Abstract
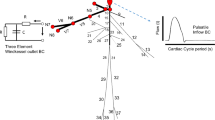
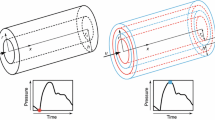
The clinical implications of the pressure-deformation characteristics of a curved tapered elastic tube segment simulating the aortic arch without branches, subjected to an internal pressure, are presented. A finite-element technique was employed to analyse the asymmetrical deformation of the tube. Large deformation characteristics and the non-linear stress-dependent elastic stiffness property of the vessel wall were incorporated by a step-wise incremental analysis method, with a linear small deformation finite-element formulation being employed for the analysis at each time step increment.
For a healthy vessel, simulated by uniform Young's modulus against stress characteristics, and a simulated arteriosclerotic vessel (having some wall segments with elevated Young's modulus against stress characteristics), the distributions of the deformations, wall stress and compliance were determined during the cardiac cycle, and graphically illustrated. The results enabled us to appreciate the sensitivity and utility of pressure-deformation characteristics to distinguish between healthy and arteriosclerotic vessels.
The methodology can be employed to generate pulse pressure-deformation patterns which, by comparison with fluoroscopically or echocardiographically monitored deformation patterns, may help determine the distribution of the stress-dependent Young's modulus of the vessel wall. This technique may provide a tool for the detection of arteriosclerosis in the human circulatory system especially with the recent developments in the image-processing techniques, such as videodensitometric analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathe, K. J., Wilson, E. L. andPeterson, F. E. (1974) SAP IV: A structural analysis program for static and dynamic response of linear systems. University of California, Berkeley, Report EERC73-11.
Burton, A. C. (1971)Physiology and biophysics of the circulation, Yearbook Medical Publishers, Chicago, IL, USA.
Fung, Y. C. (1972) Stress-strain-history relations of soft tissues in simple elongation. InBiomechanics—its foundation and objectives,Fung,Y. C.,Perrone,N., andAnliker,M. (Eds.), Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 181–208.
Haut, R. C., Gang, B. D., Metke, M., Jose, M. andKaye, M. P. (1980) Mechanical properties of the canine aorta following hypercholesterolemia.J. Biomech. Eng.,102, 98–102.
Liu, Y. K., Ray, G. andHirsch, C. (1975) Shear resistance to lumbar spine.Clin. Orthop. of North America,6, 1.
Lin, H. S., Liu, Y. K. andRay, G. (1978) Systems identification of material properties of the intervertebral joint,J. Biomech.,11, 1–14.
Mohan, D. andMelvin, J. W. (1977) Effect of age on failure properties of human aortic tissue.30th ACEMB, Los Angeles, CA, November 5–9th, 35.
Selzer, R. H., Blankenhorn, D. H., Bechenbach, E. S., Crawford, D. W. andBrooks, S. H. (1975) Digital image processing of vascular angiograms—cardiovascular imaging and image processing—theory and practice. InHarrison, D. C., Sandler, H. andMiller, H. A. (Eds.). The Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandran, K.B., Ray, G. Clinical implications of pressure deformation analysis of curved elastic tubes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 20, 145–150 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441349
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441349