Abstract
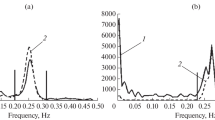
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) is sometimes hard to identify in neonates, in particular when the respiratory rate approaches half the mean heart rate. It is shown that the analysis of the cardiac event series may reveal RSA in cases where traditional heart rate variability analysis methods fail. A signal analysis approach to event series processing is reviewed. The validation of the spectral analysis of event series is illustrated with the help of simulation results. In accordance with this approach, the event series spectrum of a neonate shows a RSA component at 0·9 Hz, which was in agreement with the frequency of the simultaneously measured respiration. The possible implications for research into the causes of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelone, A. andCoulter, N. A. (1964) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: a frequency dependent phenomenon.J. Appl. Physiol.,19, 479–482.
Bayly, E. J. (1968) Spectral analysis of pulse frequency modulation in the nervous system.IEEE Trans.,BME-15, 257–265.
Brady, J. P. andGould, J. B. (1983) Sudden infant death syndrome: the physician's dilemma.Adv. Paediatrics,30, 635–672.
Coenen, A. J. R. M., Rompelman, O. andKitney, R. I. (1977) Measurement of heart-rate variability: Part 2—Hardware digital device for the assessment of heart-rate variability.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,15, 423–430.
Fleming, P. J., Goncalves, A. L., Levine, M. R. andWoolard, S. (1984) The development of stability of respiration in human infants: changes in ventilatory responses to spontaneous sighs.J. Physiol.,347, 1–16.
Fitch, E. (1947) The spectrum of modulated pulses.J. IEE,94-3A, 556–564.
Gordon, D., Cohen, R. J., Kelly, D., Akselrod, S. andShannon, D. C. (1984) Sudden infant death syndrome: abnormalities in short term fluctuations in heart rate and respiratory activity.Pediatr. Res.,18, 921–926.
Guntheroth, W. G. (1982)Crib death (sudden infant death syndrome). Futura, New York.
Hathorn, M. (1978) Analysis of periodic changes in ventilation in newborn infants.J. Physiol.,285, 85–99.
Hirsh, J. A. andBishop, B. (1981) Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans: how breathing pattern modulates heart rate.Am. J. Physiol.,241, H620-H629.
Hyndman, B. W. andMohn, R. K. (1973) A pulse modulator model of pacemaker activity. Digest 10th Int. Conf. on Med. & Biol. Eng., Dresden, 223.
Kitney, R. I. andRompelman, O. (Eds.) (1980)The study of heart rate variability. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Kitney, R. I. (1984) New findings in the analysis of heart rate variability in infants.Automedica,5, 289–310.
Kitney, R. I. andOng, H. G. (1986) An analysis of cardiorespiratory control in babies and its relation to sudden infant death syndrome. ——Ibid.,7, 105–126.
Kitney, R. I., andRompelman, O. (Eds.) (1987)The beat-by-beat investigation of cardiovascular function. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Koeleman, A. S. M., van den Akker, T. J., Ros, H. H., Janssen, R. J. andRompelman, O. (1984) Estimation accuracy of P wave and QRS complex occurrence times in the ECG: the accuracy for simplified theoretical and computer simulated waveforms.Signal Process,7, 389–405.
Moss, S. A. (1948) Frequency analysis of modulated pulses.Phil. Mag. & J., Ser. 7,39, 663–691.
Porges, S. W. (1983) Heart rate patterns in neonates: a potential diagnostic window to the brain. InInfants born at risk; physiological, perceptual and cognitive processes.Field, T. andSostek, A. (Eds.). Grune & Stratton, New York.
Richards, J., Alexander, J. andShinebourne, E. (1984) Sequential 24-hour profiles of breathing patterns and heart rate in 110 full-term infants during their first six months of life.Paediatrics,74, 763–777.
Rompelman, O., Coenen, A. J. R. M. andKitney, R. I. (1977) Measurement of heart-rate variability: Part 1—Comparative study of heart-rate variability analysis methods.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,15, 233–239.
Rompelman, O., Snijders, J. B. I. M. andvan Spronsen, C. J. (1982) The measurement of heart rate variability spectra with the help of a personal computer.IEEE Trans. BME-29, 503–510.
Rompelman, O., Janssen, R. J., Koeleman, A. S. M., van den Akker, T. J. andRos, H. H. (1986) Practical limitations for the estimation of P-wave and QRS-complex occurrence times.Automedica,6, 269–284.
Rompelman, O. (1986) Processing the cardiac event series: a signal analysis approach. ——Ibid.,7, 191–212.
Selman, A. C., McDonald, A. H., Kitney, R. I. andLinkens, D. A. (1982) The interaction between heart rate and respiration: Part 1: experimental studies in man. ——Ibid.,4, 131–139.
Valdes-Dapena, M. (1980) Sudden infant death syndrome: a review of the medical literature.Paediatrics,66, 597–614.
Watkins, P. J., andMackay, J. (1980) Cardiac denervation in diabetic neuropathy.Ann. Int. Med.,92, 304–307.
Waggener, T., Stark, A., Cohlan, B. andFrantz, I. (1984) Apnea duration is related to ventilatory oscillation characteristics in the newborn infant.J. Appl. Physiol.: Respirat. Environ. Exer. Physiol.,57, 536–544.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rompelman, O., Pijnacker Hordijk, W.P. New method for the assessment of neonatal respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 25, 481–486 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441738
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441738