Abstract
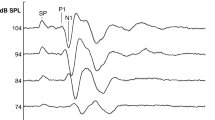
A low-cost, microprocessor-based instrument is designed to simulate the human auditory brainstem response (ABR) to acoustic clicks. the device normally delivers a continuous simulated EEG signal in the absence of click input. When an acoustic click is sensed, its onset and intensity are recognised promptly and an appropriate ABR waveform is superimposed on the ongoing EEG. Fast recognition of onset and intensity are achieved by using analogue detector circuits which issue microprocessor interrupts. The output waveform is synthesised by a 16-bit D/A convertor to preserve realistic signal (ABR) to noise (EEG) ratios. As multiplication operations cannot be performed at speeds appropriate for ABR waveform simulation, superposition is accomplished by position-weighted loading operations in a 16-bit register. The instrument is tested using a microcomputer-based signal averager. it satisfactorily simulates the randomness of single sweeps. Upon averaging enough sweeps, an ABR waveform is obtained. The device, believed to be the first available of its kind, is used to test and calibrate clinical EP systems and is expected to prove useful as a clinical engineering tool in hospitals and medical centres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aunon, J. I., McGillem, C. D. andChilders, D. G. (1981) Signal processing in evoked potential research: averaging and modeling.CRC Crit. Rev. Bioeng.,5, 323–367.
Bach, M., Stegmaier, J. andRover, J. (1984) A versatile simulator of evoked potentials.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,57, 97–98.
Boston, R. (1981) Spectra of auditory brainstem responses and spontaneousEEG. IEEE Trans. BME,-28, 334–341.
Caballero, F. S., Mahedro Balsera, B. andBernal, J. J. P. (1978) A circuit for obtaining periodic signals for bioelectric waveform generation.Electron. Eng.,50, 28.
Clark, W. A., Brown, R. M., Goldstein, M. H., Molnar, C. E., O'Brian, D. F. andZieman, H. E. (1961) The average response computer (ARC): a digital device for computing averages and amplitude and time histograms of electrophysiological responses.IRE Trans. BioMed. Electron. BME,-8, 46–51.
Galambos, R., Makeig, S. andTalmochoff, P. J. (1981) A 40-Hz auditory potential recorded from the human scalp.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci.,78, 2643–2647.
Greene, M., Runcie, D. andRowe, F. (1984) A microprocessor-based system for measuring evoked potentials. InBiomedical engineering III: Recent developments.Sheppard, L. C. (Ed.), Pergamon Press, 186–192.
Hecox, K. andGalambos, R. (1974) Brain stem auditory evoked responses in human infants and adults.Arch. Otolaryngol.,99, 30–33.
Jewett, D. L., Romano, M. N. andWilliston, J. S. (1970) Human auditory evoked potentials: possible brainstem components detected on the scalp.Science,167, 1517–1518.
Jewett, D. L. andWilliston, J. S. (1971) Auditory-evoked far fields averaged from the scalp of humans.Brain,94, 681–696.
Mintz, G. D., Frecker, R. C. andJoy, M. L. G. (1980) Specification and design of an evoked response data acquisition system.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,18, 167–178.
Miskiel, E., Özdamar, Ö. andPeterson, E. A. (1984) Microcomputer-basedautomatic ABR monitoring in the ICU. Proc. 37th ACEMB, Los Angeles, California, 168.
Miskiel, E. andÖzdamar, Ö. (1987) Computer monitoring of auditory brainstem responses.Comp. Biol. & Med., (in press).
Özdamar, Ö. andKraus, N. (1983) Auditory brainstem response in infants recovering from bacterial meningitis: neurologic assessment.Arch. Neurol.,40, 499–502.
Özdamar, Ö., Kraus, N. andStein, L. (1983) Auditory brainstem responses in infants recovering from bacterial meningitis: audiological evaluation.Arch. Otolaryngol.,109, 13–18.
Özdamar, Ö., Kaplan, R., Miskiel, E. andDelgado, R. (1987) Human-machine interface for an interactive evoked potential electrodiagnostic system. InTrends in ergonomic/human factors IV.Asfour, S. (Ed.), North Holland, Amsterdam, 1121–1129.
Starr, A. andAchor, J. (1975) Auditory brainstem responses in neurological disease.Arch. Neurol.,32, 761–768.
Starr, A. andHamilton, A. (1976) Correlation between confirmed sites of neurological lesions and abnormalities at farfield auditory brainstem responses.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,41, 595–608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaplan, R., Özdamar, Ö. Microprocessor-based auditory brainstem response (ABR) simulator. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 25, 560–566 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441749
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441749