Abstract
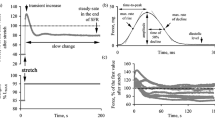
A model which relates the left ventricular (LV) geometry, structure and sarcomere properties to its global function, recently proposed by the authors, is extended to account for contractility changes which are a function of the heart rate, prematurity of the beat and calcium transients within the cell. To characterise LV function and relate it to fibre function under varying rhythm conditions, a model of muscle force restitution, based on calcium kinetics, was used to calculate the maximum fibre stress at the optimum sarcomere length σ0 as the parameter which depends on the heart rate, the test pulse interval TPI, the action potential duration APD and the restitution time constant. The global LV force interval relationship FIR was then calculated, and by comparing the calculated FIR to the experimental measurement (in dogs) at the ventricular level, the constants of the restitution of force at the fibre level were derived. Based on these constants, the LV function under ejecting conditions at various rhythm disturbances was calculated and related to the local, distributed parameters. This approach provides a tool to describe ventricular function as well as transmural distribution of stress and sarcomere length at a wide variety of loading and rhythm conditions based on given ‘muscle level’ parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a 1,a 2 :
-
constants, eqn. 1
- APD :
-
action potential duration
- b 1,b 2 :
-
constants, eqn. 3
- c 1,c 2 :
-
constants, eqn. 5
- C R max :
-
maximum(dp/dt) max assuming sufficient restitution time
- (dp/dt) max :
-
maximum pressure/time derivative
- (dp/dt) max, n :
-
normalised(dp/dt) max [=(dp/dt) max /(dp/dt) max, ss ]
- (dp/dt) max, ss :
-
maximum pressure/time derivative at steady state
- EF :
-
ejection fraction
- E max :
-
maximum elastance
- FIR:
-
force interval relationship
- HR :
-
heart rate, min−1
- SL :
-
sarcomere length
- ss :
-
steady state
- TC :
-
time of contraction, including systolic and relaxation durations
- TDI :
-
time from end of depolarisation to beginning of next depolarisation wave
- TPI :
-
time interval between the previous pulse and the test pulse
- T es :
-
time to reach point of end systole
- π0 :
-
maximum stress at optical sarcomere length
- π0,n :
-
normalised maximum stress [=π0/π0,ss]
- σ R max :
-
maximum stress at optimal sarcomere length assuming complete restitution of the contractility at the given basalHR
- τ:
-
time constant for mechanical restitution of the LV system
References
Anderson, R. W. A., Manning, A. andJohnson, E. A. (1973) The force frequency relationship: a new basis for an index of cardiac contractility.Circ. Res.,33, 665–671.
Anderson, P. A. W., Rankin, J. S., Anentzen, C. E., Anderson, R. W. A. andJohnson, E. H. (1976) Evaluation of force frequency relationship as a description of the isotropic state of canine left ventricular myocardium.,39, 832–839.
Anderson, P. A. W., Manning, A., Serwen, G. A., Benson, D. Q., Edward, S. B., Armstrong, B. E., Sierba, R. J. andFloyd, R. D. (1979) The force interval relationship of the left ventricle.Circ.,60, 334–348.
Antoni, H. (1977) Elementary events in excitation contraction coupling of mammalian myocardium.Basic Res. Cardiol.,72, 140–146.
Beyar, R. andSideman, S. (1984) A computer study of left ventricular performance based on fiber structure, sarcomere dynamics and transmural electrical propagation velocity.Circ. Res.,55, 358–375.
Beyar, R. andSideman, S. (1986) Left ventricular mechanics related to the local distribution of oxygen demand throughout the wall.,58, 664–677.
Burkhoff, D., Yue, D. T., Franz, M. R., Hunter, W. C. andSagawa, K. (1984) Mechanical restitution of isolated perfused canine left ventricle.Am. J. Physiol. (Heart Circ. Physiol.,15)246, H8-H16.
Edman, K. A. P. andJohannsson, M. (1976) The contractile state of rabbit papillary muscle in relation to stimulation frequency.J. Physiol.,254, 565–581.
Elzinga, G., Lab, M. J., Noble, M. I. M., Papadoyannis, D. F., Pidgeon, J., Seed, A. andWohlfart, B. (1981) The action potential duration and contractile response of the intact heart related to the preceding interval and preceding beat in the dog and the cat.,314, 481–500.
Fabiato, A. andFabiato, F. (1979) Calcium and cardiac excitation contraction coupling.Ann. Rev. Physiol.,41, 473–484.
Fozzard, H. A. (1977) Heart: excitation contraction coupling.,39, 201–220.
Johnson, E. A. (1975) Force interval relationship of cardiac muscle. InHandbook of physiology. The cardiovascular system. Vol. 1.Berne, R. M. (Ed), Am. Physiol. Soc., Washington DC, 475–496.
Kaufmann, R., Bayer, R., Furniss, T., Krause, H. andTritthart, H. (1974) Calcium movement controlling cardiac contractility II. Analog computation of cardiac excitation contraction coupling on the basis of calcium kinetics in a multicompartmental model.J. Mol. Cel. Cardiol.,6, 543–559.
Maughan, W. L., Sunagawa, K., Burkhoff, D., Graves, W. L., Hunger, W. C. andSagawa, K. (1985) Effect of heart rate on the canine and systolic pressure volume relationship.Circ.,72, 654–659.
Morad, M. andGoldman, Y. (1973) Excitation contraction coupling in heart muscle control of development of tension.Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol.,27, 257–313.
Pidgeon, J., Miller, G. A. H., Noble, M. I. N., Papadoyannis, D. andSeed, W. A. (1982) The relationship between the strength of the human heart beat and the interval between beats.Circ.,65, 1404–1410.
Sonnenblick, E. H. (1980) The structural basis and importance of restoring forces and elastic recoil for the filling of the heart.Europ. Heart J., Suppl. A, 107–110.
Spaan, J. F. Jr.,Bussino, R. A., Sonnenblick, E. E. andBraunwald, E. (1967) Contractile state and cardiac muscle obtained from cats with experimentally produced ventricular hypertrophy and heart-failure.Circ. Res.,21, 341–354.
Spotnitz, H. M., Sonnenblick, E. H. andSpiro, D. (1966) Relation of ultrastructure to function in the intact heart: sarcomere structure relative to pressure volume curves of intact left ventricles of dog and cat.,18, 40–66.
Streeter, D. D., Spotnitz, H. M., Patel, D. J., Ross, J. andSonnenblick, E. H. (1969) Fiber orientation in the canine left ventricle during diastole and systole.,24, 339–347.
Streeter, D. D. andHanna, W. T. (1973) Engineering mechanics for sucessive states in canine left ventricular myocardium.,33, 639–655.
Sunagawa, K., Burkhoff, D., Lim, K. O. andSagawa, K. (1982) Impedance loading servo pump system for excised canine ventricle.Am. J. Physiol. (Heart Circ. Physiol.,12)243, H346-H350.
Wohlfart, B. (1979) Relationship between peak force, action potential duration and stimulus interval in rabbit myocardium.Acta Physiol. Scand.,106, 395–409.
Yellin, E. L., Kennish, A., Yoran, H., Laiado, S., Buckley, N. M. andFrater, W. M. (1979) The influence of left ventricular filling on post extra-systolic potentiation in the dog heart.Cir. Res.,44, 712–722.
Yoran, C., Covell, J. W. andRoss, J. Jr. (1973) Structural basis for the ascending limb of left ventricular function.,32, 297–303.
Yue, D. T., Wien, W. G. andSagawa, K. (1984) Direct measurement of intracellucal Ca++ transient underlying the cardiac FIR (abstract). VIth Proc. Cardiovasc. System Dynamics Society.
Yue, D. T., Burkhoff, D., Franz, M. R., Hunter, W. C. andSagawa, K. (1985) Postextrasystolic potentiation of the isolated canine left ventricle. Relationship to mechanical restitution.Circ. Res.,56, 340–350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyar, R., Burkhoff, D. & Sideman, S. Force interval relationship (FIR) related to the global function of the left ventricle: a computer study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 28, 446–456 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441968