.
Schuder, J. C., Stoeckle, H. andDolan, A. M. (1964) Transthoracic ventricular defibrillation with square-wave stimuli: one-half cycle, one cycle, and multicycle waveforms.Circ. Res.,15, 258–264.
Schuder, J. C. andGold, J. H. (1976) Design of an ultrahighenergy hydrogen thyratron/SCR research defibrillator.Med. Instrum.,10, 146–150.
Schuder, J. C., Gold, J. H., Stoeckle, H., Roberts, S. A., McDaniel, W. C. andMoellinger, D. W. (1980a) One-cycle bidirectional rectangular wave shocks for open chest defibrillation in the calf.Abst. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs,9, 16.
Schuder, J. C., Gold, J. H., Stoeckle, H., Granberg, T. A., Dettmer, J. C. andLarwill, M. H. (1980b) Transthoracic ventricular defibrillation in the 100 kg calf with untruncated and truncated exponential stimuli.IEEE Trans.,BME-27, 37–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuder, J.C., Gold, J.H. & McDaniel, W.C. Ultrahigh-energy hydrogen thyratron/SCR bidirectional waveform defibrillator. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 20, 419–424 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442400
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442400