Abstract
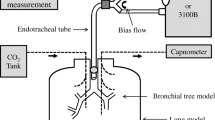
In an in vitro study, the influence of different basic characteristics of high-frequency oscillation (HFO) circuits upon pressure and flow patterns was investigated for a wide variety of lung surrogates. A distinct resonant amplification was observed: the delivered oscillatory volume was found to exceed the piston displacement up to a factor of 1.6. In the whole frequency range of 0–70 Hz the delivered oscillatory volume and its resonance characteristics were entirely determined by the HFO circuit and independent of the properties of the lung surrogates investigated. Accordingly, it appears to be possible to determine the delivered oscillatory volume in vitro and to calibrate the HFO circuit also for use under physiological conditions. in the formation of mean pressure, contributions were found which emerged outside the lung surrogate. They were highly dependent on the HFO circuit arrangement and were superimposed to the local mean pressure components in the lung.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohn, D. J., Miyasaka, K., Marchak, B. E., Thompson, W. K., Froese, A. B. andBryan, A. C. (1980) Ventilation by high-frequency oscillation.J. Appl. Physiol.,48, 710–716.
Brusasco, V., Beck, K. C., Crawford, M. andRehder, K. (1986) Resonant amplification of delivered volume during high-frequency ventilationIbid. J. Appl. Physiol.,60, 885–892.
Chang, H. K. (1984) Mechanisms of gas transport during ventilation by high-frequency ocillationIbid. J. Appl. Physiol.,56, 553–563.
Crone, R. K. andO'Rourke, P. P. (1986) Pediatric and neonatal intensive care. InAnesthesia.Miller, R. D. (Ed.), Churchill Livingstone, New York, 2339.
Gavriely, N., Solway, J., Loring, S. H., Butler, J. P., Slutsky, A. S. andDrazen, J. M. (1985) Pressure-flow relationships of endotracheal tubes during high-frequency ventilation.J. Appl. Physiol.,59, 3–11.
Hamilton, P. P., Onayemi, A., Smith, J. A., Gillan, J. E., Cutz, E., Froese, A. B. andBryan, A. C. (1983) Comparison of conventional and high-frequency ventilation: oxygenation and lung pathology.Ibid. J. Appl. Physiol.,55, 131–138.
Knopp, T. J., Kaethner, T., Meyer, M., Rehder, K. andScheid, P. (1983) Gas mixing in the airways of dog lungs during high-frequency ventilation.Ibid. J. Appl. Physiol.,55, 1141–1146.
Kolton, M., Cattran, C. B., Kent, G., Volgyesi, G., Froese, A. B. andBryan, A. C. (1982) Oxygenation during high-frequency ventilation compared with conventional mechanical ventilation in two models of lung injury.Anesth. Analg.,61, 323–332.
Saari, A. F., Rossing, T. H., Solway, J. andDrazen, J. M. (1984) Lung inflation during high-frequency ventilation.Am. Rev. Respirat. Dis.,129, 333–336.
Schmid, E. R., Knopp, T. J. andRehder, K. (1981) Intrapulmonary gas transport and perfusion during high-frequency oscilation.J. Appl. Physiol.,51, 1507–1514.
Schmid, E. R. (1985) Theoretical evluation of high-frequency ventilation: determinants of pulmonary gas exchange. InHigh-frequency ventilation in intensive care and during surgery. pp. 187–217.Carlon, G. C. andHowland, W. S. (Eds.), Marcel Dekker, New York, Basel.
Schuster, D. P., Karsch, R. andCronin, K. P. (1986) Gas transport during different modes of high-frequency ventilation.Crit. Care Med.,14, 5–11.
Simon, B. A., Weinmann, G. G. andMitzner, W. (1984) Mean airway pressure and alveolar pressure during high-frequency ventilation.J. Appl. Physiol.,57, 1069–1078.
Theissen, J., Lunkenheimer, P. P., Niederer, P., Bush, E., Frieling, G. andLawin, P. (1987) Hochfrequenzbeatmung I. Verteilung der alveolaeren Druckamplituden bei hochfrequenter Oszillation im Lungenmodell.Anaesthesist.,36, 480–485.
Thompson, W. K., Marchak, B. E., Froese, A. B. andBryan, A. C. (1982) High-frequency oscillation compared with standard ventilation in pulmonary injury model.J. Appl. Physiol.,52, 543–548.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spahn, D.R., Bush, E.H., Schmid, E.R. et al. Resonant amplification and flow/pressure characteristics in high-frequency ventilation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 26, 355–359 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442291
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442291