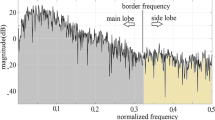
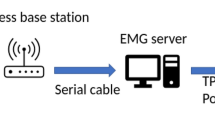
Abstract
A system is described which monitors spectral changes of the surface EMG. It is shown analytically that a relationship exists between the zero crossing rate (ZCR) and the mean, Fa, and median, Fm, frequencies of the surface EMG. Under the existing conditions of this relationship a system can be built which can estimate and monitor the Fa or Fm of the surface EMG from the measured ZCR. It is shown experimentally on the biceps, extensor digitorum and first dorsal interosseus muscles that an excellent agreement exists between the time averages of Fm and ZCR in normal muscles under a variety of muscle length tension and fatigue conditions. A simple portable microcomputer unit which performs the ZCR calculations and which can be used as a muscle fatigue monitor is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, G. C. andGottlieb, G. L. (1975) An analysis of the electromyogram by Fourier, simulation and experimental techniques.IEEE Trans.,BME-22, 225–229.
Bendat, J. S. andPiersol, A. G. (1971)Random data analysis and measurement procedures, Wiley Interscience.
Broman, H. andKadefors, R. (1979) A spectral moment analyzer for quantification of electromyograms. 4th Congress of Isek, Boston, USA.
Chang, S.-H., Pihl, G. E. andEssigmann, M. W. (1951) Representations of speech sounds and some of their statistical properties.Proc. IRE, 147–153.
Christakos, C. N. (1980) A population stochastic model of skeletal muscle and its use in the study of the frequency characteristics of muscle output activity with particular reference to tremor. Ph.D. Thesis, Chelsea College, University of London.
Christakos, C. N. andLal, S. (1980) Lumped and population stochastic models of skeletal muscle: implications and predictions.Biol. Cybernetics,36, 73–85.
Cobb, S., andForbes, A. (1923) Electromyographic studies of muscular fatigue in man.Am. J. Physiol.,65, 234–251.
DeLuca, C. J. (1979a) Physiology and mathematics of myoelectric signals.IEEE Trans.,BME-26, 313–325.
DeLuca, C. J. (1979b) Automated muscle fatigue monitor.Bull. Prosth. Res.,32, 235–237.
Graupe, D. andCline, W. K. (1975) Functional separation of EMG signals via ARMA identification methods for prosthesis control purposes.IEEE Trans.,SMC-5, 252–259.
Hary, D., Belman, M. J., Propst, J. andLewis, S. (1982) Special communication: A statistical analysis of the spectral moments used in EMG tests of endurance.J. Appl. Physiol. Resp. Environ. Exc. Physiol.,53, 779–783.
Inbar, G. F., Allin, J., Golos, E., Koehler, W. andKranz, H. (1981) EMG spectral shift with muscle length, tension, and fatigue. Proceedings of the IEEE MELECON Conference, May 1981, Israel.
Inbar, G. F. andNoujaim, A. (1982, 1984) On surface EMG spectral characterization and its application to diagnostic classification. Proceedings of the 5th ISEK conference, Ljubljana, 1982,IEEE Trans.,BME-31, 597–604.
Inbar, G. F., Allin, J. andKranz, H. (1983) Surface EMG spectral changes with muscle length. EE Pub. No. 433 (available from the Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion).
Kadefors, R., Kaiser, E. andPetersen, I. (1968) Dynamic spectrum analysis of myo-potentials with special reference to muscle fatigue.Electromyography,8, 39–74.
Kedem, B. andSlud, E. (1982) Time series discrimination by means of higher order crossings'.Ann. of Statistics,10, 786–794.
Kedem, B. (1982) Some graphical considerations in time series analysis.IEEE Trans.,PAMI-4, 493–499.
Kranz, H., Chan, H., Caddy, D. J. andWilliams A. W. (1981) Factors contributing to the decrease in the frequency content of the electromyogram during muscle contraction. New approaches to nerve and muscle disorders. Proceedings of the Second Symposium of the Foundation for Life Sciences, Sydney, 3rd–6th February 1981, 104–113.
Kranz, H., Williams, A. M., Cassell, J. F., Caddy, D. J. andSilberstein, R. B. (1983) Factors determining the frequency content of the electromyogram.J. Appl. Physiol. Resp. Exerc. Environ. Physiol.,55, 392–399.
Lago, P. andJones, N. B. (1977) Effect of motor-unit firing statistics on EMG spectra.Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,15, 648–655.
Lindstrom, L., Magnusson, R. andPetersen, I. (1970) Muscle fagigue and action potential conduction velocity changes studied with the aid of frequency analysis of EMG signals.Electromyography,4, 341–356.
Lindstrom, L., Kadefors, R. andPetersen, I. (1977) An electromyographic index for localized muscle fatigue.J. Appl. Physiol.,43, 750–754.
Lindstrom, L. H. andMagnusson, R. I. (1977) Interpretation of myoelectric power spectra: A model and its applications,Proc. IEEE,65, 653–662.
Marsden, C. D., Meadows, J. C. andMerton, P. A. (1971) Isolated single motor units in human muscle and their rate of discharge during maximal voluntary effort.J. Physiol.,217, 12P-13P.
Milner-Brown, H. S., Stein, R. D. andLee, R. G. (1975) Synchronization of human motor units: possible rates of exercise and supraspinal reflexes.Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,38, 245–254.
Mortimer, J. T., Magnusson, R. andPetersen, I. (1970) Conduction velocity in ischemic muslce: Effort on EMG frequency spectrum,Am. J. Physiol.,219, 324–329.
Rice, S. O. (1945) Mathematical analysis of random noise,Bell Syst. Tech. J.,24, 46–156.
Schweitzer, T. W., Fitzgerald, J. A., Bowden, J. A. andLynne-Davis, P. (1979) Spectral analysis of human inspiratory diaphragmatic electromyograms.J. Appl. Physiol: Respirat. Environ. Exercise Physiol.,46, pp. 152–165.
Stulen, F. B. (1980) A technique to monitor localized muscle fatigue using frequency domain analysis of the EMG signal. Ph.D. Thesis, MIT.
Stulen, F. B. andDeLuca, C. J. (1981) Frequency parameters of the myoelectric signal as a measure of muscle conduction velocity.IEEE Trans.,BME-28, 515–523.
Stulen, F. B. andDeLuca, C. J. (1982) Muscle fatigue monitor: A non-invasive device for observing localized muscular fatigue'.IEEE Trans.,BME-29, 760–768.
Zetterberg, L. H. (1977) Means of methods for processing of physiological signals with emphasis on EEG analysis. InAdvances in biological and medical physics, vol. 16, New York Academic Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inbar, G.F., Paiss, O., Allin, J. et al. Monitoring surface EMG spectral changes by the zero crossing rate. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 24, 10–18 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441600
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441600